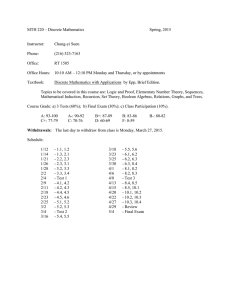
Chabot College Fall 2004 – Discrete Mathematics Workshop
advertisement

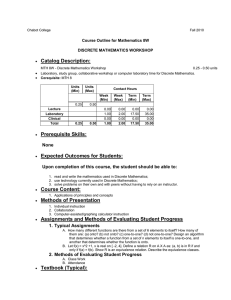
Chabot College Fall 2004 Course Outline for Mathematics 8W DISCRETE MATHEMATICS WORKSHOP Catalog Description: 8W – Discrete Mathematics Workshop .25 - .5 units Laboratory, study group, collaborative workshop or computer laboratory time for Discrete Mathematics. Corequisite: Mathematics 8. 1 - 2 hours laboratory. [Typical contact hours: 17.5-35] Prerequisite Skills: None Expected Outcomes for Students: Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to: 1. 2. 3. read and write the mathematics used in Discrete Mathematics; use technology currently used in Discrete Mathematics; solve problems on their own and with peers without having to rely on an instructor. Course Content: 1. Applications of principles and concepts Methods of Presentation: 1. 2. 3. Individual instruction Collaboration Computer-assisted/graphing calculator instruction Assignments and Methods of Evaluating Student Progress: 1. 2. Typical Assignments a. How many different functions are there from a set of 6 elements to itself? How many of them are: (a) onto? (b) not onto? (c) one-to-one? (d) not one-to-one? Design an algorithm that determines whether a function from a set of n elements to itself is one-to-one, and another that determines whether the function is onto. b. Let f(x) = x2 +1, x is real on [ -2, 4]. Define a relation R on A X A as: (a, b) is in R if and only if f(a) = f(b). Show R is an equivalence relation. Describe the equivalence classes. Methods of Evaluating Student Progress a. Attendance b. In–class assignments Textbook(s)(typical) Discrete Mathematics, Kenneth Rosen, McGraw-Hill Publishers, 2002 Discrete Mathematics, James A Anderson, Prentice Hall, 2001 Special Student Materials: None CS:al Revised 10/16/03