Study guide Chapter 26 RNA metabolism 1. Describe how RNA polymerase works
advertisement

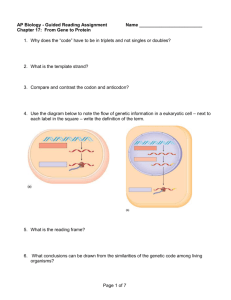
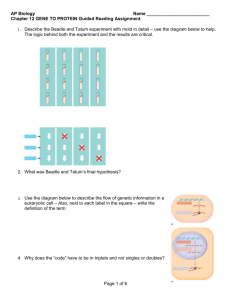
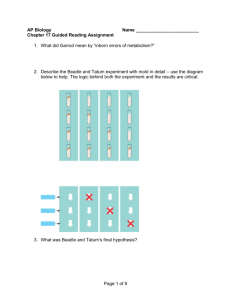
Study guide Chapter 26 RNA metabolism 1. Describe how RNA polymerase works 2. Compare and contrast RNA polymerase with DNA polymerase I or III 3. What are mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, the template strand, the coding strand, a promoter, a consensus sequence, a snRNP, a spliceosome, a ribozyme, a reverse transcriptase, a retrovirus 4. Describe the structure of the E coli promoter sequence, how does the promoter regulate the process of RNA synthesis 5, How is transcription terminated in E coli 6. What are the three kinds of Eukaryotic RNA polymerases and how are they different 7. Describe the action of Euakriotic RNA polymerase II, and how it is used to transcribe Eukaryotic RNA. What additional factors are needed in the this process? How is it similar to or different than prokaryotic transcription? 8. What are some antibiotics that inhibit RNA transcription? 9. Describe the four classes on introns. How are they similar? Different? 10. Describe the process that go in to making a mature eukaryotic mRNA, tRNA, or rRNA. What enzymes are required, what is done to the RNA 11. How much of the above processing goes on in the synthesis of prokaryotic RNA? 12. Describe the life cycle of a retrovirus, describe the sequence of a retrovirus’s RNA and how does this sequence play a role in the retrovirus’s life cycle. 13. What is a telomere? How does telomerase function? Why is telomerase activity important for Eukaryote? Why is it unimportant for prokaryotes?