Oxford Molecular Genetics Laboratory
advertisement
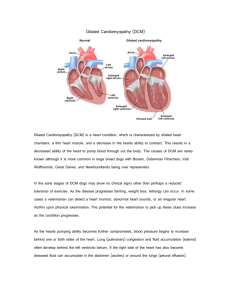
Oxford Molecular Genetics Laboratory Genetics Laboratories, Churchill Hospital, Old Road, Headington, Oxford, OX3 7LE www.ouh.nhs.uk/geneticslab Dilated Cardiomyopathy: 36 Gene Panel INTRODUCTION Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a myocardial disorder defined by the presence of a dilated and poorly functioning left ventricle, meaning the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. Idiopathic DCM is estimated to affect ~1 in 2,500 adults and often presents with reduced exercise tolerance or dyspnoea. More severe signs of heart failure may ensue in some cases if left untreated. Some affected individuals also have cardiac conduction defects. Familial DCM is usually inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern with incomplete penetrance. Mutations in >30 genes, including those that encode protein components of the sarcomere and Z-disc, are known to predispose to the disorder. The Oxford Medical Genetics Laboratory provides molecular genetic testing for 36 DCM-relevant genes (see table below). The multi-gene panel includes not only genes primarily related to DCM, but also genes more closely related to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), both of which may clinically overlap with DCM. The overall clinical sensitivity for probands screened on this panel is 20-30%. Gene Primary Related Disorders Gene Primary Related Disorders ACTC1 ACTN2 ANKRD1 BAG3 CRYAB CSRP3 DES DMD DSC2 DSG2 DSP FHL1 FHL2 FLNC GLA JUP LAMP2 LMNA DCM, HCM, LVNC DCM, HCM, LVNC HCM, DCM DCM, myofibrillar myopathy DCM, skeletal myopathy. HCM ARVC, skeletal myopathy D/BMD, X-linked DCM ARVC ARVC ARVC, Carvajal syndrome, DCM HCM, skeletal myopathy DCM HCM, myofibrillar myopathy Anderson-Fabry disease ARVC, Naxos syndrome Danon’s disease DCM, skeletal myopathy, other laminopathies MYBPC3 MYH7 MYL2 MYL3 PKP2 PLN PRKAG2 RBM20 SCN5A TAZ TMEM43 TNNC1 TNNI3 TNNT2 TPM1 TTN TTR VCL HCM, LVNC DCM, HCM, LVNC, RCM HCM HCM ARVC ARVC, DCM, HCM HCM, WPW DCM Brugada syndrome, DCM Barth syndrome ARVC DCM, HCM DCM, HCM, RCM DCM, HCM, LVNC, RCM DCM, HCM, LVNC DCM Amyloidosis DCM DCM: dilated cardiomyopathy. D/BMD: Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. HCM: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. LVNC: left ventricular non-compaction. RCM: restrictive cardiomyopathy. WPW: Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. REFERRAL PROCEDURE • Diagnostic referrals are accepted for probands with a suspected or confirmed diagnosis of DCM. o o o • Family test referrals are only accepted from Clinical Genetics specialists. o o • • This multi-gene panel may also be appropriate for probands with left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) or an undefined genetic cardiomyopathy. Referrals are accepted from Cardiology, Clinical Genetics and Consultants from other relevant medical specialities. Clinical information and details of relevant family history should be provided with all referrals either on the original request form or on a separate pre-referral form (DCM pre-referral form). Referrals for affected family members (i.e. segregation analysis) must be accompanied by appropriate clinical information. Referrals for unaffected family members will only be considered for variants with clear evidence for pathogenicity. Clinical advice is available from Dr Edward Blair, Consultant Clinical Geneticist, at the Churchill Hospital (Ed.Blair@ouh.nhs.uk). Further information about the test can be obtained from the laboratory (OxfordCardiac@nhs.net). SAMPLE REQUIREMENTS • • This analysis requires >4 μg of DNA at >30 ng / μl. DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue may be suitable. o o >300 ng (preferably >1,000 ng) at >30 ng / μl is required. Total gene coverage may be lower due to the poor quality of DNA obtained from FFPE tissue. STRATEGY AND TECHNICAL INFORMATION • Diagnostic Screens: o o Gene target enrichment is undertaken using Agilent’s HaloPlex Target Enrichment System. Libraries are sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq Desktop Sequencer. o o o • This will involve sequence data generation in-house or by the High Throughput Genomics Group at the Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, Oxford. Sequence data are analysed on a custom-designed bioinformatic pipeline. Where possible, regions of interest (ROIs) in the following genes are 100% covered either by >30 reads or by Sanger sequencing: DSP, LMNA, SCN5A. Coverage of ROIs in the remaining genes varies, but is typically 85–100% at >30 reads. Family Tests: o Familial variants are targeted for analysis by Sanger sequencing of the relevant exon, with DNA from a family member used as a positive control where possible. TARGET REPORTING TIMES • • • Diagnostic screens: Family tests: Urgent analysis: 60-80 working days 10 working days Please contact the laboratory. PRICING Please see the current price list on the Oxford Genetics Laboratories Molecular Genetics page. N.B. Details are correct for the date of printing only. Updated: 12/10/2015.