The Use of ePortfolios to Assess General Education
advertisement

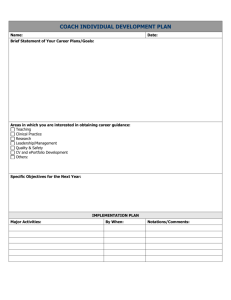
The Use of ePortfolios to Assess General Education Essential Questions What is the purpose of the ePortfolio? How will students understand our expectations? What competencies do we wish to assess? Who will do the evaluation? What kind of rubrics do we need? How can we use our findings to improve general education? Overview of Clemson ePortfolio 2006 – 2007 ePortfolio implemented as a mechanism to evaluate general education Implemented with 2006-07 freshman class (transfers as well) 2007 – 2008 Year 2 Assessment implemented (formative: peer feedback; Summative: faculty assessment) 2008 – 2009 Year 3 Google and CUePort 2009 – 2010 Year 4 First Graduating Class with ePortfolios Where are we now? Building an Infrastructure • Clearly articulated purpose • Build support • Build Assessments • Select the technology Challenges • How to Integrate ePs within a Gen Ed curriculum with multiple moving parts Faculty • Buy-in vs. engagement • Role in artifact development, selection • Scaffolding of eP for students • Available platforms Competency Development Used consistently across institution and assessment type Designed by faculty/Revised by faculty (22,19,8) Must be measurable Communicate the criterion clearly Examples help Iterative Rubric Development Used consistently across institution and assessment type Designed by faculty/Revised by faculty Communicate the criterion clearly Examples help Iterative 2 Paradigms of Assessment (Ewell) • • • • • • Formative (Improvement) Internal Engagement Multiple/triangulation Qualitative and quantitative Overtime, comparative, established goal • Multiple internal channels and media • Multiple feedback loops • • • • • • Summative (judgment) External Compliance Standardized Quantitative Comparative or fixed standard • Public Communication • Reporting Framework for Discussion With apologies to Nike, move away from “Just Do It!” For Students For Faculty From Faculty “Buy-In” to Faculty Engagement What does the research say? Instructional Design – Diffusion of innovation (Rogers) Higher ed lit - Furco & Moely (2012) Copyright © 2013 by Gail Ring, Clemson University & Kathryne Drezek McConnell, Virginia Tech Purpose Clearly Communicated Clarity of purpose Be clear about the time commitment – Change doesn’t happen overnight! Be transparent about the evolving nature of the project on your campus - THINGS WILL CHANGE! Informing Students of Our Expectations Syllabi “It’s on the syllabus; so where is the disconnect?” Common freshman experience On-Line and face-to-face support _______________________________ Quality Enhancement Plan Faculty Buy-in (Engagement) Clemson: Challenges Encountered Lack of clearly understood purpose Limited engagement: faculty and students Adopting/inventing a tool that is multi-faceted and allows for student ownership Helping students make the transition from collecting “stuff” to collecting evidence. Do we really want to know what our students don’t know? How will we make the initiative sustainable? Added Value to the General Education Program • Assessment • Provides an opportunity for improvement Gathering data on student learning outcomes (SLO) for 6 years Conversation about Gen Ed. Data Driven Decision Making - Closing the Loop Providing data on SLO back to colleges/departments Courses are changing AH Part of the QEP Communication is part of the conversation again Why the Struggle is Worthwhile • Direct information on student learning outcomes • Evidence of high impact practices • Documentation of student attainment of General Education competencies (even for transfer students) • Better understanding of overall curriculum and a link to general education competencies • Message to students: learning is not a “check off” ePortfolio Assessment as Iterative Process Implementation Faculty Development Gather Evidence Review Evidence Engage in Change Analyze Results Make Recommendations References • Ewell, P. (2012). Assessment, Accountability and Improvement: Revisiting the Tensions. http://www.learningoutcomeassessment.org/doc uments/PeterEwell_005.pdf • Furco & Moely (2012). Using Learning Communities to Build Faculty Support for Pedagogical Innovations. Journal of Higher Ed. • Rogers, E. (2003). The Diffusion of Innovations, 5th Edition