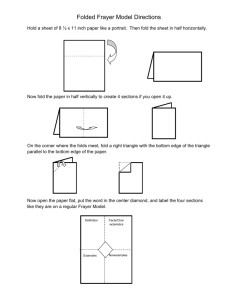
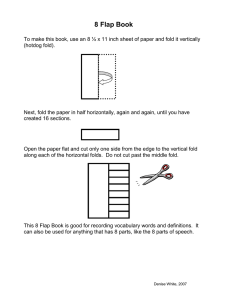
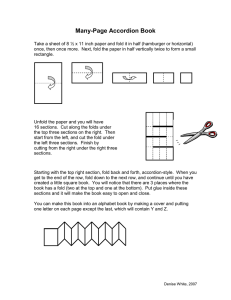
FOLD TERMS
advertisement

FOLD DEFINITIONS ASYMMETRIC FOLDS: Folds in which the limbs are of unequal length. AXIAL SURFACE: the surface joining the hinge lines of a set of nested folds; may also be called the axial plane if planar. AXIAL TRACE: the line representing the intersection of the axial surface and another surface. CREST LINE: line on the surface of the fold at which the dip changes direction with respect to the horizontal CROSS SECTION: a plane perpendicular to horizontal. CYLINDRICAL FOLD: a fold generated by a straight line moving parallel to itself in space. ENVELOPING SURFACE: planes drawn tangent to the crest and trough lines. FOLD AXIS: the straight line that generates a cylindrical fold. Unlike the hinge line, the fold axis is not a specific line but rather a hypothetical line defined by its attitude. Only cylindrical folds, or cylindrical segments of folds, have fold axes. FOLD LIMB: area of folded surface between hinge zones. HINGE LINE: line of maximum curvature (smallest radius of curvature) on a folded surface INFLECTION POINT: the point on a fold where the rate of change of slope is zero; usually chosen as the midpoint of each straight section of the fold limb INTERLIMB ANGLE: the angle between adjacent fold limbs. LINE of INFLECTION: locus of inflection points of a folded surface MEDIAN SURFACE: surface that joins the successive lines of inflection of a folded surface. PROFILE PLANE: a plane perpendicular to the fold axis. SYMMETRIC FOLDS: Folds in which the median surface is planar, the axial plane is perpendicular to the median surface, and the folds are bilateral symmetrical about their axial planes. TROUGH LINE: same as crest line except that the dip directions point toward one another. FOLD TERMS Fold description based on interlimb angle Interlimb Angle Fold Type Parasitic asymmetric folds asymmetric “Z” folds dextral axial surface trace asymmetric “S” folds sinistral enveloping surface TYPES OF FOLDS ANTICLINE: a fold with older rocks in its core. ANTIFORM: a fold that closes upward. ANTIFORMAL SYNCLINE: an antiform with with younger rocks in the core. OVERTURNED FOLD: a fold in which one limb has been tilted more than 90°, resulting in both limbs dipping in the same direction. RECLINED FOLD: a fold whose axial surface is inclined and whose hinge plunges down the dip of the axial surface. RECUMBENT FOLD: a fold whose axial surface is horizontal. SYNCLINE: a fold with younger rocks in its core. SYNFORM: a fold that closes downward. SYNFORMAL ANTICLINE: a synform with oldest rocks in the core. TIGHTNESS: fold classification based on interlimb angle. VERGENCE: the direction towards which the fold is turned (clockwise = dextral or "z" folds, counterclockwise = sinistral, "s" folds) viewed down plunge. VERTICAL FOLD: a fold whose hinge line is vertical. Fold description based on orientation of axial plane and hinge line > 120° 120 to > 30° 30 to > 10° 10 to 0° < 0° gentle open tight isoclinal elasticas