Socket Programming Socket address structure in <sys/socket.h>:
advertisement

Socket Programming
Socket address structure in <sys/socket.h>:
struct sockaddr{
u_short sa_family;
char
sa_data[14];
}
/* address family: AF_xxx value */
/* up to 14 bytes of protocol- */
/* specific address */
Socket Programming
Socket address structure in <netinet/in.h>:
(Internet family)
struct in_addr{
u_long s_addr; /* 32-bit netid/hostid */
/* network byte ordered */
}
Socket Programming
struct sockaddr_in{
short sin_family;
u_short sin_port;
/* AF_INET */
/* 16-bit port number */
/* network byte ordered */
struct in_addr sin_addr; /* 32-bit netid/hostid */
/* network byte ordered */
char
sin_zero[8];
/* unused */
}
Socket Programming
socket : specify the type of communication
protocol desired (TCP, UDP etc.)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int socket(int family, int type, int protocol);
family:
AF_UNIX (UNIX internal protocol)
AF_INET (Internet protocols)
AF_NS (Xerox NS protocols)
AF_IMPLINK (IMP link layer)
(AF: address family)
Socket Programming
type:
SOCK_STREAM (stream socket, TCP)
SOCK_DGRAM (datagram socket, UDP)
SOCK_RAW (raw socket)
SOCK_SEQPACKET (sequenced packet socket)
SOCK_RDM (reliably delivered message socket)
(not implemented yet)
protocol: typically set to 0 for most user applications
The output of the system call is the socket descriptor.
Socket Programming
bind: assign a name to an unnamed socket
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int bind(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *myaddr, int addrlen);
sockfd: socket descriptor (return by*myaddr: a pointer to a
protocol-specific address
addrlen: the size of this address structure
The output > 0 if success; otherwise, it fails.
Socket Programming
connect: establish a connection with a server
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int connect (int sockfd, struct sockaddr *servaddr, int addrlen);
same as the system call bind.
The output > 0 if success; otherwise, it fails.
Socket Programming
listen: is used by a connection-oriented server
to indicate that it is willing to receive
connections
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int listen (int sockfd, struct backlog);
backlog: specify how many connection requests can be queued by
the system while it waits for the server to execute the accept
system call (default as 5).
The output > 0 if success; otherwise, it fails.
Socket Programming
accept: take the first connection request on the
queue and create another socket with the same
properties as sockfd.
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int accept (int sockfd, struct sockaddr *peer, int *addrlen);
peer: the address of connected peer process (the client).
addrlen: the size of peer.
The output of the system call is the socket descriptor.
Socket Programming
send, sendto, recv and recvform
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int send(int sockfd, char *buff, int nbytes, int flags);
int sendto(int sockfd, char *buff, int nbytes, int flags, struct
sockaddr *to, int addrlen);
int recv(int sockfd, char *buff, int nbytes, int flags);
int recvfrom(int sockfd, char *buff, int nbytes, int flags, struct
sockaddr *to, int addrlen);
flag: usually zero
Socket Programming
close: close a socket
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int close (int fd);
bzero: writes the specified number of null bytes
to the specified destination.
bzero(char *dest, int nbytes);
Socket Programming
htonl: convert host-to-network to long integer
htons: convert host-to-network to short integer
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
u_long htonl(u_long hostlong);
u_short htons(u_long hostshort);
Socket Programming
inet_addr: convert a character string in dotteddecimal notation to a 32-bit Internet address
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
unsigned long inet_addr(char *ptr);
Socket Programming
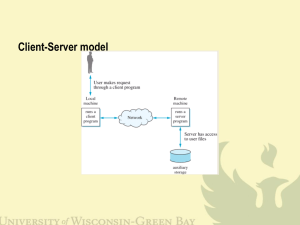
Server
socket ( )
bind ( )
Connection-oriented
Protocol
Client
listen ( )
accept ( )
blocks until connection from client
read ( )
connection
establishment
data (request)
socket ( )
connect ( )
write ( )
process request
write ( )
data (reply)
read ( )
Socket Programming
Server
socket ( )
Connectionless
Protocol
bind ( )
Client
recvfrom ( )
blocks until data
received from a client
socket ( )
bind ( )
data (request)
sendto ( )
process request
sendto ( )
data (reply)
recvfrom ( )
Socket Programming
int tcp_serv() /* server program: setup a TCP connection */
{
int sockfd, newsockfd, clilen;
struct sockaddr_in cli_addr, serv_addr;
if ((sockfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0)
err_dump(“server: can't open stream socket”);
bzero((char *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
/* INADDR_ANY: any Internet interface on the system */
