PAT Particle Size Analyzer (PSA) Application for Milling Manufacturing Process
advertisement

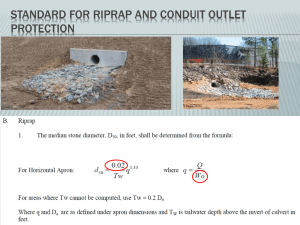
PAT Particle Size Analyzer (PSA) Application for API Milling Manufacturing Process ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting Eric J. Correa Sr. PAT Process Engineer Abbott- North Chicago ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 1 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 1 Agenda • PAT Background • PAT Case Study • Insitec® Particle Size Analyzer • PAT PSA Current State and Setup • Online Milling Engineering Study • Milling PAT Implementation • Closed Loop Feedback Control Results • Summary and Next Steps • Acknowledgements ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 2 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 2 What is PAT? Diagnosis • Process analytical technology (PAT) has been defined by FDA as a mechanism to design, analyze, and control pharmaceutical manufacturing processes through the measurement of Critical Process Parameters (CPP). • PAT is process analysis in real-time. Real-time analytical measurements can replace off-line time consuming chemical analyses and reduce process cycle time. • PAT - An Innovative Way to Achieve Continuous Process Improvements and Quality by Design. • PAT tools and technology includes; Near Infrared (NIR) spectrophotometers, Raman, laser diffraction for particle size analysis, NIR chemical imaging, etc. ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 3 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 3 PAT Monitoring Understanding Control PAT Case Study: API Milling Operation • Typical API Pharmaceutical Process: Reaction Crystallization Drying Milling • API PSD acceptance range: D50 within [30, 80] microns • Non-critical, no final testing on the composite sample. • API milling in-process test target range: D50 within [50, 65] microns • Two mills, fixed feed rate RPM, blower speed, and screen size. • Initial milling speed @ 3600 RPM, mill ~ 1-5 kg, PSD testing (offline). • Adjust milling speed to reach the target range, mill remainder lot. • Offline method • Wet method using Malvern MasterSizer® 2000. ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 4 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 4 Insitec® Online Particle Size Analyzer • Laser diffraction technology (0.1, 1000 um). • First principles measurement, model independent analysis. • Wide range of mass concentration – Low mass concentration – Beer’s Law. – High mass concentration – Multiple scattering correction. li ed r e t t Sca • Easily integrated into the process. ght Incident light Refracted light Scatt ered light Illustrations from Malvern Instruments ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 5 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 5 How Does it Work? • A laser diffraction instrument does not measure particle size (PS). • Laser diffraction measures light scattering, which is dependent of PS. • Laser beam hits the sample and generates light scattering. • Scattering signal is collected by the detectors (32 in total). • Scattering pattern is generated. Illustrations from Malvern Instruments ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 6 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 6 How to Generate the Size Distribution Illustrations from Malvern Instruments ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 7 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 7 Mill/Insitec® Current Setup at Abbott Facility OSI-PI Controls Nitrogen Wireless TCP/IP Network Software/Server/Interface Insitec PSA Sample In RS232 Wall Interface RS5422 Return Control PC Allen Bradley PLC Wireless TCP/IP Network ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 8 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 8 PSA Operational Sequence and Logistics Initial Start-Up 2 3 PLC HMI Analyzer perform background check Operator collects background Data Tag Operator enter Batch ID Batch ID Enable Mill RPM Measurement Active Mill Starts Start Malvern's Auto Shut Down D10, D50, D90 4 D10, D50, D90 Auto Shut Down Low Scattering Mill Stops ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 OSI-PI Operator Enters D50 & Control parameters PLC setups parameters Start-Up 1 Backgrd Ref. Analyzer 9 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 9 API Milling Operation – Current State • API PSD acceptance range: D50 within [30, 80] microns • Non-critical, no final testing on the composite sample. • API On-line milling • On-line milling using PSA-PAT. • Define initial parameters (i.e. Initial milling speed, desired D50, etc). • Milling speed via feedback control. • PAT PSD Process Monitoring • Support via remote desktop connection. • PSD data available for viewing in OSI-PI. • PSD data track and trending. ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 10 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 10 Engineering Study • To establish the feasibility of process monitoring. • To demonstrate the correlation between online Insitec® and offline Mastersizer® particle size results. • To demonstrate feasibility of feedback control during the milling operation. • To study and optimize the following parameters: – – – – – Flow Titration Flute Optimization System Sensitivity Process Control Parameters Feedback Control ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 11 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 11 ES Outcome- Feed Back Control Parameters Parameter Setting Venturi Eductor flow rate (SCFM) 2.5 D50 set point (microns) 58 Target mill speed at startup (RPM) The nitrogen flow rate needed for proper aspirating a representative sample stream from the main process stream 3600 Particle size cycle time (sec) 10 ~ 20 (15) Mill speed adjustment step size (RPM) 50 ~ 100 (50) Mill speed adjustment limit (RPM) +/- 2600 D50 dead band range (microns) +/- 2 Particle size deviation alarm (microns) +/- 20 D50 rolling average window size (sec) 30 ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 12 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories Comments 12 Target particle size value Start up mill speed target, same as the current milling starting RPM Frequency of changes to the mill speed if the rolling average D50 value is outside the dead band range Value of change to the mill speed during every cycle time