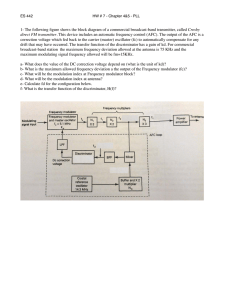
a AN-585 APPLICATION NOTE AD5232–Programmable Oscillator Using Digital Potentiometers
advertisement

a AN-585 APPLICATION NOTE E02749–0–5/03(0) One Technology Way • P.O. Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106 • Tel: 781/329-4700 • Fax: 781/326-8703 • www.analog.com AD5232–Programmable Oscillator Using Digital Potentiometers By Alan Li GANGED TOGETHER CS 1nF B RP 100k⍀ A W AD5232 7 3 AD5232 + ωo = V+ AD711/AD 6 – V– 1 5 V– R2A 2.21k⍀ R2B 100k⍀ To sustain oscillation, we set the loop gain to unity such that D1 D2 D1N4148 R2 =2 R1 Figure 1. Programmable Wien-Bridge Oscillator with Amplitude Stabilization This digital potentiometer is so versatile that it can be used in various filter and waveform generation applications. In such applications, users should be aware that its bandwidth is a function of programmable resistance at a given setting. As a result, the bandwidth performance of the digital potentiometer is usually published in the data sheets. If the application does not violate the bandwidth limitation, the digital potentiometer can be applied in a programmable oscillator where the programmable resistance can be used to set the programmable frequency. Figure 1 shows one implementation where a popular Wien-Bridge oscillator with amplitude stabilization is furnished by D1 and D2. If we set CP = CS = C, RP = RS = R, and R2 = R2A || (R2B + RDIODE), it can be shown that the loop gain equation simplifies to 1 + R 2 / R1 L(s ) = 3 + sCR + 1 / sCR (3) is the end-to-end resistance. D1N4148 R1 10k⍀ 1 CR R= N1 4 (5) By using 1 nF for C, 100 kΩ for R (end-to-end resistance of the digital potentiometer), and with D set to 0, 128 , and 196, oscillations occur, respectively, at 1.59 kHz, 3.18 kHz, and 6.36 kHz with amplitude of ±1 V (See Figure 2). 8 7 D = 0, VO + 6V 6 5 4 D = 128, VO + 3V 3 2 D = 196, VO + 0V 1 0 –1 –2 0 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.004 0.005 0.006 0.007 0.008 0.009 0.010 TIME – Sec (1) Figure 2. For D = 0, 128, and 196, Oscillations Occur at 1.59 kHz, 3.18 kHz, and 6.36 kHz, Respectively © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies. REV. 0 (2) 256 – D RAB (4) 256 where D is the decimal equivalent of the digital code of the AD5232 dual 256-step digital potentiometer and RAB VO N2 2 1 + R2 / R1 3 + j (ωCR + 1 / ωCR ) W V+ U1 VO – C CP 1nF L( jω ) = RS A 100k⍀ B