Exam III
advertisement

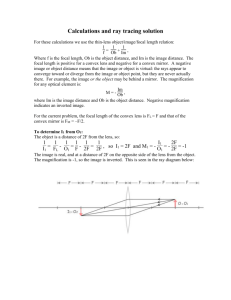
Physics 142! Summer 2013 Exam III Solutions Part A. Multiple choice questions. Check the best answer. Each question carries a value of 4 points. 1.! In as class demonstration the AC circuit consists of the 120 V (rms) voltage from the wall outlet as generator, a light bulb of 60 Ω resistance, and a capacitor and inductor, each of which has 300 V (rms) across it. Which of the following is wrong? ! The circuit is in resonance. ! The capacitor and inductor each consume zero power in a cycle. √ ! [The current is 2 A so XL = XC = 150 Ω .] ! ! 2.! The reactances of the capacitor and inductor are XL = XC = 300 Ω . One of the above is wrong. Which of the following devices, when used as intended, produces a (final) real image to be viewed by an observer? ! A magnifying glass. ! An astronomical telescope. √ ! ! A slide projector. An optical microscope. ! 1 Physics 142! 3.! Summer 2013 Unpolarized light is incident at angle θ1 from a medium with refractive index n1 onto the interface with a medium of refractive index n2 . The light is totally reflected. Which of the following is wrong? ! If θ1 < 90° then n2 < n1 . ! If n2 > n1 then θ1 = 90° . √ ! The reflected light is partially polarized with E perpendicular to the plane of incidence. [No polarization for total reflection.] If n2 < n1 then θ1 is at least as large as the critical angle. ! 4.! A person cannot focus effectively on objects closer than 50 cm or farther away than 5 m. The bifocal lenses to correct the vision (with effective near point at 25 cm) should have focal lengths: ! –50 cm and +5 m. √ ! +50 cm and –5 m. ! –50 cm and –5 m. ! +50 cm and + 5 m. Part B. True-false questions. Check T or F depending on whether the statement is true or false. Each question carries a value of 3 points. 5.! If a surface absorbs energy E from a beam of light, it also absorbs momentum E/c from the beam. √ 6.! T Total reflection for incident angles less than 90° can occur when light is reflected from a medium with a higher index of refraction. T 7.! F √ F [Must be lower.] The transmission axis of polarizing sunglasses is horizontal to absorb reflected glare from horizontal surfaces. T √ F [Vertical.] 2 Physics 142! Summer 2013 Part C. Problems. Work problem in space provided, using extra sheets if needed. Explain your method clearly. Problems carry the point values shown. 1.! The input voltage (rms) to the filter is Vin at frequency ω . a.! Find the current through the resistor in terms of Vin and the circuit elements shown. b.! Find Vout /Vin in terms of ω and the circuit What is this ratio for ω → 0 ? For ω → ∞ ? d.! For what value of ω is the ratio equal to 1? Vin R L elements. c.! C [20 points] a.! The impedance is Z = R 2 + (XL − XC )2 so the current is I = Vin / R 2 + (XL − XC )2 . Vout = Vin R b.! Since Vout = IR we have c.! For both limits the ratio vanishes. d.! When ω L − 1/ω C = 0 the ratio is 1. This means ω 2 = 1/LC , i.e., resonance. R 2 + (ω L − 1/ω C)2 3 . Vout Physics 142! 2a.! Summer 2013 Light is incident from air onto a block of a transparent material in the shape of an equilateral triangle. a.! The angle of refraction at the top surface is θ 2 and the angle of incidence of this ray on the side of the triangle is θ 3 . Show that θ 2 + θ 3 = 60° . [Draw the ray.] b.! θ1 60° Show that if n ≥ 2 then reflection is total at the side of the triangle, no matter what θ1 is. [Show it for θ1 = 90° and argue it must be true for smaller values of θ1 . Use sin 30° = 1/ 2 .] [10 points] a.! See drawing. The angles of the dotted triangle are θ 2 , θ 3 , and 120°, so θ 2 + θ 3 = 60° . b.! For θ1 = 90° , nsin θ 2 = 1 , or sin θ 2 = 1/n ≤ 1/ 2 . This means θ 2 ≤ 30° , so θ 3 ≥ 30° and sin θ 3 ≥ 1/n . Thus θ 3 is at least equal to the critical angle for total reflection. If θ1 < 90° then θ 3 is even larger. 2b.! The magnifying powers of telescopes and microscopes are inversely proportional to the focal length of the eyepiece. Why is it not possible to obtain arbitrarily large magnifying powers by making that focal length extremely small? [5 points] ! ! Reducing the focal length requires reducing radii of curvature of the lens surfaces. This increases the problem of spherical aberration, making it necessary to use only the very center of the lens, which reduces the brightness of the image. 4 Physics 142! 3a.! ! Summer 2013 Shown is a flashlight battery connected in a circuit with a current I as shown. The radius of the battery is a and its length is L. The potential difference between its ends is ΔV. P I + a.! At point P shown, what are the magnitudes and directions of the electric and magnetic fields (assuming the E-field is uniform along the length of the battery)? b.! What is the Poynting vector S (direction and magnitude) at P? Explain the physical significance of the direction. c.! Show that the outward flux of S through the battery’s surface is equal to the power it supplies. [15 points] a.! E is to the left (toward lower potential), B is out of the page (right hand rule). The magnitudes are E = ΔV /L , B = µ0 I / 2π a . b.! S is up the page, with magnitude S = EB IΔV = . The direction shows power is µ0 2π aL leaving the battery through its sides. c.! The surface area of the sides is A = 2π aL and the total power is P = SA = IΔV , as expected. (There is no power outward through the ends of the battery because of the direction of S.) 3b.! Explain why swimmers and scuba divers wear goggles when under water. [5 points] The material of the eye has almost the same index of refraction as water, so the focusing power of the eye in water is very small. Placing a layer of air in front of the eye restores normal vision. This is what the goggles do. 5 Physics 142! 4.! Summer 2013 An object is 15 cm if front of a mirror of focal length 10 cm as shown. The dots are spaced 5 cm apart. At 50 cm from the mirror is a lens of focal length –10 cm. 1st image • • • • • • • 2nd image • • • • • a.! Use the formulas to locate the image formed by the mirror and find its magnification. b.! Use this image as the object for the lens, locate the final image and find the overall magnification. c.! Draw careful principal ray diagrams to show how these images are formed. The vertical lines represent the location of the mirror and lens in paraxial ray approximation. d.! Suppose the lens is only 25 cm from the mirror. Use the formulas to locate the final image and find the overall magnification. [What is the object distance for the lens?] [20 points] a.! Here p1 = 15 so we have b.! Now p2 = 20 so 1 1 1 1 = − = , so q1 = 30 . Also m1 = −30/15 = −2 . q1 10 15 30 1 1 1 3 −20/3 = − =− so q2 = −20/3 . Also m2 = − = 1/3 . q2 −10 20 20 20 The overall magnification is m = m1m2 = −2/3 . c.! Drawing shown. Red rays for mirror, blue for lens. d.! Now the object for the lens is virtual. We have p2 = −5 and find s2 = 10 , so it is a real image. The magnification is m2 = +2 and the overall magnification is −4 . [Ray diagram on next page for those curious.] 6 Physics 142! Summer 2013 1st image • • • • • • • • • • • 2nd image 7 • Physics 142! Summer 2013 Exam III 25 Median = 81.5 St Dev = 13 Students 20 15 10 5 0 <40 40 50 60 70 80 90 80 90 Exam Average 25 Median = 74.3 St Dev = 13.4 Students 20 15 10 5 0 <40 40 50 60 8 70