Impulse & Momentum Worksheet 1 Impulse and the Change in Momentum
advertisement

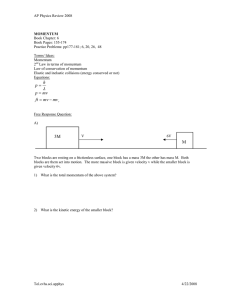
Name Period Date Impulse & Momentum Worksheet 1 Impulse and the Change in Momentum 1. Two objects, A and B, have identical velocities. Object A has 3 times the mass of object B. a. Calculate the value of the ratio of b. Calculate the value of the ratio of momentum A to momentum B. kinetic energy A to kinetic energy B. 2. Two other objects, C and D, have identical masses. Object C has twice the velocity of object D. a. Calculate the value of the ratio of b. Calculate the value of the ratio of momentum C to momentum D. kinetic energy C to kinetic energy D. 3. If you throw a ball horizontally while standing on roller skates, you roll backwards. Will you roll backwards if you go through the motions of throwing the ball, but hold on to it instead? Explain your reasoning. 4. Which has the greater change in momentum, a 50. gram clay ball that strikes a wall at 1.0 m and sticks or a 50. gram superball that strikes a wall at 1.0 m and s s rebounds from the wall at 0.8 m ? Explain your reasoning. s Impulse and Momentum Worksheet 1 page 2 5. A Hummer and a VW Beetle traveling at equal speeds have a head-on collision. a. Which vehicle will experience the greatest force of impact? Justify your answer. b. Which vehicle will experience the greatest change in momentum? Justify your answer. c. Which vehicle will experience the greatest acceleration? Justify your answer. 6. Discuss the following in terms of impulse and momentum: a. Why are padded dashboards safer than hard dashboards in automobiles? b. Why are nylon ropes, which stretch considerably under stress, favored by mountain climbers? Impulse and Momentum Worksheet 1 page 3 7. While being thrown, a net force of 132 N acts on a baseball (mass = 140 g ) for a period of 4.5 10 2 s . a. What is the magnitude of b. If the initial speed of the baseball is the change in momentum vi 0.0 m , what will its speed be when it s of the ball? leaves the pitcher's hand? c. When the batter hits the ball, a net force of 1320 N , opposite to the direction of the ball's initial motion, acts on the ball for 9.0 10 3 s during the hit. What is the final velocity of the ball? d. What force does the ball exert on the bat? Explain. 8. A rocket, weighing 4.36 10 4 N , has an engine that provides an upward force of 8.9 10 5 N . It reaches a maximum speed of 860 m . s a. Draw a force b. For what period of time, after launch, must the engine diagram for the burn in order to reach this speed? rocket. Impulse and Momentum Worksheet 1 page 4 9. A golf ball that weighs 0.45 N is dropped from a height of 1.0 m. Assume that the golf ball has a perfectly elastic collision with the floor so that no energy is dissipated. a. Calculate the b. Calculate the c. Calculate the velocity of the ball instantaneous instantaneous as it reaches the momentum of the golf momentum of the golf ground. ball immediately before ball immediately after it it strikes the floor. rebounds from the floor. d. What will be the ball’s change in momentum, ( p ) from the instant before the ball collides with the floor until the instant after it rebounds from the floor? 10. A tennis player returns a 30. m e. Suppose that the golf ball was in contact with the floor for 4.0 10 4 s . What was the average force on the ball while it was in contact with the floor? serve straight back at 25 m , after making contact s s with the ball for 0.50 s . If the ball has a mass of 0.20 kg , what is the force she exerted on the ball? Impulse and Momentum Worksheet 1 page 5 11. A 7.5 kg block moving on a frictionless surface at 5.0 m collides with a stationary s 3.0 kg ball so that the force exerted by the block on the ball as a function of time is given by the graph below. 5.0 m 7.5 kg a. What impulse did the block give to the ball? s 3.0 kg F N 24 b. What impulse did the ball give to the block? t s 1.0 c. What is the final velocity of the ball after the collision? d. What is the final velocity of the block after the collision? e. Is this an elastic collision? Calculate the total kinetic energy before and after the collision and compare.