Study Guide Chapter 4 1. Def of solvent and solute
advertisement

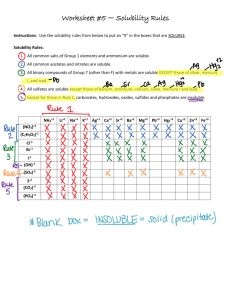
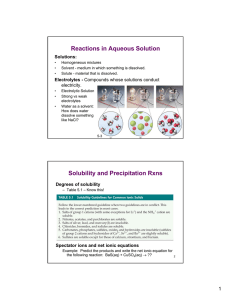
Study Guide Chapter 4 - Chemical Reactions 1. Def of solvent and solute 2. Talk about the structure of water 3. What happens to ionic compounds in solution? 4. Strong vs weak vs non-electrolytes Strong - Strong acids, Strong bases, Soluble salts 5. Molarity M = mol/V; MV = mol; 6. Types of reactions Ppt acid/base Redox 7. How to predict outcome of precipitation reaction 1. Mix and match cations and anions 2. Find the guy that is not soluble Rules A. NO3- soluble B. Li,Na,K,Cs,Rb, NH3 soluble C. Cl,Br,I usually soluble, but not with Ag+,Pb2+ , or Hg 22+ D. Most OH not soluble except Na, K; Ba, Sr, Ca slightly E. S 2-, CO32-, CrO42-, PO43-, slightly sol 8. Molecular equation vs complete ionic equation vs net ionic equation 9. Acid-Base reactions A. Def of Acid and Base (proton Donor and acceptor) B. What is a neutralization reaction C. Calculate how much strong acid neutralizes a strong base M1V1 = M2V2 10. Basics of volumetric analysis A. Concepts like titration, indicator, primary standard, secondary standard, difference between endpoint and equivalence point. B. Calculate equivalence points for different acid/base titrations 11.Oxidation Reactions A. What is a redox reaction B. Find oxidation state of atoms (rules table 4.2 page 167) C. Balance redox reactions in acid (Steps 1-5 page 173) D. Balance Redox reactions in base (add OH- to both sides of equation)