Math 2270 Assignment 3: Matrix Operations & Elimination
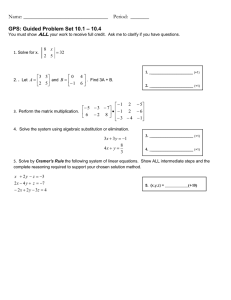
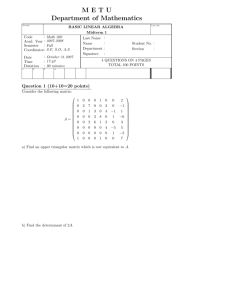
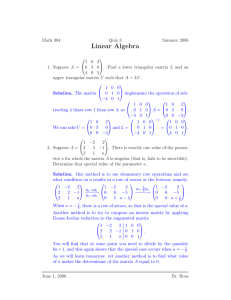
advertisement

Math 2270 Assignment 3
-
Dylan Zwick
Fall 2012
Section 2.3 1,2,3,7,17
Section 2.4 1,2,13,14,32
-
-
1
Section 2.3 Elimination Using Matrices
-
2.3.1 Write down the 3 by 3 matrices that produce these elimination steps:
21 subtracts 5 times row 1 from row 2.
(a) E
39 subtracts —7 times row 2 from row 3.
(b) E
(c) P exchanges rows 1 and 2, then rows 2 and 3.
Ii
oO\
b)
oat]
(IL(l(j5L)
0
071
1
32 to b
21 and then E
2.3.2 In Problem 1, applying E
(
0
gives
\o)
7Z)
2
1
b=
3
2
E
21 gives
Applying E
32 before E
(-5
S. C)
1
2
b=
2
3
E
3
When E
32 comes first, row
2
feels no effect from row
C’”
E
z
bO
Ct
I.
0
z
C’,
U
Ct
-cU
:
-d
cD
©
CSI
CN
S
L
0
0
0
0
Ljj
C)
3
Ui
0
0
C)
00—
(I
0—0
00
I’
LU
00—
ri
D
NJ
2.3.7 Suppose E subtracts 7 times row 1 from row 3.
(a) To invert that step you should
torow
3
7 times row
(b) What “inverse matrix” E’ takes the reverse step (so E’E
=
I)?
(c) If the reverse step is applied first (and then E) show that EE’
(:)
CD
4
=
2 goes through the points (x, y) =
2.3.17 The parabola y = a + bi + ci
(1, 4) and (2, 8) and (3. 14). Find and solve a matrix equation for the
unknowns (a, b, c).
ii
19
I
Lq)
(I
\t
4
(
ioo
/q
J 1
/fr I
0
-‘
Oo I
I
—‘
0
0
OC)
/H
/f,
J( /((
(111)79)
C
Ic 0
( )
Ut c:i
Ho
i
3)
‘3)/b)
0 L /
c
/
6f)
C
/ (0
q
/010)
(o/)
D
( 0o
7( 0
\
-L
II (
/
/ (oo/q)
OJ/05 )/b)/ 010
//q
/
/(
OZy
/
0f /( Id
fill
(0(5
I
2
Section 2.4 Rules for Matrix Operations
-
bvf
2.4.1 A is a 3 by 5, B is a 5 by 3, C is a 5 by 1. All entries are I. Which of
these matrix operations are allowed, and what are the results
BA
/\3c
I)
1H
DBA
ABD
AB
I
A(B+C).
—,
5 55
55
ill
(
\
I
(I I [1
I.
‘I
j
\
( I I I i
3
3 3
I Il
33 3 53
48 ::
/
/
5
5y
5
55
cJ
A
(*c)
‘
f
5)/i’) (
clfocije
aI1o
6
(Wed 1 addi
xJ )-
i5
I)
15/
2.4.2 What rows or columns or matrices do you multiply to find
(a) the third column of AB?
(b) the first row of AB?
(c) the entry in row 3, column 4 of AB?
(d) the entry in row 1, column 1 of CDE?
a)
qri’
A
e *h
e
A
m
Tk
c
A
4 Fob
prac o *Ae
* Ctj
of
7
irr
f
B
C
irf
2.4.13 Which of the following matrices are guaranteed to equal (A
—
:
2
B)
-B
A
,
2
A-B)-B(A-B),
BA ±
aie
/cq4ked
8
Je
ej/
2.4.14 True or false:
2 is defined then A is necessarily square.
(a) If A
(b) if AB and BA are defined then A and B are square.
(c) If AB and BA are defined then AB and BA are square.
(d) If AB
B then A
=
I.
Tr
b)
/
A
í
(d h
M
Ti
6{)
/
/17)
9
4
(
40
4 (efQfr
2.4.32 (Very important) Suppose you solve Ax
sides b:
1
Ax
=
()
2
and Ax
=
()
=
b for three special right
and Ax
3
=
().
If the three solutions x
,x
1
,x
2
3 are the columns of a matrix X, what is
A times X?
AX=
10
![Quiz #2 & Solutions Math 304 February 12, 2003 1. [10 points] Let](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010555391_1-eab6212264cdd44f54c9d1f524071fa5-300x300.png)