if D50 is outside of the dead band range Maximum value of change to the mill speed, allowed by PLC The range around the rolling average D50 set point, within which no change is made to the mill speed The range around the rolling average D50 set point, outside which Malvern Insitec® issues an alarm signal. D50 acceptable range is 30 – 80 microns. The window size of the time over which the average is reported Offline-Online Correlation Mastersizer Offline D50 (um) 80 75 70 65 y = 1.0023x + 1.4477 R2 = 0.9417 60 55 50 50 55 60 65 70 75 Insitec Online D50 (um ) ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 13 Offline Sample 1 Offline Sample 2 Offline Average Linear (Offline Average) © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 13 80 Engineering Study Conclusions • On-line particle size analyzer can monitor the milling operation continuously. • On-line results have good correlation to the results from the off-line method. • Feedback loop using Insitec® provides consistent and well controlled particle size distribution throughout the whole milling operation. • Analyzer needs to be integrated into the milling system for regular implementation. ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 14 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 14 Implementation Strategy & Outcome Engineering Study System Qualification PAT Implementation Strategy Manufacturing Implementation ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 15 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories Communication Established Correlation to offline method Established Critical Parameters Defined Analyzer & Mill HMI PLC, Software, OSI-PI PAT Operation Procedure PV/PQ Manufacturing Direction Training Monitor and Control Track and Trend 15 Qualification Approach Equipment & APC OSI-PI Malvern Analyzer IOQ APC Controls & Interface IOQ Engineering Study URS PAT OSI-PI OPC Configuration API PSA Tags Malvern PSA Software API Process ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 16 PAT Software Operational Qualification (SOQ) PAT Process Integration © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 16 API Process Impact • In-Process (offline testing) sample was removed. • Mill RPM via feedback control. • Continuous Monitoring of D50 PSD. • Reduction in cycle time for milling stage. • Integration of PSA into the Mill. • Integration of PSA into the API process. • Modification of current HMI PLC program and APC interface. • PAT BOP to incorporate PAT system along with personnel training. ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 17 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 17 Closed Loop Feedback Control Transmission Dv90 Dv50 Process Upset ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 18 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 18 End of a Batch Closed Loop Feedback Control • Step 1: D50 SP = 58 ± 2 m, mill speed startup SP = 2600 RPM – Took 5 minutes to reach dead band – Offline sample D50 = 61 m • Step 2: D50 SP = 58 ± 2 m, mill speed startup SP = 3800 RPM • Step 3: D50 SP = 50 ± 2 m • Step 4: D50 SP = 58 ± 2 m 80 4000 4500 75 3500 75 70 3000 70 65 2500 2000 55 1500 50 1000 45 500 D50 (um) 60 Mill Speed (RPM) D50 (um) SP=58um SP=50um SP=58um 4000 65 3500 60 3000 55 50 2500 45 40 23:11:02 40 0 22:56:38 22:58:05 22:59:31 23:00:58 23:02:24 23:03:50 23:05:17 23:06:43 23:08:10 23:13:55 23:16:48 23:19:41 Avg D50 UCL ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 19 LCL 23:25:26 23:28:19 2000 23:31:12 Time Time D50 23:22:34 UDB LDB Target © 2011 Abbott Laboratories D50 MILL RPM 19 Avg D50 UDB LDB Target MILL RPM Mill Speed (RPM) 80 D50 Feedback Control Using PAT for 2009 Campaign Initial D50 Constant RPM D50 Adjustment Feedback Controlled D50 Mill Speed Adjustment D50 Rolling Average D50 Particle Size (real-time value) Mill Speed D50 Set Point 57m | Mill Start-UP 3600RPM ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 20 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 20 On-Line Milling PSA Benefits • Integrated milling system leads to real time particle size distribution monitoring, control, and process understanding. • Removing In-Process testing leads to streamlined operation and reduction in cycle time. • Data integration to OSI-PI leads to real time tracking and trending and improved trouble shooting capability. Previous Process In-Process Sample RPM Manual Adjustment Offline testing Limited PSD Data Archived QA Data ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 21 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories Current Process No In-Process Sample RPM Feedback Control On-line testing Continuous PSD Data Data Historian OSI-PI 21 Summary and Next Steps • PAT initiative encourages the pharmaceutical industry to embrace new analytical approaches with the aim of transforming process development and manufacture. • PAT On-Line Particle Size Analyzer (PSA) for Fitz-Mill was implemented during 2009 API manufacturing campaign successfully and it represents the first OnLine PAT PSA project completed and used in Abbott commercial production. • PAT PSA has replaced the In-Process sample and reduced the cycle time during the milling staged as well as improved the process in overall. • API Manufacturing will continue to use the PAT PSA for future campaigns. • Currently evaluating other APIs and Drug Products (DP) pharmaceutical processes in order to determine PAT PSA feasibility. ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 22 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 22 Last Word: Vendor-Customer Partnership ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 23 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 23 Acknowledgements • Abbott • • Adrian Del Moral Ballesteros, Elvin Negron, Osvaldo Rodriguez, Amarillys de Jesus, Amarillys Carde, Angel Roman, Maricely Colon, Yamilda Cruz, Ana Cocero, Xenia Guerrero, Jose Restituyo, Li Sun, Jay Paterson, Cynthia Curty, Dan Crandall, Yahui Hu, Eric Nielsen, William Kloud, Michael Hoffman, Radames Garcia, Kenneth Wierzba, Radames Garcia. Malvern Instruments • • Alon Vaisman, Boris Makovoz, Jeff Denigris, Gerard Michel. Fitzpatrick • Joe Ream ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 24 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 24 ISPE Great Lakes Chapter 2011 Meeting GDS_100671_v1 25 © 2011 Abbott Laboratories 25