An evaluation of AIR forecast for Norwegian core
advertisement

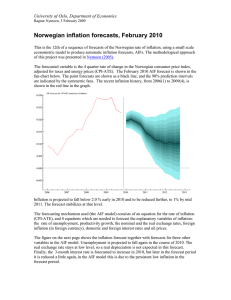
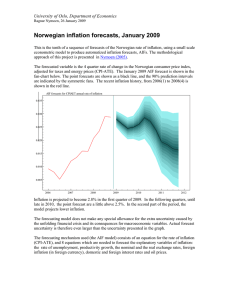
AIR-Automatized Inflation Reports 15 February 2007, Ragnar Nymoen An evaluation of AIR forecast for Norwegian core inflation for the period 2004q2-2006q4. Automatized econometric inflation forecasts have been published twize a year, starting in July 2004. The forecasts are automatized, with a minimum of intervention after the econometric specification of the forecasting mechanism is completed. Therefore these econometrically based forecasts have been dubbed Automatized Inflation Reports forecasts (AIR for short). Nymoen (2005) gives an evaluation of how the forecasting model underlying AIR performs relative to Norges Bank’s inflation forecasts in 2002 and 2003. Here, we evaluate the true ex-ante forecasts based on forecast errors for the period 2004q2-2006q4. The forecasted variable is the annual rate of inflation. The graphs in the upper panel in the figure show the mean forecast errors, MFE. A negative MFE means that the inflation forecasts are on average higher than the actual inflation rates in the period. The biases of the AIR forecasts are small for forecast horizons 1, 2, 3 and 4: the MFEs are less than 0.25 percentage points. Norges Bank’s IR forecasts are markedly biased over these horizons. The 4-quarter-ahead forecasted rates of inflation in the Inflation Reports are on average 0.8 percentage points higher than actual rates inflation. 0.0 Econometric AIR forecasts MFE -0.5 -1.0 Norges Bank's Inflation Reports 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 10 11 Length of forecast horizon (quarters) 2.5 2.0 1.5 Norges Bank's Inflation Reports 1.0 Econometric AIR forecasts 0.5 1 2 3 4 5 6 Length of forecast horizon (quarters) 7 8 9 Figure 1: First panel: Mean forecast errors, MFE, for core inflation (annual rate of change in CPIATE). Inflation report forecast in red, and AIR forecast in blue. Second panel: Mean squared forecast errors, MSFE. Source: Inflation Reports 2/04 - 3/06 and AIRs published at http://folk.uio.no/rnymoen/forecast_air_index.html 1 AIR-Automatized Inflation Reports 15 February 2007, Ragnar Nymoen The biases of the AIR forecasts become markedly bigger for forecasts of length 5 and 6 quarters, but they are still less than 0.5 percentage points higher compared to the actual annual rates of inflation. The graph shows forecast biases for all forecast horizons form one quarters to 10 quarters i.e. one and a half year. The biases in Norges Bank’s forecasts are consistently larger than the AIR biases, with the exception of the 1 quarter horizon where the two biases are almost identical. The second panel of the figure shows the mean squared forecast errors, MSFE, to which large forecast errors contribute relatively more than small errors. Based on this measure, the AIR is practically as good as the IR for one quarter forecasts. For the other horizons, the AIR forecasts are better, so the picture is more or less the same as in the first panel. This evaluation of AIR forecasts will be updated in April 2007. Previous evaluation of AIR: November 2006. 2