PHY 121 ... You may refer to this handout on quizzes and exams. ...
advertisement

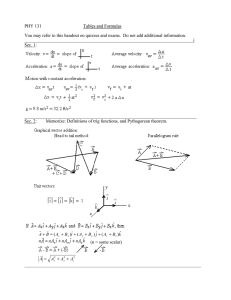
PHY 121 Tables and Formulas You may refer to this handout on quizzes and exams. Do not add additional information. e Sec. 1: ________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 2: Projectiles: No new formulas. ________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 3: Weight: W = mg -2- _______________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 4: _______________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 5: _______________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 6: ________________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 7: Newton's 3rd law: If A exerts a force on B, then B exerts an equal and opposite force on A. Momentum: p mv -3________________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 8: Moments of inertia: Particle of mass m, following orbit of radius r: I = mr2 Rigid bodies, total mass = M, outside radius = R: Hoop or tube, rotating about center: I = MR2 Solid cylinder or disk, rotating about center: I = (½)MR2 Solid sphere, rotating about center: I = (2/5)MR2 Thin spherical shell, rotating about center: I = (2/3)MR2 Thin rod, length L, rotating about center: I = (1/12)ML2 Thin rod, length L, rotating about one end: I = (1/3)ML2 ________________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 9: _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 10: ________________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 11: Pascal's Principle: P increase at one point in an enclosed fluid = P increase at any other point. Archimedes' Principle: Buoyant force = weight of displaced fluid = (ρV)g -4- Ideal gas law: PV = nRT P & T: Absolute pressure and temperature, V = volume, n = number of moles, R = 8.314 J/mole.K Sec. 12: Heat gained from a change of temperature: Q = m c ΔT c = specific heat Heat gained from a change of state: Q = mLf or Q = mLv L = heat of fusion or vaporization _ In an insulated container, ∑Q = 0 ________________________________________________________________________________ Sec. 13: First law of thermodynamics: Q = ΔEint + W Q = heat added, ΔEint = internal energy gained, Isobaric process = no pressure change, Isothermal = No temperature change, 2nd law: Entropy won't spontaneously decrease. (Or, Heat won't spontaneously go cold to hot.) Work done in a cycle = Area enclosed on P-V diagram. e W QIN = W + QOUT emax 1 TOUT QIN TIN Efficiency: Efficiency of Carnot Cycle: ________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ -5- 2 Quadratic Formula: If ax + bx + c = 0 then x b b2 2a 4ac Some fundamental constants: Speed of light: c = 2.998 x 108 m/s Electron rest mass: me= 9.110 x 10-31 kg = (.5110 MeV)/c2 Proton rest mass: mp = 1.673 x 10-27 kg = (938.3 MeV)/c2 Neutron rest mass: mn = 1.675 x 10-27 kg = (939.6 MeV)/c2 Universal gas constant: R = 8.314 J/mole K Avogadro's Number: N0 = 6.022 x 1023 molecules/mole Some Physical Properties: Density of air at 20 C and 1 atmosphere 1.29 kg/m3 Density of water at 20 C 1000 kg/m3 (=1.0 gram/cm3) Mass of earth 5.99 x 1024 kg Radius of earth 6.37 x 106 m Standard atmospheric pressure 1.013 x 105 Pa Approximate Coefficients of Friction: S k wood on wood 0.5 0.3 steel on steel 0.74 0.57 teflon on teflon 0.04 0.04 S k rubber on dry concrete 1.0 0.8 rubber on wet concrete 0.7 0.5 metal on ice 0.03 0.01 -6- Expansion Coefficients (near room temperature): °C-1) 24 x 10-6 20 x 10-6 17 x 10-6 9 x 10-6 3.2 x 10-6 29 x 10-6 12 x 10-6 12 x 10-6 150 x 10-6 Aluminum Brass & bronze Copper Glass (ordinary) Glass (pyrex) Lead Steel & iron Concrete Vinyl siding °C-1) Ethyl alcohol 7.5 x 10-4 Benzene 1.24 x 10-4 Acetone 1.5 x 10-4 Glycerin 4.85 x 10-4 Mercury 1.82 x 10-4 Gasoline 9.6 x 10-4 Specific heat, c (at 25 C): Substance cal/g C Aluminum 0.217 Concrete 0.2 Copper 0.093 Gold 0.0308 Ice(-25-0 C) 0.48 Iron & Steel 0.112 Lead 0.0305 J/kg C 908 840 390 129 2010 469 128 CP CV (J/mol K) (J/mol K) He Ar Ne Kr 20.8 20.8 20.8 20.8 12.5 12.5 12.7 12.3 Substance cal/g C Silver 0.056 Tin 0.054 Zinc 0.092 J/kg C 234 226 385 Ethyl alcohol 0.58 Mercury 0.033 Water 1.00 Steam (1atm) 0.47 2430 140 4186 1970 CP CV (J/mol K) (J/mol K) 1.67 1.67 1.64 1.69 H2 N2 O2 CO 28.7 29.1 29.2 29.2 20.4 20.8 20.9 20.9 CP CV (J/mol K) (J/mol K) 1.41 1.40 1.40 1.40 CO2 SO2 H2O CH4 36.9 40.4 35.4 35.5 Heat of Fusion of water = 79.6 cal/g = 3.34 x 105 J/kg Heat of Vaporization of water = 539 cal/g = 2.26 x 106 J/kg 28.5 31.4 27.0 27.1 1.30 1.29 1.30 1.31 -7Units: Fundamental Units: Standard SI Unit: Conversion Factors: LENGTH meter = m 1 m = 3.28 ft, 1 mile = 1609 m = 5280 ft, 1 inch = 2.54 cm TIME second = s 1 hour = 3600 s, 1 day = 86,400 s, 1 year = 3.16 x 107 s MASS kilogram = kg TEMPERATURE kelvin = k 1kg = .0685 slug, weighs 2.21 lb in standard gravity 1 atomic mass unit = 1 u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg T (in kelvins) = T (in Celsius) + 273.15 VOLUME m3 1 Liter = 10-3 m3 = 10+3 cm3 SPEED m/s 1 mi/hr = 0.447 m/s = 1.47 ft/sec FORCE newton = N 1 N = 0.225 pound ENERGY & WORK joule = J 1 calorie = 4.186 J 1 J = 0.738 ft lb 1 electronvolt = 1.602 x 10-19 J, 1 BTU = 252 cal POWER watt = W 1 horsepower = 746 W = 550 ft lb/sec ANGLE radian = rad 1 revolution = 360 = 2π rad Derived Units: FREQUENCY hertz = Hz 1 Hz = 60 rev/min = 1 cycle/sec IMPULSE & MOMENTUM kg m/s = N S PRESSURE pascal = N/m2 1 atmosphere = 1.013 x 105 Pa = 14.7 lb/in2 SI prefixes: Power: 10-24 10-21 10-18 10-15 10-12 10-9 10-6 10-3 10-2 10-1 Prefix: yocto zepto atto femto pico nano micro milli centi deci Abbreviation: y z a f p n Power: 101 102 103 106 109 1012 m c d 1018 1021 1024 Prefix: deka hecto kilo mega giga tera peta exa zetta yotta Abbreviation: da h k M G T P E Z Y