Collaborative Systems Thinking:
advertisement

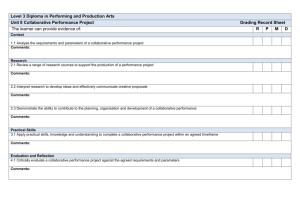
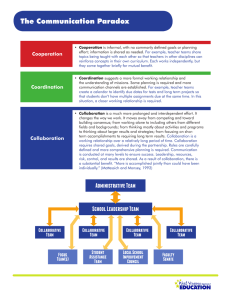
Collaborative Systems Thinking: Biography Your Picture Identifying the enablers and barriers of higher-level systems thinking in aerospace engineering teams Related Publications D.H. Rhodes, C.T. Lamb and D.J. Nightingale (2008). “Empirical Research on Systems Thinking and Practice in the Engineering Enterprise”, IEEE International Systems Conference, Montreal, Canada C.T. Lamb and D.H. Rhodes (2008). “Collaborative Systems Thinking Research: Exploring systems thinking within teams”, INCOSE International Symposium, Utrecht, Netherlands C.T. Lamb and D.H. Rhodes (2009). “Collaborative Systems Thinking: Case study research investigating enablers of team-level systems thinking” AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Orlando, Florida Caroline Twomey Lamb, PhD in Aero/Astro (expected in 2009) Committee: Prof. Deborah Nightingale, chair; Prof. Annalisa Weigel; Dr. Donna Rhodes Motivation Research Design Systems thinking development takes time and experience. Why then, study team-level systems thinking? Literature Review The literature review identified concepts and theories related to collaborative systems thinking. Good Design Enablers of Creativity Process Pilot Interviews Case Studies Team Diversity Systems Engineering Process Systems Engineering Design Thinking Team Experience Strong Team Cognition Analysis & Synthesis Team Environment Well Designed (and utilized) Technical Process Team-level systems thinking is influenced by team culture and technical process Personality Type Thinking Preferences in Engineering Systems Systemsthinking thinking teams teamshave have three threetiers tiers Systems Systemsand anddesign designprocesses processesare are recognized, recognized,but butnot notnecessarily necessarilyused used •• 1) 1) Strong Strongsystems systems leadership leadership 2) 2) Developing Developing systems systems professionals professionals with withfunctional functional backgrounds backgrounds 3) Functional 3) Functionalspecialists specialists •• •• Experienced Experiencedsystems systemsprofessionals professionalsrely relyon on past pastexperience experience Less Lessexperienced experiencedteams teamsuse usediscussion discussionof of process processas asmeans meansto todevelop develop documentation, documentation,learn learn Both groups identify with following spirit if Both groups identify with following spirit if not notrule ruleof ofprocess process Systems Thinking Manned Fighter Program Starts by Decade (Murman et al 2002) Transactive Memory Engineering Culture Team Cognition Integrated Design Practices: Integrated Product Development (IPD) improves design through early integration of multiple disciplines. IPD is predicated on teams of engineers working closely together on systems-level issues. Collaborative Systems Thinking (evaluated through 1st and 3rd person assessments) •• •• •• •• Fifteen formal case studies and five abbreviated cases focus are used to collect grounded data. Organizational Culture Work Design for Teams Systems Systemsthinking thinkingteams teamsare arediverse diverse Collaborative Systems Thinking Engineering Behaviors Culture Teams Leadership Team Roles Past Pastexperience experience Variety Varietyof ofearned earneddegrees degrees Mix Mixof ofteam teamroles roles Unique Uniqueoutside outsideinterests interests Systems awareness / curiosity Team Teamleaders leadersrespect respectthe theindividuality individualityof of team teammembers members Pilot interviews were used to validate these initial ideas and directions Team Composition Workforce Development: It is hoped that team-level systems thinking will provide the supportive environment and career guidance required to develop good systems thinking engineers. Results This research follows grounded theory methods and uses surveys and interviews to collect data on the role of culture, process, and team composition in collaborative systems thinking. Demographics: 50% of the aerospace workforce, those with the greatest levels of experience, are eligible to retire by 2013. Program Trends: The aerospace industry has fewer (larger and longer) programs than 50 years ago. This results in fewer opportunities to gain systems experience. Caroline Twomey Lamb is pursuing her