Groundwater and Lakes Monitoring Options Wisconsin Lakes Conference April 2010 N. Turyk
advertisement

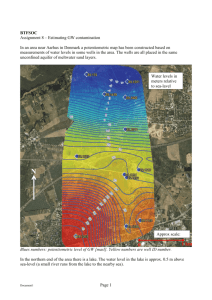
Groundwater and Lakes Monitoring Options Wisconsin Lakes Conference April 2010 N. Turyk Water Resource Scientist Groundwater Monitoring How much/what proportion of groundwater is entering a lake? Where groundwater is entering a lake? What is the water quality of groundwater entering a lake? What are the options for sampling groundwater that is entering a lake? Water Budget for a Lake The amount of groundwater entering each lake is different! Precipitation Streamflow In Streamflow Out Groundwater Runoff Tributary Inflow Precipitation Options for Measuring Groundwater Volume and Water Quality Wading in the shallows Observations – open water in winter Mini wells Seepage meters Private wells Mini Piezometers (wells) Seepage Meters Open Ice Observations Early in the day or on a cloudy day 30oF to 45oF not below zero the night before Estimate the distance from shore to where the ice begins Talk with ice fishers and residents to determine if there are other areas that are frequently open Open Ice and Mini Piezometers Private Well Samples Water Quality Analyses and measurements depend upon the question you are trying to answer! Some Common Measurements Temperature pH Specific conductance Nutrients (laboratory) Pesticides (laboratory) Chloride (laboratory) A Few Water Quality Results Landuse affects amount of nutrients & contaminants in soil Groundwater and Landuse Rain soaks through soil, dissolves nutrients, & becomes groundwater Groundwater that flows to lake carries minerals, nutrients, & contaminants Septic systems and water quality Byron Shaw, 1999