Chabot College Fall 2009 1A - Beginning Italian
advertisement

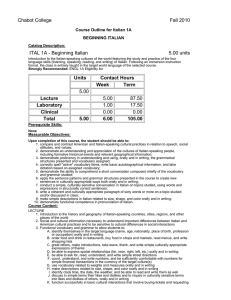
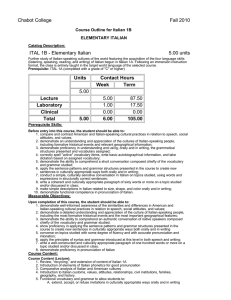
Chabot College Fall 2009 Replaced Fall 2010 Course Outline for Italian 1A BEGINNING ITALIAN Catalog Description: 1A - Beginning Italian 5 units Introduction to the Italian-speaking cultures of the world featuring the study and practice of the four language skills (listening, speaking, reading, and writing) of Italian. Strongly recommended: eligibility for English 1A. 5 hours lecture, 1 hour laboratory. [Typical contact hours: lecture 87.5, laboratory 17.5] Prerequisite Skills: None Expected Outcomes for Students: Upon completion of the course the student should be able to: 1. compare and contrast American and Italian-speaking cultural practices in relation to speech, social attitudes, and values; 2. demonstrate an understanding and appreciation of the cultures of Italian-speaking people, including formative historical events and relevant geographical information; 3. demonstrate proficiency in understanding and using, orally and in writing, the grammatical structures presented and vocabulary assigned; 4. correctly spell "active" vocabulary items, write basic autobiographical information, and take dictation based on assigned vocabulary; 5. demonstrate the ability to comprehend a short conversation composed chiefly of the vocabulary and grammar studied; 6. apply the sentence patterns and grammar structures presented in the course to create new sentences in culturally appropriate ways both orally and in writing; 7. conduct a simple, culturally sensitive conversation in Italian on topics studied, using words and expressions in structurally correct sentences; 8. write a coherent and culturally appropriate paragraph of sixty words or more on a topic studied and/or discussed in class; 9. make simple descriptions in Italian related to size, shape, and color orally and in writing; 10. demonstrate functional competence in pronunciation of Italian. Course Content (Lecture): 1. Introduction to the history and geography of Italian-speaking countries, cities, regions, and other places of the world 2. Social and cultural information necessary to understand important differences between Italian and American cultural practices and to be sensitive to cultural differences in social interactions 3. Functional vocabulary and grammar to allow students to: a. identify themselves in the target language (name, age, nationality, place of birth, profession or occupation) orally and in writing b. order food and drink in restaurants, buy food in shops and markets, read menus, and write shopping lists c. greet others, make introductions, take leave, thank, and write simple culturally appropriate expressions of thanks d. be able to express spatial relationships (far, near, right, left, etc.) orally and in writing e be able to ask for, read, understand, and write simple street directions f. count, understand, and write numbers, and be sufficiently comfortable with numbers for simple financial transactions in the currency of the target culture(s) g. use vocabulary related to weights and measures orally and in writing h. make descriptions related to size, shape, and color orally and in writing i. identify clock time, the date, the weather, and be able to read and write them as well Chabot College Course Outline for Italian 1A, Page 2 Fall 2009 j. discuss in simple terms their likes and dislikes and to inquire in culturally sensitive terms into likes and dislikes of others, orally and in writing k. function successfully in basic cultural interactions that involve buying tickets and requesting and paying for services (public transportation, taxis, post offices, hotels) 4. Introduction to the principles of Italian pronunciation 5. Syntax and grammar that allows students to correctly use orally and in writing: a. nouns and adjectives, their singular and plural forms, their placement, gender, and gender and number agreement b. definite and indefinite articles, singular and plural c. cardinal numbers d. present, imperfect, and passato prossimo tenses of the irregular verbs essere, avere, andare, dare, fare, stare, dire, uscire, venire, conoscere, sapere, piacere e. present, imperfect, and passato prossimo tenses of the three regular conjugations (-are, -ere, and –ire) f. idiomatic expressions based on avere g. the three Italian verbs “to leave”: lasciare, partire, and uscire h. reflexive verbs i. imperative mood j. subject, object, and disjunctive pronouns k. the impersonal pronouns si, ne, ci l. possessive pronouns and adjectives m. cardinal numbers n. adjectives and their comparative forms o. adverbs and their comparative forms p. preposition and article combinations q. interrogative pronouns and adjectives r. write simple declarative and interrogative sentences Course Content (Laboratory): 1. Activate lecture content using interactive audio and audiovisual programs on CDs, DVDs, CD ROMS, target language websites, etc., featuring culturally authentic and contextual guided speaking, reading, and writing activities such as cued repetition of native speech, dictations, cued oral responses, listening comprehension, and interactive realia (culturally authentic texts). 2. Organized laboratory activities including conversation groups. 3. Fundamentals of Italian pronunciation: a. The seven Italian vowels, including both open and closed e and o b. Consonants and consonant clusters c. Soft and hard c and g d. Tonic accent and written accent e. The sounds of the letter s (sorda, sonora, single s and double s) f. Single and double g g. The combination sc h. The combinations qu and cu i. The sounds of the letter z j. The letter h k. Diphthongs and triphthongs Methods of Presentation: 1. 2. 3. 4. Lecture/discussion in target language Choral/individual repetition of model speech Re-creation of dialogues and improvisation Small group activities leading to skits, dialogues, etc. curriculum 0809 dk 11/12/08 Chabot College Course Outline for Italian 1A, Page 3 Fall 2009 Assignments and Methods of Evaluating Student Progress: 1. Typical Assignments a. Demonstrate "ordering" skills in a restaurant skit. b. Demonstrate aural understanding of street directions by tracing examples of such directions on a map. c. Laboratory assignment: Demonstrate proficiency in the fundamentals of Italian pronunciation by making a recording of the poem "I fiumi" by Giuseppe Ungaretti. d. Write a paragraph that includes basic biographical information, such as nationality, place of birth, birthday, and current residence. 2. Methods of Evaluating Student Progress a. Tests, quizzes, and interviews to evaluate the four language skills in relation to material presented b. Student participation in class activities c. Homework assignments d. Recordings from the language laboratory to evaluate pronunciation skills e. Final examination Textbook(s) Typical: Prego! An Invitation to Italian, seventh edition, Graziana Lazzarino, McGraw Hill, 2008. Workbook to accompany Prego! An Invitation to Italian, seventh edition, Andrea Dini and Graziana Lazzarino, McGraw Hill, 2008. Special Student Materials: None curriculum 0809 dk 11/12/08