NIST Smart Grid Standards Roadmap Project Goals j
advertisement

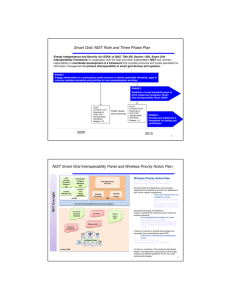
NIST Smart Grid Standards Roadmap Project j Goals George W. Arnold, Eng.Sc.D. National Coordinator for Smart Grid Interoperability N ti National l IInstitute tit t off Standards St d d and d Technology T h l April 23, 2009 The NIST Role Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA) of 2007 Title XIII XIII, Section 1305 1305. Smart Grid Interoperability Framework In cooperation with the DoE, NEMA, IEEE, GWAC, and other stakeholders, NIST has “primary responsibility to coordinate development of a framework that includes protocols and model standards for information management to achieve interoperability of smart grid devices and systems…” Why NIST? Smart Grid standards require q integration g of many y NIST skills: • Electric utility industry measurement research • Advanced network technology • Industrial I d t i l controls t l and d iinterfaces t f • Buildings and electrical infrastructure • Computer and network security • Documentary standards expertise • Testing and certification experience • Reputation as a neutral “honest broker”, facilitator, and convener Progress to Date 2007 2008 2009 • EISA Assigned g Standards Coordination Responsibility p y to NIST in December 2007 • NIST Engaged Key Stakeholders, Stakeholders Including DOE and FERC, FERC Other Agencies, and Industry • NIST Formed Domain Expert Working Groups With Over 100 Companies Participating • Launched Twiki Collaboration Website to Enhance Public Participation p • Initiated Development of Interoperability Knowledge Base • Convened 3-day Workshop at Grid Interop Conference in November 2008 • Key priority of new Administration • $4.5 billion DOE ARRA funding for Smart Grid, including $10 million for NIST • Urgency to establish standards becomes paramount • NIST develops plan to accelerate progress There is an Urgent g Need for Standards Example: Smart Meters $40 - $50 billion dollar p y nationwide deployment Underway now ARRA will acclerate Rapid technology evolution Absence of firm standards Source: Congressional Research Service Report 5 How Many Standards are Needed? How Long? By Analogy – Next Generation Network for Telecom (Verizon FiOS is one example – integrates voice, video, data) • Initial field trials in 2004 • Nationwide full deployment will take 10-15 years • Standards work started in 2003 • Three principal standards bodies involved • Release 1 standards finalized year-end 2005 • Release 2 finalized early 2008 • About 600 standards documents • Mostly “mix mix & match” match and extensions of existing standards • Standards continue to evolve with new technology Smart Grid is about the same magnitude • Key difference: many more standards bodies involved • Strong coordination role needed Domains Where Standards Are Needed IEC 61970/61968 for Enterprise “IT” Integration IEC 61850 for Real Real-Time Time Field Automation, Automation DER and RT Customer Systems/Vehicle Integration IEEE C37.118 For Phasor Measurement Units SAE/61850 For PEVs ANSI C12 Revenue Metering g ISA for Industrial ASHRAE/ANSI 135 for Building Automation 7 NIST Plan to Accelerate Progress Phase 1 Ph Roadmap and Smart Grid Release 1 • • • • • EPRI Contract Awarded April 2, 2009 Roadmap Workshops April 28-29 & May 19-20, 2009 Sec.Commerce/Energy CEO-level meeting, early May Standards “Congress” g July y 2009 Publication September 2009 Reflecting Consensus on • Architecture • Standardization Priorities • Selection of Release 1 Standards • Assignment of Responsibilities to Standards Development Organizations for Further Development • Timetable Phase 2 Public-Private Partnership for LongerTerm Evolution • RFP in May 2009 • Smart Grid Interoperability Standards Panel Launch by End of 2009 • Evolve Roadmap • Ongoing Coordination • Ensure Implementation Phase 3 T ti and Testing d Certification C tifi ti Framework • Develop Plan by End of 2009 • Begin B i IImplementation l t ti 2010 • Address both Interoperability and Security Phase 1: Roadmap p and Release 1 Standards April 28-29 28 29 Workshop • Define Architecture • Evaluate existing standards • Consensus on which can b endorsed be d d now (R1) • Identify issues May 19 19-20 20 Workshop • Identify additional standards needed • Priorities • Responsibilities • Timeline July Workshop • Refine and complete roadmap September 2009 Report 9 Smart Grid Organizational Structure: “Coordination Machinery” Smart Grid Task Force DOE, FERC, NIST DHS, NIST, DHS … Advisory Committee Smart Grid I t Interoperability bilit Framework F k Coordination Office George NIST Arnold, NIST Smart Grid Interoperability Standards Panel Board of Directors Standards Development Organizations Organizations (IEEE (IEEE, (NEMA, (NEMA IEC IEC, NAESB, IEEE, NEMA, IEC …) …) Full Panel (Organizational Membership) Working Groups (Evolved from NIST Domain Expert p Working g Groups) NIST Recognized Interoperability Specifications (Model standards and Protocols) ¾FERC rulemaking ¾DOE pilots and prototype implementations ¾DOE Clearinghouse ¾C f ¾Conformity it assessmentt