In104 Graphics Java has
advertisement
In104
Graphics
Java has some API support for graphics in the
java.awt (abstract windowing toolkit) package.
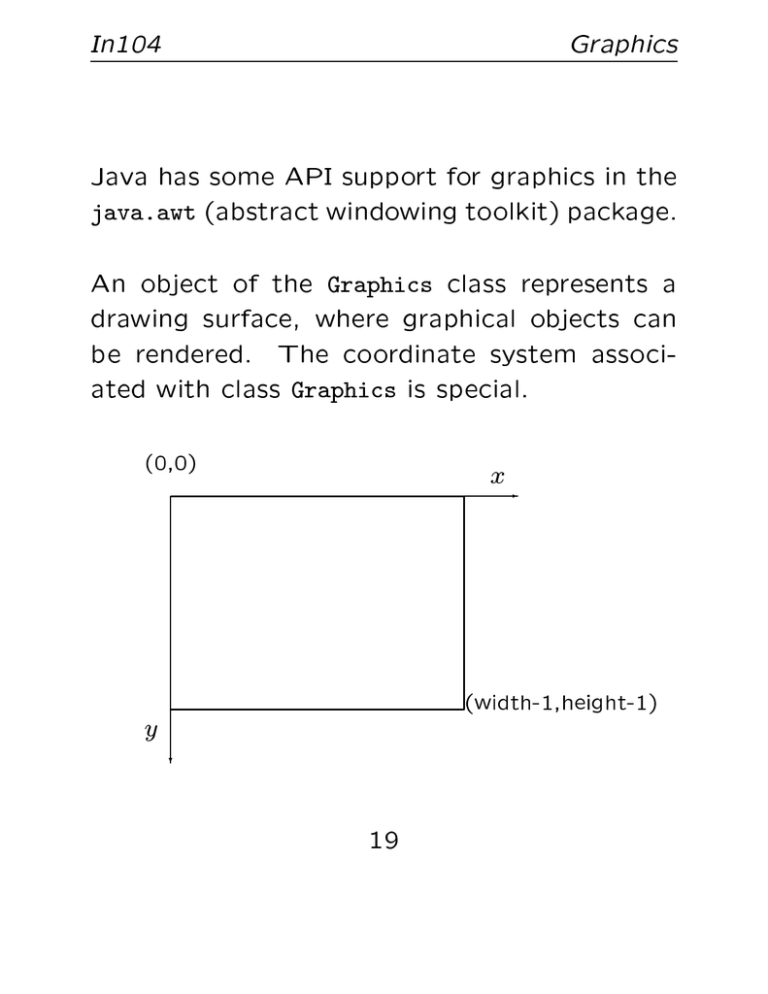
An object of the Graphics class represents a
drawing surface, where graphical objects can
be rendered. The coordinate system associated with class Graphics is special.
(0,0)
y
x-
(width-1,height-1)
?
19
In104
Graphics
The Graphics class also contains methods for
drawing dierent shapes:
drawLine,
drawRect,
drawOval,
drawPolygon,
drawString,
drawImage,
and several more.
Example:
page.drawRect (50,50,40,40);
page.drawString ("Hello",110,70);
The operating system or a web browser is responsible for providing users with Graphics objects.
20
In104
GUI
Graphical user interface (GUI) in Java can be
built up by putting together several GUI components.
A Java GUI component is a visual entity that
displays information and/or allows user interaction.
The Component class hierarchy looks as follows:
Container,
TextComponent,
Button,
Canvas,
Label,
Scrollbar,
and several more.
21
In104
Applet
The Applet class from the java.applet package
is a special subclass of Component:
Component
"
Container
"
Panel
"
Applet
(An Applet is a Panel, a Panel is a Container, a
Container is a Component.)
Applet can
include other Java GUI components
into its graphical layout, therefore creating a
complete GUI.
22
In104
Applet
Java applets are a type of Java programs that
are intended to be embedded into an HTML
document, transported across a network and
excecuted using a web browser.
On local computer:
Applet source code ! Java compiler
code.
!
byte-
On remote computer:
Bytecode ! web browser
23
!
Java interpreter
In104
Applet
Java applets, unlike standard \stand-alone" Java
applications, do not have the main method.
But there are important methods associated
with class Applet:
\init" initializes the applet's environment and
permanent data. Called just after the applet
is loaded.
\start" starts the applet. Called just after the
applet is made active.
\stop" stops the applet. Called just after the
applet is made inactive.
\destroy" destroys the applet. Called when
the browser is exited.
\paint" is invoked automatically to \draw and
refresh" the graphical layout of the applet.
24
In104
Applet
To program a new applet implies:
To extend a new subclass of Applet;
To override method init;
To override method paint possibly;
To override other methods of Applet if necessary;
To introduce other new methods.
25
In104
GUI
The layout of multiple GUI components is controlled by a so-called layout manager in Java.
