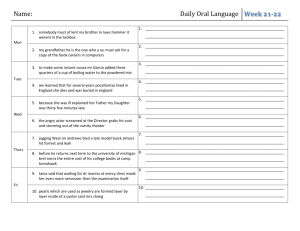
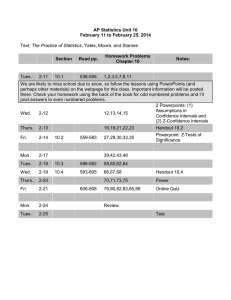
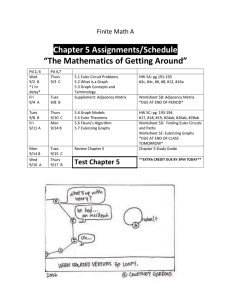
Cleveland State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
advertisement

Cleveland State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering EEC 492/592 and MCE 493/593 Prosthesis Design and Control Fall 2014 Recommended References: A. Bennett Wilson, A Primer on Limb Prosthetics D. Simon, Optimal State Estimation D. Simon, Evolutionary Optimization Algorithms D. Winter, Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement (fourth edition) Recommended Weekly Seminar: Human Motion Seminar Series - 10:15 Wednesday, FH 103 https://docs.google.com/spreadsheet/ccc?key=0AiQBXpGG8GfdFY5N2xjb1Q5MTJDbWVhajZQNEhfQ0E&usp=sharing#gid=1 Prerequisites: EEC 440 or MCE 441, and proficiency in MATLAB programming Days, Time, and Classroom: T/Th 6:00-7:50, FH 309 Goals and Objectives: This course is designed to provide students with a basic understanding of human biomechanics, and lower limb prosthetic design and control technologies. After taking this course, students will be able to explain the similarities and differences between current prosthesis designs, the important factors in prosthesis designs, simulate prosthesis operation, design prosthesis controllers, and optimize prosthesis design and control algorithms. Course Ethics: See www.csuohio.edu/engineering/ece/docs/Ethics%20Policy.doc Grading Criteria: Homework Midterm Project Final Exam Undergraduate 35% 30% N/A 35% Graduate 25% 25% 25% 25% All exams are open book and open notes, but no electronic devices are allowed. Homework Assignments: See http://academic.csuohio.edu/simond/courses/prosthesi s/homework.htm Project Guidelines: See http://academic.csuohio.edu/simond/courses/prosthesis/ project.htm Projects are required only from 500-level students. See the course schedule below for project due dates. Grading scale: A A minus B plus B B minus C plus C D 93-100 90-93 87-90 83-87 80-83 77-80 (this range is a C for grad students) 70-77 60-70 (this range is an F for grad students) Instructors: Phone Email Office Office Hours Dan Simon 687-5407 d.j.simon@csuohio.edu FH 343, FH 310 T 3:30-5:30 W 1:30-3:30 Hanz Richter 687-5232 h.richter@csuohio.edu FH 242, FH 25 MW 4:00-6:00 Antonie van den Bogert 687-5329 a.vandenbogert@csuohio.edu FH 246, FH 232 MW 2:00-4:00 Course Schedule: Week Date Tues. Aug. 26 Thurs. Aug. 28 Tues. Sep. 2 Thurs. Sep. 4 Instructor Simon Simon Richter Richter 3 Tues. Sep. 9 Thurs. Sep. 11 van den Bogert van den Bogert 4 Tues. Sep. 16 Simon 1 2 Topic Notes Introduction Intro.pptx Introduction Robot kinematics, dynamics, models kin_dyn1.pdf Robot kinematics, dynamics, models kin_dyn2.pdf Nonsquare Jacobians and the Moore-Penrose Pseudoinverse Matlab code to calculate robot dynamics Biomechanics Sep. 9 Slides Biomechanics Sep. 11 Slides muscle.m State estimation State Estimation.pdf Week 5 Date Thurs. Sep. 18 Tues. Sep. 23 Thurs. Sep. 25 Instructor Simon Simon van den Bogert Topic State estimation State estimation Measurements and signal processing Tues. Sep. 30 van den Bogert Measurements and signal processing Thurs. Oct. 2 Tues. Oct. 7 Thurs. Oct. 9 Tues. Oct. 14 Thurs. Oct. 16 Richter Richter Richter van den Bogert Electromechanical power conversion Electromechanical power conversion Midterm Robot drive systems Kinematics, kinetics, amputee gait Tues. Oct. 21 van den Bogert Kinematics, kinetics, amputee gait Thurs. Oct. 23 Tues. Oct. 28 Thurs. Oct. 30 Richter Richter Richter Robot control Robot control Prosthesis control Tues. Nov. 4 Thurs. Nov. 6 Tues. Nov. 11 Thurs. Nov. 13 Tues. Nov. 18 Thurs. Nov. 20 Tues. Nov. 25 Thurs. Nov. 27 Tues. Dec. 2 Thurs. Dec. 4 Tues. Dec. 9 Thurs. Dec. 11 Simon Simon Evolutionary Optimization Gradient-Based Optimization Holiday Evolutionary Optimization Evolutionary Optimization Modeling and simulation of gait (1) Modeling and simulation of gait (2) Holiday Project Presentations Project Presentations No Class Final Exam, 6:00 PM 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Simon Simon van den Bogert van den Bogert Notes State Estimation.zip 2014-09-25 Measureme 1.pdf 2014-09-30 Measureme 2.pptx 2014-10-16 Kinematics Kinetics 1.pdf 2014-10-21 Kinematics Kinetics 2.pdf Due - Project Letter of Intent Due - Project Proposal Due - Project Report ABET objectives: Electrical Engineering: (1) Practice electrical engineering in one or more of the following areas: communications, computers, controls, power electronics, and power systems (2) Define and diagnose problems, and provide and implement electrical engineering solutions in an industrial environment (6) Develop knowledge beyond the undergraduate level and keep current with advancements in electrical engineering Mechanical Engineering: (2) Practice mechanical engineering in environments that require a variety of roles including engineering problem definition, application of advanced methods of analysis, problem diagnosing, and solution of real-world engineering design problems that are subject to realistic constraints such as cost, safety, etc. (3) Actively contribute in a multidisciplinary engineering environment (4) Enhance knowledge beyond the BS level, engage in life-long learning, and keep current with advancements in engineering and technology. ABET outcomes: Electrical and Mechanical Engineering: (a) Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering (b) Design and conduct engineering experiments, as well as analyze and interpret data (c) Design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs (e) Identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems (g) Communicate effectively (h) Understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global and societal context (j) Knowledge of contemporary issues (k) Use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice