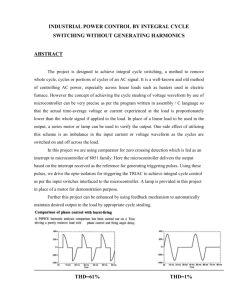
Chabot College Fall 2011 Replaced Fall 2012
advertisement

Chabot College Fall 2011 Replaced Fall 2012 Course Outline for Electronic Systems Technology 55A MICROCONTROLLER SYSTEMS Catalog Description: 55A – Microcontroller Systems 2 units Architecture, programming, application and troubleshooting of single-chip microcontroller electronic systems. Digital building blocks, number systems, programming in high-level and assembly language. Interfacing the microcontroller for practical applications, measurement techniques and instrumentation, troubleshooting techniques. Co-requisite: ESYS 50 or equivalent. 1 hour lecture, 2 hours laboratory. [Typical contact hours: 17.5 lecture; 35 laboratory] Prerequisite: None Expected Outcomes for Students: Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to: 1. trace timing, inputs, and outputs of a single-chip microcontroller with appropriate test equipment and schematic diagrams; 2. create simple programs in high-level and assembly language for practical and diagnostic purposes; 3. interpret manufacturers’ data sheets for microprocessor devices; 4. use test equipment to troubleshoot microprocessor-based electronic systems; 5. analyze the operation of microprocessor systems. Course Content: 1. Course Content, Lecture a. Basic principles of digital systems b. Microcontroller architectures c. Software for microcontrollers d. Diagnostic and program verification techniques e. Digital signal processing 2. Course Content, Laboratory a. Simulating a microcontroller in Assembly Language b. Observe and measure the inputs and outputs of digital systems c. Assembling and loading a program to a single-chip microprocessor d. Observe and measure the effect of assembly language commands and directives on microprocessor outputs e. Tracing microprocessor program execution Chabot College Course Outline for Electronic Systems Technology 55A, Page 2 Fall 2011 Methods of Presentation: 1. Online learning objects 2. Small group discussion/lecture 3. Laboratory Assignments and Methods of Evaluating Student Progress: 1. Typical Assignments a. Program a microcontroller with a given program and verify the operation of the system meets specifications. b. Write a high-level program to use a microcontroller as a temperature control system, monitoring a temperature sensor and controlling a fan to maintain a stable temperature. 2. Methods of Evaluating Student Progress a. Homework and laboratory written reports b. Class participation c. Observation and critique of laboratory exercises d. Quizzes, Midterm, and Final Examinations Textbook(s) (Typical): Lessons in Electric Circuits, Vol. 1 & 2, Kuphaldt, open source, hosted on openbookproject.net Special Student Materials: None wap ESYS55A_S11.doc New: September 2, 2008 Revised: October 11, 2010