Math 2270 Spring 2004 Homework 4 Solutions
advertisement
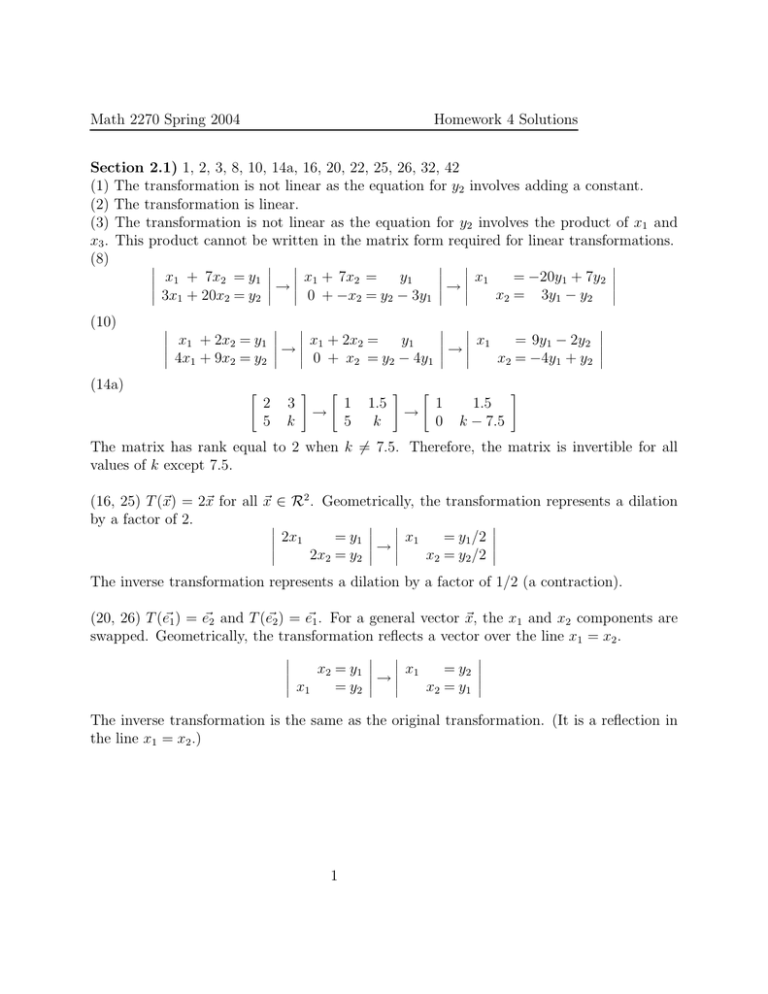
Math 2270 Spring 2004 Homework 4 Solutions Section 2.1) 1, 2, 3, 8, 10, 14a, 16, 20, 22, 25, 26, 32, 42 (1) The transformation is not linear as the equation for y2 involves adding a constant. (2) The transformation is linear. (3) The transformation is not linear as the equation for y2 involves the product of x1 and x3 . This product cannot be written in the matrix form required for linear transformations. (8) x x + 7x = x + 7x = y = −20y1 + 7y2 y1 1 1 1 2 2 1 → → 0 + −x2 = y2 − 3y1 3x1 + 20x2 = y2 x2 = 3y1 − y2 (10) (14a) x1 + 2x2 = y1 4x1 + 9x2 = y2 " 2 5 → 3 k # x1 + 2x2 = y1 0 + x2 = y2 − 4y1 → " 1 5 1.5 k # → " → 1 0 x1 = 9y1 − 2y2 x2 = −4y1 + y2 1.5 k − 7.5 # The matrix has rank equal to 2 when k 6= 7.5. Therefore, the matrix is invertible for all values of k except 7.5. (16, 25) T (~x) = 2~x for all ~x ∈ R2 . Geometrically, the transformation represents a dilation by a factor of 2. 2x = y1 x1 = y1 /2 1 → 2x2 = y2 x2 = y2 /2 The inverse transformation represents a dilation by a factor of 1/2 (a contraction). (20, 26) T (e~1 ) = e~2 and T (e~2 ) = e~1 . For a general vector ~x, the x1 and x2 components are swapped. Geometrically, the transformation reflects a vector over the line x1 = x2 . x2 = y1 x1 = y2 → x1 = y2 x2 = y1 The inverse transformation is the same as the original transformation. (It is a reflection in the line x1 = x2 .) 1 Math 2270 Spring 2004 Homework 4 Solutions (22) T (e~1 ) = e~1 and T (e~2 ) = −~ e2 . For a general vector ~x, the x1 component stays the same and the x2 component becomes negative. Geometrically, the transformation reflects a vector over the x1 − axis. x = y1 = y1 x1 1 → x2 = −y2 −x2 = y2 The transformation is its own inverse. (The inverse transformation is also a reflection in the x1 − axis.) (32) 3I = (42) 0 T 0 = 0 = 0 T 0 = 1 = " 1 T 0 = 1 " " 0 0 # 0 1 # −1/2 1/2 3 0 ··· ··· 0 3 0 ··· 0 0 3 0 ··· ··· ··· ··· 0 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 0 ··· 0 ··· 0 ··· ··· 0 3 " # 1 −1/2 T 0 = −1/2 0 # " 1 1/2 T 1 = −1/2 0 # # " 1 1/2 T 1 = 1/2 1 Here, s is an arbitrary real number. 2 # " 0 1 T 1 = 0 0 # " 0 1 T 1 = 1 1 # " 2s 0 T s = 0 s