doctorate through the MIT Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics. Caroline received her S.B and S.M from MIT in 2003 and 2005 respectively. Her educational philosophy has been to construct a broad tool box of skills and experiences. Upon graduation, Caroline plan to work in the industry as either a design or test engineer. Technical excellence •• Treat Treateach eachas asunique uniquerather ratherthan than addressing addressingthe theminimum minimumcommon commonabilities abilities Manned Spacecraft Program Starts by Decade (Neal 1995) Systems thinking team members are selected for their social skills as much as their technical skills Strong interpersonal skills Time Theory Expected Outcomes and Future Work Case Study Insights Team Experience Years 18 Average team experience is not an indicator of collaborative systems thinking: Teams with <7 years of average experience behave similarly to those with >20 years of experience 16 Transactive TransactiveMemory Memory(Wegner (Wegner1985) 1985) Systems SystemsThinking Thinking(Davidz (Davidz 2006) 2006) Systems Systemsthinking thinkingisisutilizing utilizingmodal modal elements elementsto toconsider considerthe the componential, componential,relational, relational,contextual, contextual, and anddynamic dynamicelements elementsof ofthe thesystem system of ofinterest. interest. Component Complexity Interrelationship s Context Emergence Wholes Number of Team Members Number of Individuals 14 Collaborative systems thinking is a transaction based manifestation of Davidz’s definition of systems thinking. Individuals with unique knowledge synthesize a systems perspective through interacting as a team. 12 10 8 An internally consistent view of decision making is an enabler of collaborative systems thinking Teams with higher self-reported and observe CST have more consistently shared views of how decision are made 6 4 2 Team Experience Years 0 8 7 Number ofofTeam Members Number Individuals 1. 1. Transactive Transactivememory memoryisisaaconcept conceptthat that facilitates facilitatesunderstanding understandingof ofgroup groupthinking thinking 2. 2. Transactive Transactivememory memoryisisthe thecombination combinationof of individual memory systems and the individual memory systems and the communications communications(or (ortransactions) transactions)between between individuals individuals 3. 3. Individuals Individualswith withcomplementary complementaryknowledge knowledge synthesize synthesizenew newknowledge knowledgeby byinteracting interacting Design DesignThinking Thinking(Dym (Dymet etal al2005) 2005) 1. 1. Design Designisisaasocial socialprocess process 2. 2. Designers Designersthink thinkand andcommunicate communicateusing using design designlanguages languages(e.g. (e.g.sketching, sketching,modeling, modeling, prototyping) prototyping) 3.Groups 3.Groupsutilize utilizedivergent divergentand andconvergent convergent thinking thinkingto toexplore exploreoptions optionsand andchoose choose between betweenalternatives alternatives © 2008 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6 High collaborative systems thinking team members identify themselves as team players who are reliable performers. Lower systems thinking teams’ members rate themselves relatively higher in detail orientation and coordination 5 4 3 2 1 0 <5<5 5-10 5-10 10-15 10-15 15-20 15-20 20-25 20-25 25-30 25-30 30-35 30-35 35-40 35-40 >40 >40 Years of Experience Years of Experience Case study sample includes a wide variety of aerospace program types and sizes Conceptual Design; Small Program Aircraft (Hardware) Detailed Design; Large Program Spacecraft (Hardware) Mini Case Government Commercial Private Customer For more information, please visit: http://seari.mit.edu Understanding team-level systems thinking. A possible tool for workforce development. Expected Outcomes 1. An operational definition of collaborative systems thinking 2. Heuristics for enabling collaborative systems thinking 3. Descriptive theory of collaborative systems thinking 4. Data for improving workforce development initiatives Future Work 1. Tracking members of ‘middle tier’ to measure effectiveness of participation for systems skill development 2. Longitudinal study to explore relationships rls between final system performance and and collaborative system thinking in systems architecture teams