Introduction
advertisement

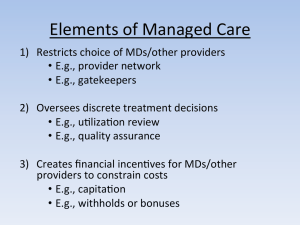
Introduction The Question: Is HMO market share associated with adoption of cardiac-care technologies, and, in turn with treatments and outcomes for heart attack patients Approach: Use hospital-level hazard models to study relationships between HMO market share and adoption Use patient-level models to study relationship between availability and treatments and outcomes Cardiac Care Technologies We focus on three cardiac technologies Diagnostic: Cardiac catheterization Therapeutic: PTCA Therapeutic: CABG All involve the adoption of equipment and staff Catheterization and CABG first developed in the 1960s; PTCA in the 1970s Catheterization equipment is used to do PTCA PTCA and CABG are usually adopted together Hospital-Level Data We focus on 2,873 hospitals in MSAs in operation in 1985 We use Medicare Claims data from 1985-2000 to identify hospitals that adopt these technologies and the year of adoption Hospitals with 10 claims for a given service in a calendar year are defined as having the technology in that year Based on patterns in the data, we study 3 adoption states: none, catheterization only, and all techologies Hospital-Level Data We classify hospitals according to the average 19901999 HMO market share in their MSA Low: <10% Medium: 10-30% High: >30% Hospital-Level Adoption Modeling Discrete-time hazard models Competing risks for probability of moving from none to cath only or none to all Standard hazard model for probability of moving from cath only to all Controls include a range of potential confounders, including urbanization, demographics, hospital characteristics Hazard Model Results None to Cath Only Medium HMO 0.174 (0.119) [1.190] 0.170 (0.120) [1.186] 0.175 (0.120) [1.191] High HMO 0.616 ** (0.213) [1.851] 0.611 ** (0.215) [1.843] 0.611 ** (0.215) [1.842] 0.711 ** (0.127) 0.713 ** (0.127) CICU in 1982 --- MSA AMI mortality --- --- 0.703 (1.381) yes yes yes State dummies Standard errors in parentheses. Relative Hazards in brackets. Models include additional covariates. * denotes p<0.05; ** denotes p<0.01 Hazard Model Results Cath Only to All Medium HMO -0.202 (0.134) [0.817] -0.209 (0.134) [0.812] -0.223 (0.136) [0.800] High HMO -0.431 # (0.231) [0.650] -0.426 # (0.231) [0.653] -0.440 # (0.231) [0.644] 0.501 * (0.225) 0.505 * (0.227) CICU in 1982 --- MSA AMI mortality --- --- -0.815 (1.330) yes yes yes State dummies Standard errors in parentheses. Relative Hazards in brackets. Models include additional covariates. * denotes p<0.05; ** denotes p<0.01 Technology availability, treatments, and outcomes HMO activity affects the probability a heart attack patient will be treated in a hospital with the technology Whether or not the hospital of treatment has the technology affects the probability of actually receiving a treatment Receiving treatments affects mortality rates Medicare AMI Data Claims data on a 20% sample of FFS Medicare patients in MSAs with a new AMI between 1996 and 2000 N=148,170 Measure technology status of index hospital, treatment receipt within 90 days of initial admission, and 1 year mortality Data also contain detailed data on comorbidities and other characteristics Statistics Estimate individual-level models Control for a range of characteristics sex; race; age; admission in the prior 2 years for IHD, CHF, VA, or any other cause; conditions at admission: cancer, diabetes, dementia, heart failure, hypertension, stroke, peripheral vascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, respiratory failure, renal failure, or hip fracture; area per capita income, total area population and population density; % population graduated high school/college; % of the work force white collar; squared terms for area characteristics; year Index Hospital Capabilities Multinomial Logit (results relative to all technologies) Probability that index hospital has Nothing Cath only Medium HMO -0.004 (0.068) 0.220 ** (0.050) High HMO -0.586 ** (0.089) 0.430 ** (0.071) % of cases 12.5 29.4 Models are multinomial logit regressions and include additional covariates and state