Syllabus Workshop Part II: Backward Design & Learning Outcomes
advertisement

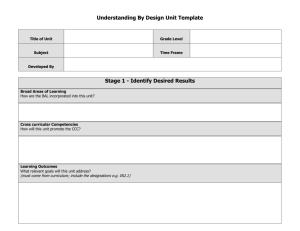
Syllabus Workshop Part II: Backward Design & Learning Outcomes Focus on Teaching & Learning Paula DeHart School of Education Assessment Coordinator Welcome to UWSP! UWSP has a strong focus on teaching, learning, and assessment Our campus has worked to develop learning outcomes at all levels (GEP, Department/Program, and Course) This session will provide foundational information on developing a syllabus and determining learning outcomes for each of your courses What do you already know? Raise your hand if you have had courses in pedagogy/course development as part of your graduate education. Raise your hand if you have had prior experience with course/syllabus development. Turn to a neighbor and share your first steps in putting a syllabus together. Content Expert/ Delivery System Recipient Recipient Recipient Recipient Content Centered Model of Teaching and Learning Learning Outcome Model of Teaching And Learning Knower/ Inquirer Knower/ Inquirer Knower/ Inquirer Enduring Understandings Essential Knowledge, Skills and Dispositions Knower/ Inquirer Knower/ Inquirer (Learning Outcomes ) Knower/ Inquirer Knower/ Inquirer Knower/ Inquirer Content + + + ... + Assessment Curriculum, Instruction, and Assessment in a Content Coverage Model What We imagine (hope) learning looks like within the content coverage model Maybe A More Accurate Picture of the Learning (Especially over time) Course/Syllabus Development Utilizing “Backward Design” Stage 1: Start with desired results Identify what students should understand, know, value, and be able to do as a result of completing the course (course/class activities, assignments, and assessments) Focus on enduring understandings (big ideas) that students will explore and learn during the course (link to professional standards, GEP learning outcomes, and program area outcomes--ask your dept. chair for these) Enduring Understandings Enduring understandings are big ideas, larger concepts, or real-world insights that have endured or will endure over time because they are so important and useful. Enduring understandings are ones that will last in the minds of students because they help them make sense of and organize content, and transfer key ideas to other courses and contexts beyond the classroom. Belts’ Test Examples of Enduring Understandings Students will understand that: Plant abundance and distribution is contextdependent (Biology) Human behaviors, lifeways, and interactions are shaped by culture (Anthropology) Statistical results are only useful if they can be explained and interpreted (Forest Biometrics) The physiology of disease and the aging process impact the capacity of individuals to participate in exercise (Exercise Programming) Examples of Essential Questions Why do some plant populations decline while others grow or simply persist? (Biology) What is culture? Why do people fight over it? (Anthropology) What role does the level of uncertainty play when making statistical decisions? (Forestry Biometrics) How can specific populations be encouraged to exercise? (Exercise Programming) Knowledge, Skills, and Dispositions Instructor identifies what students must know, be able to do, and value throughout the course (written as learning outcomes). Instructor particularly needs to consider knowledge, skills, and dispositions necessary to uncover enduring understandings and complete performance task(s) and other assessments. What is a Learning Outcome? A statement that describes what a student will know (knowledge), be able to do (skill), and/or value/appreciate (disposition) as a result of a learning experience Learning outcomes can be written for activities, lessons, courses, areas of emphasis, majors, programs, and degrees Written in the form: 1) Student can/will be able to| 2) action verb| 3) specific action/skill they will be able to do Learning outcomes are measureable (provide evidence of specific learning) Aligning Learning Outcomes UWSP LOs Program/Professional LOs GEP Category LOs Course Learning Outcomes Where Do I Find Active Verbs for Learning Outcomes? Websites with learning outcome verbs aligned with Bloom’s Taxonomy: http://cstep.csumb.edu/Obj_tutorial/bloomwheel.html Verb wheel based on Bloom’s Taxonomy http://www.au.af.mil/au/awc/awcgate/edref/bloom.ht m Learning objective verbs at each Bloom Taxonomy level Examples of Learning Outcomes Students can explain how plant survival, growth, and fecundity are affected by abiotic and biotic factors. (Biology) Students can utilize anthropological concepts to describe different cultural practices. (Anthro) Students can apply rules of probability to determine probabilities in the context of natural resources. (Forest Biometrics) Students can explain how group identities shape intergroup relations in harmful or helpful ways. (Psychology) Stage 2: Determine acceptable evidence of understanding Identify tasks, performances, and products that will demonstrate student understanding, as well as demonstrate key knowledge, skills, and dispositions (learning outcomes) Often framed in a real world context to add authenticity and meaning (What would a real person in a real situation/context do related to the theme and big ideas/enduring understandings?) Learning Outcomes Can be Assessed in a Variety of Ways (Written, Oral, Visual) Project Essay Portfolio Discussion Exam PowerPoint Debate Problem solution Research report Performance Poster Re-enactment Menu Speech Business plan Architectural Design Model Examples of Performance Tasks Research proposal for experiment on plant ecology (Biology) Ethnographic observation on UWSP campus (Anthropology) Statistical sampling exercise on UWSP campus (Forest Biometrics) Exercise program/plan for special population with specific circumstances (Exercise Programming) Stage 3: Plan Learning Experiences & Instruction Focus of course activities, assignments, and assessments is helping students “uncover” and leave with enduring understandings Class activities and assignments help students develop the knowledge, skills and dispositions (achieve course learning outcomes) they need to complete performance task(s) and other assessments