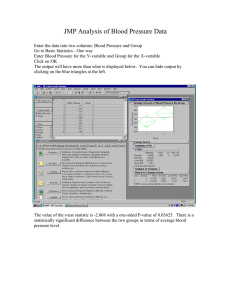
STATISTICS 402 - Assignment 4 Due March 5, 2010
advertisement

STATISTICS 402 - Assignment 4 Due March 5, 2010 1. In the study involving memory on assignment 3, there was actually a second factor – Age or the participant. On assignment 3 you looked only at the older literate adults but there was also a set of younger literate adults that were assigned at random to the five learning groups: Counting, Rhyming, Adjective, Imagery and Intentional. After subjects read through a list of words three times, they are asked to write down all the words they can remember. The number of words correctly recalled is noted for each subject. The experiment involves 50 younger literate adults and 50 older literate adults. a) b) c) d) Is age group an observational or an experimental variable? Explain briefly. Is learning group an observational or an experimental variable? Explain briefly. How many treatment groups are there in the full experiment? What is the size of the difference in age group means (younger literate adults compared to older literate adults) that can be detected with Alpha = 0.01 and Beta = 0.20? e) What is the size of the difference in leaning group means that can be detected with Alpha = 0.05 and Beta = 0.05? f) Will the experiment be able to detect a 2.0 standard deviation difference in treatment means with Alpha = 0.05 and Beta = 0.10? Explain briefly. 2. A JMP data table for the experiment described in 1 is on the course web site: www.public.iastate.edu/~wrstephe/stat402.html Use JMP to analyze the data from the experiment. Turn in the JMP output and us it to answer the following questions. a) Analyze and comment on the distribution of the number of words recalled. b) Fit a model that includes Age Group, Learning Group and Age Group*Learning Group interaction effects. Give the value of R2 and the value of the estimate of the error standard deviation, σ. c) Test the hypothesis that there are no differences among the population treatment means. Be sure to include the F statistic, P-value, decision, reason for the decision and a conclusion within the context of the problem. d) Test the hypothesis that the age group effects are zero. Be sure to include the F statistic, P-value, decision, reason for the decision and a conclusion. e) Is there a “best” age group in terms of number of words recalled? Explain briefly. f) Test the hypothesis that the learning group effects are zero. Be sure to include the F statistic, P-value, decision, reason for the decision and a conclusion within the context of the problem. g) Where are the statistically significant differences among the learning group means? Use the HSD (Tukey-Kramer) multiple comparisons procedure. h) Is there a “best” learning method? Explain briefly. i) Test the hypothesis that the interaction effects are zero. Be sure to include the F statistic, P-value, decision, reason for the decision and a conclusion within the context of the problem. j) Construct and comment on the interaction plot. k) Construct plots of residuals versus each of the factors in the experiment. Comment on the plots, specifically, what do the plots tell you about the Fisher conditions? l) Analyze the distribution of residuals. Comment on what the analysis of residuals says about the Fisher conditions. 1