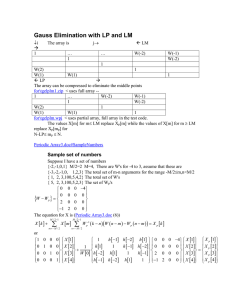
Multi-dimensional Array
advertisement
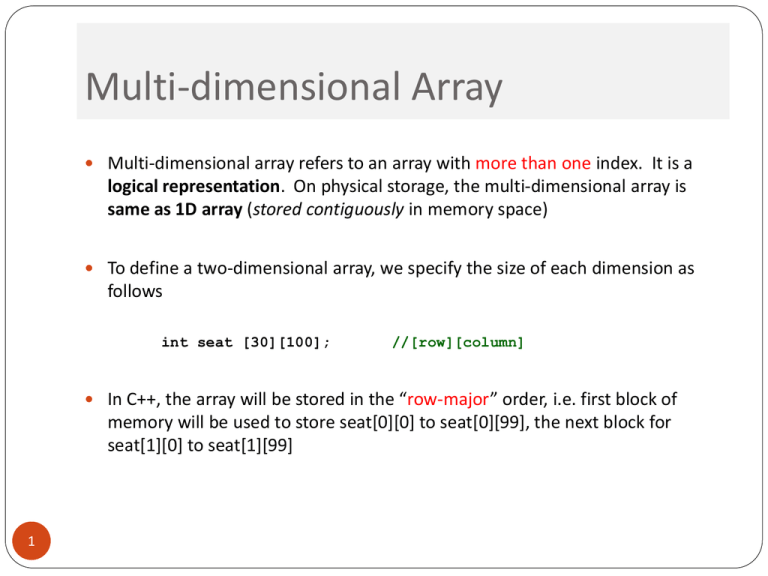
Multi-dimensional Array
Multi-dimensional array refers to an array with more than one index. It is a
logical representation. On physical storage, the multi-dimensional array is
same as 1D array (stored contiguously in memory space)
To define a two-dimensional array, we specify the size of each dimension as
follows
int seat [30][100];
//[row][column]
In C++, the array will be stored in the “row-major” order, i.e. first block of
memory will be used to store seat[0][0] to seat[0][99], the next block for
seat[1][0] to seat[1][99]
1
Col
Row
[0,0]
[0,1]
[0,2]
[0,3]
[1,0]
[1,1]
[1,2]
[1,3]
Row-Major
2
Memory
[0,0]
[0,1]
[0,2]
[0,3]
[1,0]
[1,1]
[1,2]
[1,3]
Multi-dimensional Array
To access an element of the array, we specify an index for each
dimension:
cin >> seat[y][x];
//[row][column]
The above statement will input an integer into row - y and
column - x of the array.
When passing a multi-dimensional array into a function, the size
of all dimensions except the first must be specified.
The function below can take any two-dimensional integer array
with size 100 in the second dimension (size of first dimension is
specified in parameter size1
void display (int a[][100], int size1)
3
BMI Program
void main()
{
const int N=10;
float data[N][2];// N records, each record holds weight and height
int i, position;
for (i=0; i<N; i++){
cout << "Weigth(kg) Height(m):";
cin >> data[i][0];
cin >> data[i][1];
}
for (i=0; i<count; i++){
cout << "BMI for " << i+1 << “is :”;
cout << data[i][0]/(data[i][1]*data[i][1]) << endl;
}
}
4
![CMPS 1053 - 2-Dimensional Array Problems 1. int A[50][7];](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010949140_1-6834a0202c0b10ad84c9231ae1d72800-300x300.png)