Internship Professional and Pedagogical Knowledge Rubric # 6
advertisement

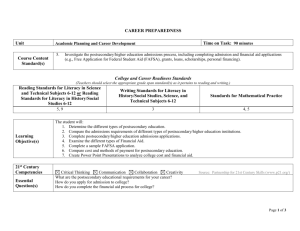
Internship Professional and Pedagogical Knowledge Rubric # 6 Alabama A & M University College of Education, Humanities, and Behavioral Sciences Assessment Completed by Cooperating Teacher and AAMU Course Instructors and Clinical Supervisors The rubric assesses thirty-seven proficiencies that the AAMU professional teacher educators and school professionals agree represent the content knowledge and core concepts of the initial programs. The rubric is to be completed by the team, consisting of the cooperating teacher and the AAMU Instructor/Supervisor. The team members complete the rubric independently of each other. Candidate’s Name: Major: Banner #: Name of Course Enrolled: Prefix Transitions Point (check one): Name of School: Subject Areas Observed: Title Pre-Entry Course Number Entry Pre-Clinical GRAD Clinical UG Completion Grade Level: Name of Cooperating Teacher: Name of AAMU Clinical Instructor/Supervisor: Name of Person Completing the Assessment: Date: Signature of Person Completing the Assessment: ________________________________________________________________ Directions: Rate the candidate in terms of how adequately the candidate is prepared to deal with each area listed below. RATING SCALE: 1 – Unacceptable This indicates that the clinical performance is not acceptable. Improvement activities must be undertaken immediately. 2 – Acceptable This indicates that the clinical performance sometimes, but not always, meets expectations. Improvement activities are required for performance to consistently meet standards. 3 – Good This indicates that the clinical performance meets and sometimes exceeds expectations for performance. Performance can be improved in area(s) indicated, but current practices are clearly acceptable. 4 – Exemplary This indicates the clinical performance is outstanding. No area for improvement is readily identifiable. NO – Not Observed This indicates the ability was not observed. The pre-service candidate demonstrates the ability to perform the following: Competence Indicator Ability to use students’ prior knowledge and experiences to introduce new subject-area related content. AQTS (1)(c)1.(iii) 2. Ability to identify student assumptions and preconceptions about the content of a subject area and to adjust instruction in consideration of these prior understandings. AQTS (1)(c)1.(iv) 3. Ability to teach explicit cognitive, meta-cognitive, and other learning strategies to support students in becoming more successful learners. AQTS (2)(c)1.(v) 4. Ability to use knowledge about human learning and development in the design of a learning environment and learning experiences that will optimize each student’s achievement. AQTS (2)(c)1.(vi) 5. Ability to recognize individual variations in learning and development that exceed the typical range and use this information to provide appropriate learning experiences. AQTS (2)(c)1.(vii) 6. Ability to plan and implement equitable and effective student access to available technology and other resources to enhance student learning. AQTS (2)(c)2.(v) 7. Ability to organize, allocate, and manage the resources of time, space, and activities to support the learning of every student. AQTS (2)(c)2.(viii) 8. Ability to organize, use, and monitor a variety of flexible student groupings and instructional strategies to support differentiated instruction. AQTS (2)(c)2.(ix) 9. Ability to communicate with parents and/or families to support students’ understanding of appropriate behavior. AQTS (2)(c)3.(iv) 10. Ability to create learning environments that increase intrinsic motivation and optimize student engagement and learning. AQTS (2)(c)3.(v) 11. Ability to use individual behavioral support plans to proactively respond to the needs of all students. AQTS (2)(c)3.(vi) 1. 1 Rating Scale 2 3 4 NO 12. Ability to create a print/language-rich environment that develops/extends students’ desire and ability to read, write, speak, and listen. AQTS (2)(c)3.(vii) 13. Ability to encourage students to assume increasing responsibility for themselves and to support one another’s learning. AQTS (2)(c)3.(viii) 14. Ability to select and support the use of instructional and assistive technologies and to integrate these into a coherent instructional design. AQTS (2)(c)4.(v) 15. Ability to make developmentally appropriate choices in selecting teaching strategies to assist diverse learners in meeting instructional objectives. AQTS (2)(c)4.(vi) 16. Ability to evaluate, select, and integrate a variety of strategies such as cooperative learning, discussion, discovery, problem-based learning, and direct instruction into a coherent lesson design. AQTS (2)(c)4.(vii) 17. Ability to adjust instruction in response to information gathered from ongoing monitoring of performance via formative assessment. AQTS (2)(c)4.(viii) 18. Ability to model appropriate oral and written communication. AQTS (3)(c)1.(iv) 19. Ability to demonstrate appropriate communication strategies that include questioning and active and reflective listening. AQTS (3)(c)1.(v) 20. Ability to foster effective verbal and nonverbal communications during ongoing instruction using assistive technologies as appropriate. AQTS (3)(c)1.(vi) 21. Ability to integrate skill development in oral and written communications into all content areas that one teaches. AQTS (3)(c)1.(vii) 22. Ability to use effective nonverbal communication and respond appropriately to nonverbal cues from students. AQTS (3)(c)1.(viii) 23. Ability to integrate reading instruction into all content areas that one teaches. AQTS (3)(c)2.(iii) 24. Ability to develop culturally responsive curriculum and instruction, i.e., model, teach, and integrate multicultural awareness, acceptance, and appreciation into ongoing instruction. AQTS (4)(c)1.(iv) 25. Ability to communicate in ways that demonstrate sensitivity to diversity such as appropriate use of eye contact, interpretation of body language and verbal statements, and acknowledgement of and responsiveness to different modes of communication and participation. AQTS (4)(c)1.(v) 26. Ability to differentiate between learner difficulties that are related to cognitive or skill development and those that are related to language learning. AQTS (4)(c)2.(ii) 27. Ability to collaborate with teachers of English language learners and to assist those students with full integration into the regular classroom. AQTS (4)(c)2.(iii) 28. Ability to help students assess their own learning styles and to build upon identified strengths. AQTS (4)(c)4.(iii) 29. Ability to design learning experiences that engage all learning styles. AQTS (4)(c)4.(iv) 30. Ability to create a learning community in which individual differences are respected. AQTS (4)(c)5.(iii) 31. Ability to involve parents and/or families as active partners in planning and supporting student learning. AQTS (5)(c)1.(iv) 32. Ability to communicate and collaborate effectively with colleagues, students, parents, guardians, and significant agency personnel who are included and valued equally as partners. AQTS (5)(c)1.(ix) 33. Ability to integrate statewide programs and initiatives into the curriculum and instructional processes. AQTS (5)(c)3.(iii) 34. Ability to communicate with students, parents, and the public about Alabama’s assessment system and major state educational improvement initiatives. AQTS (5)(c)3.(iv) 35. Ability to use and maintain confidential student information in an ethical and professional manner. AQTS (5)(c)5.(iii) 36. Ability to access resources to gain information about federal, state, district, and school policies and procedures. AQTS (5)(c)6.(iii) 37. Ability to keep accurate records including IEP’s, especially records related to federal, state, and district policies, and other records with legal implications. AQTS (5)(c)6.(iv) Total Score for Professional and Pedagogical Knowledge Assessment Rubric out of 148 possible