The java.awt package has ve layout managers:
FlowLayout,
BorderLayout,
CardLayout,
GridLayout, and
GridBagLayout.
26
In104
Layout Managers
Flow Layout
FlowLayout
Applet;
is the default layout manager for
Components are placed in a row from left to
right in the order in which they are added;
A new row is started when there is not enough
space left on the current row;
Each row is centered.
27
In104
Layout Managers
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class MyButtons extends Applet {
Button button1, button2, button3;
public void init() {
button1 = new Button("Ok");
button2 = new Button("Open");
button3 = new Button("Close");
add(button1);
add(button2);
add(button3);
}
}
<APPLET CODE="MyButtons.class" width=300 height=200></APPLET>
28
In104
Layout Managers
Grid Layout
Components are placed in a grid with userdened number of columns and rows;
Each component occupies exactly one grid cell;
All cells in the grid are of the same size.
29
In104
Layout Managers
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class ButtonGrid extends Applet {
public void init() {
setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2));
add(new Button("1"));
add(new Button("2"));
add(new Button("3"));
add(new Button("4"));
add(new Button("5"));
add(new Button("6"));
}
}
<APPLET CODE="ButtonGrid.class" width=300 height=200></APPLET>
30
In104
Layout Managers
Border Layout
Denition of ves locations: North, South,
East, West and Center;
The programmer species where a component
should appear;
The relative dimensions of the areas are determined by the size of the added components.
31
In104
Layout Managers
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class ButtonDir extends Applet {
public void init() {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add("North", new Button("North"));
add("South", new Button("South"));
add("East", new Button("East"));
add("West", new Button("West"));
add("Center", new Button("Center"));
}
}
<APPLET CODE="ButtonDir.class" width=300 height=200></APPLET>
32
In104
Layout Managers
Card Layout
Components are \stacked" such that only one
component is displayed at any one time;
Components are ordered according to the order in which they were added to the container;
Methods control which component is currently
visible.
33
In104
Layout Managers
Grid Bag Layout
The most versatile and complex among the
ve layout managers;
A two-dimensional grid of columns and rows as
in GridLayout, but not all cells are of the same
size;
Components may span multiple columns and/or
rows;
Each component is associated with a set of
constraints, dened by the GridBagConstraints
class.
34
In104
Event-Driven Programming
How to incorporate user interaction into e.g. a
Java applet?
Java treats mouse move and typing on keyboard as so-called \events". Actions applied
to GUI components also generate events, such
as pressing down a button.
Java has so-called \event listeners" that are
capable of capturing and reacting to the events.
User action ! GUI component
listener ! Applet
35
!
event
!
In104
Event-Driven Programming
Java has a set of dierent event listeners, each
associating with a particular event.
GUI components are able to generate events.
Examples:
Button ! ActionEvent ! ActionListener
Scrollbar ! AdjustmentEvent ! AdjustmentListener
Choice ! ItemEvent ! ItemListener
36
In104
Event-Driven Programming
All event listeners in the java.awt.event package are Java interfaces.
Java interfaces are a collection of contants and
abstract methods.
Every event listener has thus one or several
abstract methods, which only give the name
and syntax of the methods to be invoked when
events occur.
public interface AdjustmentListener
{
// ...
public abstract void
adjustmentValueChanged(AdjustmentEvent e)
}
Users are \forced" to implement an event listener and dene associated abstract methods.
37
In104
Event-Driven Programming
Users are responsible for dening the response
when a certain event happens. This is done
by:
1. Implement a specic listener
class MyListener implements AdjustmentListener
2. Dene response in the associated method
public void adjustmentValueChanged (AdjustmentEvent event)
{ /* ... */ }
3. Add the specic listener to a GUI component
Scrollbar bar;
MyListener my_listener;
// ...
bar.addAdjustmentListener (my_listener);
38
In104
Event-Driven Programming
39
In104
Event-Driven Programming
40
In104
Event-Driven Programming
import java.applet.Applet;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class Zoom2 extends Applet implements AdjustmentListener {
private final int SIZE = 300;
private Scrollbar bar =
new Scrollbar(Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL, 10, 64, 10, SIZE);
private int current_size = 10;
private Image picture;
public void init() {
setLayout (new BorderLayout());
setBackground (Color.white);
bar.addAdjustmentListener (this);
picture = getImage (getDocumentBase(), "owl.gif");
}
add (bar, "South");
setSize (SIZE, SIZE);
setVisible (true);
// method init
41
In104
Event-Driven Programming
public void zoom_image (int size) {
current_size = size;
repaint();
}
public void paint (Graphics page) {
page.drawImage (picture, SIZE/2-current_size/2,
SIZE/2-current_size/2, current_size, current_size, this);
}
public void adjustmentValueChanged (AdjustmentEvent event) {
zoom_image (event.getValue());
}
42