Polynomial Functions Rational Functions 2.6
advertisement

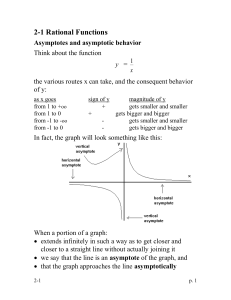
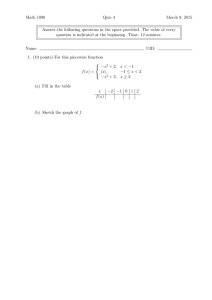
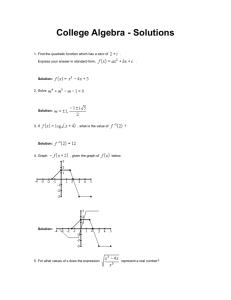
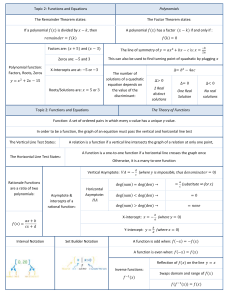
Polynomial Functions Rational Functions 2.6 Rational Functions A rational function is a ratio (fraction) of polynomials; f(x)=N(x)/D(x). Domain: x�R such that D(x) �= 0 Asymptotes (V. A.) Vertical Asymptote – Vertical Line x = a; where D(a) = 0 Find V.A. by looking for restrictions in the domain. The function cannot touch nor cross a vertical asymptote. Asymptotes (H.A.) Horizontal Asymptotes – Horizontal Line y = b; where lim f (x) = b x→±∞ Find H.A. by looking at the end behavior of the function. The function can touch or cross a horizontal asymptote. If deg(N(x)) < deg(D(x)), then y=0 is the H.A. If deg(N(x)) = deg(D(x)), then the H.A. is the ratio of leading coefficients If deg(N(x)) > deg(D(x)), then there is no H.A. Asymptotes (S. A.) Slant Asymptote If y = N (x) D(x) = ax + b + r(x) And deg(N(x)) = deg(D(x)) + 1, then the rational function has a slant asymptote; y = ax +b. Find S.A. using long division. A rational function NEVER has both a H.A. and S.A. Sketching the Graph Identify domain. Simplify Find/Plot: vertical, horizontal, and slant asymptotes Find/Plot: x-intercept(s) and y-intercept Plot: At least one point on each side of the x-intercept(s) and vertical asymptote(s) Fill in with smooth curve.