• Thevenín Equivalent Load Effect ENGINEERING-43 Lab-07
advertisement

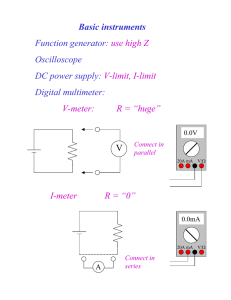
ENGINEERING-43 Load Effect • Thevenín Equivalent Lab-07 Lab Data Sheet – ENGR-43 Lab-07 Lab Logistics Experimenter: Recorder: Date: Equipment Used (maker, model, and serial no. if available) Part-1 Directions – Loading Effects 1. Note that in this and ALL OTHER Laboratory Exercises ENGINEERING UNITS must accompany ALL Data-Entries and Calculated-Quantities 2. Check out a DMM and Power/Probe Leads for the Power-Supply and DMM 3. Go to the side counter collect resistors, “bread board”, and leads required to construct the circuit shown in Figure 1. When unloaded RL = ; i.e., RL is an Open Circuit. See the instructor if the 100-330 kΩ resistors are unavailable 4. Make the Measurements and Calculations needed to complete Table I © Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291199291 • Page 1 Figure 1 • High Drive Current. Vs = 10.00 Vdc. R1 = R2 = 0.8-3.3 kΩ. RL = per Table I Table I - Hi-Drive Loading Effect COLOR-CODED Resistor Values & Tolerances R1 = R2 = Actual (DMM) Values Vs = R1 = R2 = RL Nominal RL Actual Vout (Calc) Vout (Meas) Unloaded 100-330 kΩ 10-33 kΩ 0.8-3.3 kΩ % = 100x(Vcalc – Vmeas)/Vmeas © Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291199291 • Page 2 Vout % Part-2 Directions – Loading Effects 5. Modify the previous circuit to the configuration shown in Figure 2 . Use the SAME Load Resistors as in part-1. 6. Make the Measurement and Calculations needed to complete Table II. Figure 2 • Low Drive Current. Vs = 10.00 Vdc. R1 = R2 = 5-11kΩ. RL = per Table II Table II - Lo-Drive Loading Effect COLOR-CODED Resistor Values & Tolerances R1 = R2 = Actual (DMM) Values Vs = R1 = R2 = © Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291199291 • Page 3 RL Nominal RL Actual Vout (Calc) Vout (Meas) Vout % Unloaded 100-330 kΩ 10-33 kΩ 0.8-3.3 kΩ % = 100x(Vcalc – Vmeas)/Vmeas Part-3 Directions – Introduction to Thevenín Equivalents 7. Go to the side counter collect resistors, “bread board”, and leads required to construct the simple “Ladder” circuit shown in Figure 3. 8. Make the Measurements and Calculations needed to complete Table III Deactivate a voltage supply by removing its leads and replacing the supply with a short to GND Calculate Vth, Isc, and Rth using the “Actual Values” for Vs, R1, R2 and R3 Compute the third column of Table III (Vth/Isc) as at the Quotient of columns 1 & 2. 9. Return all lab hardware to the “as-found” condition Figure 3 • Thevenin Equivalent Circuit. Vs = 9.00 Vdc. R1 = 2.5-4.9 kΩ. R2 = 5.5-8.5 kΩ. R3 = 0.8-1.8 kΩ. © Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291199291 • Page 4 Table III - V & I DMM Measurements for Figure 3 COLOR-CODED Resistor Values & Tolerances R1 = R2 = R3 = Actual Values Measured by DMM Vs = R1 = R2 = R3 = Value Determination VTH ISC VTH/ISC RTH RTH % Calculated Measured % n/a RTH % = 100x(RTH – V/I)/(V/I) %J = 100x(XJ,calc – XJ,meas)/XJ,meas Where Xj one of: o VTH o ISC o VTH/ISC o RTH © Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291199291 • Page 5 Run Notes/Comments Print Date/Time = 29-May-16/04:00 © Bruce Mayer, PE • Chabot College • 291199291 • Page 6