Crystals: d a V
advertisement

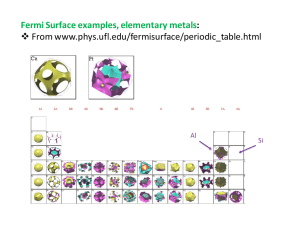
Crystals: Recall Crystal = Bravais lattice + Basis. Bravais lattice = repeated set of points, R = n1a1 + n2 a2 + n3 a3 Basis = location of atoms “decorating” the lattice ! ! ! ! di • Primitive cell: always has volume V = a1 ⋅ a2 × a3 . One option for the cell is the parallelepiped with edges a1 , a2 , a3 . • Naming convention for cell dimensions and angles: Lengths a, b, c; angles, α = (b-c angle) etc. as shown below. Lengths are the "lattice parameters". • Cubic lattice parameters always a × a × a (= conventional cell dimensions); hexagonal a × a × c, etc. 14 Bravais lattices Including point group (lattice decoration), 230 “Space Group” Symmetry classes. Example, hexagonal structures with Space group #194: Cubic primitive and conventional cells BCC (body center) FCC (face center) Examples: Iron, Na Examples: Cu, Al, Ni, Silicon*, NaCl*, etc * with basis Close packed: face center cubic close-packed, hexagonal close-packed FCC: A Bravais lattice; atoms are all the same; colors show ABCABC stacking. HCP: Atoms all the same but 2-atom basis. colors show ABAB stacking. diamond&structure: FCC&bravais,&basis&2 tetrahedral&bonding other&carbon&forms graphite graphene Silicon,&germanium Not&bravais (even&though& atoms&identical) tetrahedral&bonds nanotubes “Buckyball” GaAs (zincblende) IIIIV& semiconductors: tetrahedral&like& silicon,&can&view& roughly&as& covalent&bonded& framework&with& partial&charge& transfer,&e.g. “GaIqAs+q” GaN (wurtzite) CsCl; ionic NaCl ;&ionic These& materials:& completely& ionic&to& good&approximation;&formation& energy&=&Coulomb&energy&of& assembled& charges.& high$Tc YBa2Cu3O7 K3C60 (superconductor) FCC&structure “AlQ3” organic semiconductor Images4of4two$dimensional4tilings:444What&is&the&Bravais lattice?&&The&basis?& Lattice4Planes (200)&planes,& simple& cubic. Parallel&equalIspaced& planes& intersect&all& Bravais lattice&points. (Proof&in&terms&of&reciprocal&lattice) Indexing:&&•&atom&at&corner&of&cell,&edges&=& lattice& vectors.& •&choose&plane&nearest&origin.& •&indices& are&integer&divisors&of&the&lengths& of& cell&edges&intercepted& by&plane.& •&Usual&notation&h,&k,&ℓ. (Planes&more&than&needed& to&intersect& all& Bravais lattice&points&if&indices& have& common&denominator) Lattice4Planes (100)&planes,& FCC Note,&lattice&planes& intersect&Bravais lattice points&(not&necessarily& all&atoms) But&note,&FCC&and&BCC&are&always& indexed& as&if&they&were&simple& cubic&with& a&basis& Reciprocal Lattice: Vectors form k-space Fourier components of Bravais (direct-space) lattice. Plane waves have symmetry of lattice, ! ! ! To construct: K! = hb + kb + "b 1 2 3 ! ! ! etc.; also a ×a b1 = 2π ! ! ! a1 ⋅ a2 × a3 2 3 • Then can show: Wavefronts of e ! ! iK ⋅ R e ! ! ! iK ⋅( r + R ) =e ! ! ai ⋅ b j = 2πδ ij are Bragg planes. ! ! iK ⋅ r