Socket Programming
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(SERV_TCP_PORT);
if (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)) <
0)
err_dump(“server: can't bind local address”);
listen(socfd, 5);
clilen = sizeof(cli_addr);
if ((newsockfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &cli_addr,
&clilen)) < 0)
err_dump(“server: accept error”);
}
Socket Programming
int tcp_client() /* client program: setup a TCP connection */
{
int sockfd, newsockfd, clilen;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr;
bzero((char *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERV_HOST_ADDR);
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(SERV_TCP_PORT);
Socket Programming
if ((sockfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0)
err_sys(“client: can't open stream socket”);
if (connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr))
< 0)
err_sys(“client: can't bind local address”);
/* do the transmission */
close(sockfd);
}
Socket Programming
tcp_send(s_act, msg_ptr, msg_len)
/* ipc_send: send data message “msg” within stream domain */
int s_act;
/* actual socket descriptor of connection */
char *msg_ptr;
/* pointer to data msg unit */
int msg_len; /* length of data msg unit */
{
int cc = 0, rc;
cc = send(s_act, msg_ptr, msg_len, 0); /*UNIX system call */
if (cc == -1) {perror("send: ! "); rc = cc; }
/* error report */
else rc = OK (=1);
return (rc);
}
Socket Programming
tcp_receive(s_act, buf_ptr, buf_len) /* receive data within UNIX*/
int s_act;
/* socket descriptor of ipc connection */
union u_du *buf_ptr;
/* pointer to message buffer */
int *buf_len;
/* length of message buffer */
{
int cc, rc;
cc = recv(s_act, buf_ptr, *buf_len, 0); /* UNIX syst call */
if (cc == -1) { perror("recv: "); rc = cc; }
else {*buf_len = cc; rc = OK (= 1); }
return (rc);
}
Socket Programming
int udp_serv() /* server program: setup a UDP connection */
{
int sockfd, newsockfd, clilen;
struct sockaddr_in cli_addr, serv_addr;
if ((sockfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0)) < 0)
err_dump(“server: can't open datagram socket”);
bzero((char *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
/* INADDR_ANY: any Internet interface on the system */
Socket Programming
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(SERV_UDP_PORT);
if (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)) <
0)
err_dump(“server: can't bind local address”);
/* do the transmission */
}
Socket Programming
int udp_client() /* client program: setup a UDP connection */
{
int sockfd, newsockfd, clilen;
struct sockaddr_in cli_addr, serv_addr;
bzero((char *) &serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERV_HOST_ADDR);
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(SERV_UDP_PORT);
if ((sockfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0)) < 0)
err_dump(“client: can't open datagram socket”);
Socket Programming
bzero((char *) &cli_addr, sizeof(cli_addr));
cli_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
cli_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
cli_addr.sin_port = htons(0);
if (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &cli_addr, sizeof(cli_addr)) < 0)
err_dump(“client: can't bind local address”);
/* do the transmission */
close(sockfd);
}
Socket Programming
udp_send( msg_ptr, msg_len, addr_ptr, addr_len )
char *msg_ptr;
/* pointer to message */
int
msg_len;
/* length of message */
struct sockaddr_in *addr_ptr; /* socket address */
int
addr_len;
/* length of socket address */
{
int cc;
addr_ptr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(st_addr); /*convert address*/
cc = sendto(s_udp, msg_ptr, msg_len, 0 addr_ptr, addr_len );
if (cc == -1) {perror("sendto: "); return(cc);}
else return(OK);
}
Socket Programming
udp_receive(msg_ptr, msg_len, addr_ptr, addr_len)
char *msg_ptr;
/* pointer to message “msg”
*/
int
msg_len;
/* length of message */
struct sockaddr_in *addr_ptr; /* socket address */
int
addr_len;
/* length of socket address */
{
int cc;
cc = recvfrom(s_udp, msg_ptr, *msg_len, 0, addr_ptr, addr_len );
if (cc == -1) {perror("recvfrom: "); return(cc); }
else return(OK);
}
Thread Programming (Try the program)
#define _REENTRANT
#include <stdio.h>
#include <thread.h>
#define NUM_THREADS 12
void *change_global_data(void *);
/* for thr_create() */
main(int argc,char * argv[]) {
int i=0;
for (i=0; i< NUM_THREADS; i++)
{
thr_create(NULL, 0, change_global_data, NULL,
0, NULL);
}
while ((thr_join(NULL, NULL, NULL) == 0));
}
void * change_global_data(void *null) {
static mutex_t Global_mutex;
static int
Global_data = 0;
mutex_lock(&Global_mutex);
Global_data++;
sleep(1);
printf("%d is global data\n",Global_data);
mutex_unlock(&Global_mutex);
return NULL;
}
Use online help to find out
the information about
thread programming.
Try:
man mutex
man thr_create
man thr_join
…...