Document 11683476
advertisement

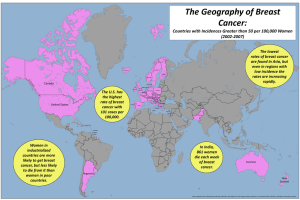
What do you know about cancer? (list 5 things) What would you like to know about cancer? (at least 3 things) http://www.yout ube.com/watch?v =O3_PNiLWBjY G1: before copying DNA, the cell checks itself to see if conditions are favorable for division G2: the cell checks for mistakes in copied DNA; enzymes make necessary corrections Mitosis checkpt: during metaphase, the cell checks that the chromosomes are attached to the spindle to ensure they divide properly Protonocogenes Oncogenes Protoncogenes that have mutated Tumor suppressor genes Genes that encode proteins which regulate normal cell growth and division Genes that restrain growth (p53: halts cell division if it senses DNA is damaged) Caretaker genes Genes that control DNA integrity by repairing DNA Determining cause is complex. damage genes or combine with existing genetic faults within cells to cause the disease Chemicals: benzopyrene, PIP: heterocyclic amine Radiation Factors that increase the risk of cancer, tobacco use, certain infections, radiation, lack of physical activity, poor diet and obesity, environmental pollutants Genetics: 5-10% Benign: mutations in ½ genes can lead to tumor Localized population of cells Proliferating cells result in cell death Metastasis: Malignant: Additional mutations lead to uncontrollable cell growth The uncontrolled growth has led to new capillaries providing a route for malignant cells to break away and travel throughout the body via blood or lymph Cell size Many nuclei Large nuclei Small amount of cytoplasm Cytoplasm to nucleus ratio Gene Screen: What are possible Treatments? chemotherapy: anti-cancer drugs act to destory the tumor cell or stop cell division radiation therapy: ionizing radiation damages DNA to destroy the cell or slows the development of abnormal cells. Surgery: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RZhL7LDPk8w Diet increase risk: obesity and alcohol consumption a diet high in fruits and vegetables Whole grain Fish low intake of red meat has being implicated but not confirmed. consumption of coffee is associated with a reduced risk of liver cancer. Stay away from animal fat and refined sugar. Screening Genetic Testing Self exams and diagnostic prevention As part of diagnostic prevention Medication Inflammatory drugs Aspirin (can reduce risk by 7%) Estrogen drugs for breast and uterine cancer Vaccination Help prevent some infection by some viruses Human papillomavirus vaccine (Gardasil and Cervarix) cervical cancer hepatitis B vaccine prevents infection with hepatitis B virus and decreases the risk of liver cancer UV radiations causes mutation in the DNA of a skin cell 75% of cancers are skin cancers Most common cancers are caused by prolonged exposure to UV radiation from sunlight Three major types: 1. Basal Cell Carcinoma Most common type of skin cancer 2/3 of these cancers appear from chronic UV exposure 2. Squamous cell carcinoma Frequent in light, pale skin over 40 years old Slow growing Surgical removal or radiation Originates from epithelial cells 3. Malignant Melanoma Arise from melanocytes Usually in trunk of body and from a mole Hard to treat Difficult to treat due to fast growing and invasion of deep tissues Risk increases with short, intermittent exposure to high-intensity sunlight. A-asymmetry B-Border C-Color D-diameter cancer that forms in tissues of the breast, usually the ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple) and lobules (glands that make milk). estimated new cases and deaths from breast cancer in the United States in 2010: New cases: 207,090 (female); 1,970 (male) Deaths: 39,840 (female); 390 (male) http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/breast For women in the U.S., breast cancer death rates are higher than those for any other cancer, besides lung cancer. Besides skin cancer, breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer among U.S. women. More than 1 in 4 cancers in women (about 28%) are breast cancer. Compared to African American women, white women are slightly more likely to develop breast cancer, but less likely to die of it. One possible reason is that African American women tend to have more aggressive tumors, although why this is the case is not known. Women of other ethnic backgrounds — Asian, Hispanic, and Native American — have a lower risk of developing and dying from breast cancer than white women and African American women. about 5-10% of breast cancers can be linked to gene mutations (abnormal changes) inherited from one’s mother or father. Mutations of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are the most common. Women with these mutations have up to an 80% risk of developing breast cancer during their lifetime, and they are more likely to be diagnosed at a younger age (before menopause). An increased ovarian cancer risk is also associated with these genetic mutations. In men, about 1 in 10 breast cancers are believed to be due to BRCA2 mutations and even fewer cases to BRCA1 mutations. About 70-80% of breast cancers occur in women who have no family history of breast cancer. These occur due to genetic abnormalities that happen as a result of the aging process and life in general, rather than inherited mutations. ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) inflammatory breast cancer male breast cancer recurrent breast cancer metastatic breast cancer testicular