dummies as well as interactions between HMO variables and year. * denotes p<0.05; ** denotes p<0.01 Treatments Received Multinomial Logit (relative to medical management) Cath Index Facility Cath Only Index Facility All N Percentage of all cases PTCA CABG -0.474 ** 0.059 -0.174 ** 0.058 -0.109 # 0.057 0.475 ** 0.040 0.979 ** 0.040 0.603 ** 0.041 148,170 0.149 148,170 0.225 148,170 0.154 Models are multinomial logistic regressions of the probability of receiving cath, PTCA, CABG, or medical management within 90 days of initial hospitalization. Models include additional covariates, state dummies, and interactions between tech variables and year. # denotes p<0.10, * denotes p<0.05; ** denotes p<0.01 Treatments and 1-year Mortality Logistic Regression Patient got Catheterization -0.222 ** (0.007) Patient got PTCA -0.292 ** (0.007) Patient got CABG -0.295 ** (0.007) N DV mean 148,170 0.339 From logistic regression of the probability of 1 year mortality. Models include additional covariates, state dummies, and interactions between tech variables and year. # denotes p<0.10, * denotes p<0.05; ** denotes p<0.01 HMO Market Share and 1-Year Mortality Logistic Regression Coefficient (SE) P-value medium HMO 0.013 (0.009) 0.128 high HMO 0.017 (0.013) 0.188 N DV mean 148,170 0.339 From logistic regression of the probability of 1 year mortality. Models include additional covariates, state dummies, and interactions between HMO variables and year. # denotes p<0.10, * denotes p<0.05; ** denotes p<0.01 Conclusions Managed care activity affected the adoption of cardiac technologies This could well be associated with worse outcomes for AMI patients impacts on other patients, and other outcomes, are unknown Means of Hospital Level Variables Low HMO prevalence Medium HMO prevalence High HMO prevalence Teaching hospital Medical school affiliation Total beds, hundreds MSA per capita income, $ thousands MSA percentage of population - urban MSA percentage of population - urban squared MSA percentage of population - 65 and older MSA percentage of population - high school MSA percentage of population - college MSA population, millions MSA population, millions squared MSA population density, millions/mile MSA population density squared MSA hospitals per thousand population MSA generalists per thousand population MSA specialists per thousand population MSA cardiologists per thousand population Mean Standard Deviation 0.148 0.355 0.653 0.476 0.199 0.400 0.289 0.453 0.265 0.442 2.63 2.03 19.4 3.49 0.842 0.129 0.725 0.202 0.121 0.030 0.766 0.058 0.217 0.057 2.01 2.35 9.56 20.2 0.968 1.49 3.15 12.10 0.023 0.008 0.082 0.033 0.722 0.371 0.065 0.036 N 2,873 Kaplan-Meier Adoption Probabilities for PTCA and CABG, 1985-2000 0.45 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 19 85 19 86 19 87 19 88 19 89 19 90 19 91 19 92 19 93 19 94 19 95 19 96 19 97 19 98 19 99 20 00 Cumulative Adoption Probability 0.40 PTCA CABG Mortality patient got catheterization catheterization*1997 catheterization*1998 catheterization*1999 catheterization*2000 patient got PTCA PTCA*1997 PTCA*1998 PTCA*1999 PTCA*2000 patient got CABG CABG*1997 CABG*1998 CABG*1999 CABG*2000 coefficient -0.218 -0.002 -0.004 0.008 0.002 -0.287 0.000 -0.003 -0.003 0.010 -0.292 0.005 -0.001 -0.002 0.014 SE 0.007 ** 0.011 0.011 0.011 0.011 0.007 ** 0.010 0.010 0.010 0.010 0.007 ** 0.011 0.011 0.011 0.011 Models are OLS regressions of the probability of 1 year all-cause mortality. Models include additional covariates. * denotes p<0.05; ** denotes p<0.01 Predicted PTCA adoption probability in low, medium, and high HMO markets Cumulative Probability of PTCA adoption 1.000 0.900 Cumulative Adoption Probability 0.800 0.700 0.600 low HMO 0.500 medium HMO high HMO 0.400 0.300 0.200 0.100 0.000 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 Year Predicted CABG adoption probability in low, medium, and high HMO markets Cumulative Probability of CABG adoption 1.000 0.900 Cumulative Adoption Probability 0.800 0.700 0.600 low HMO 0.500 medium HMO high HMO 0.400 0.300 0.200 0.100 0.000 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 Year