Be sure this exam has 5 pages including the cover
advertisement

Be sure this exam has 5 pages including the cover
The University of British Columbia
MATH 215/255, Section 102
Midterm Exam I – October 2009
Name
Signature
Student Number
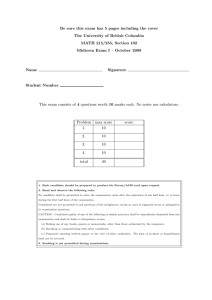
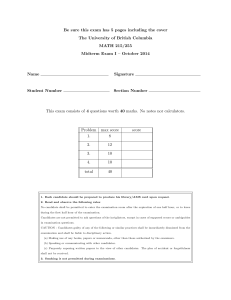
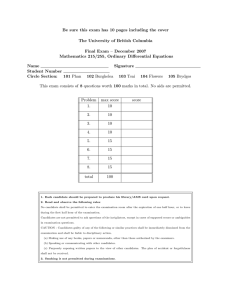
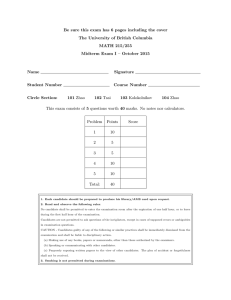
This exam consists of 4 questions worth 10 marks each. No notes nor calculators.
Problem
1.
max score
10
2.
10
3.
10
4.
10
total
40
score
1. Each candidate should be prepared to produce his library/AMS card upon request.
2. Read and observe the following rules:
No candidate shall be permitted to enter the examination room after the expiration of one half hour, or to leave
during the first half hour of the examination.
Candidates are not permitted to ask questions of the invigilators, except in cases of supposed errors or ambiguities
in examination questions.
CAUTION - Candidates guilty of any of the following or similar practices shall be immediately dismissed from the
examination and shall be liable to disciplinary action.
(a) Making use of any books, papers or memoranda, other than those authorized by the examiners.
(b) Speaking or communicating with other candidates.
(c) Purposely exposing written papers to the view of other candidates. The plea of accident or forgetfulness
shall not be received.
3. Smoking is not permitted during examinations.
October 2009
Math 215/255 Midterm 1, Section 102
Page 2 of 5
(10 points) 1. Answer YES or NO for each of the following questions, and give a reason.
dy
= ty + 3y 1/3 with y(215) = 255 has at most one solution near
(a) The problem
dt
(t, y) = (215, 255).
YES.
The function f (t, y) = ty + 3y 1/3 and its partial derivative ∂f /∂y = t + y −2/3 are both
continuous near (t, y) = (215, 255). Thus the solution is unique by the unique existence
theorem.
(b) If y1 (t) and y2 (t) are two solutions of the equation y 00 + p(t)y 0 + q(t)y = 0 for 0 < t < 3,
and their Wronskian W (y1 , y2 ) is positive at t = 1, then W (y1 , y2 ) cannot be negative at t = 2.
YES.
The Wronskian W (t) = W (y1 , y2 )(t) is either always zero or never zero. Since W (1) > 0 and
W (t) 6= 0, we have W (t) > 0 for all t ∈ (0, 3).
October 2009
Math 215/255 Midterm 1, Section 102
Page 3 of 5
(10 points) 2. A bath contains water. Let the depth of water at time t be y = y(t) inches. At time t = 0 the
plug is pulled and water exits via the drain at the rate of 2y inches per minute.
(a) The bath is filled to an initial depth of 10 inches. Find the depth y as a function of time.
dy
= −2y
dt
y = y0 e−2t = 10e−2t
(b) Same problem as in the previous part except that at time t = 0, in addition to pulling
the plug, the tap is also turned on and water enters the bath at rate 3 inches per minute.
dy
= −2y + 3
dt
dy 2t
e + 2ye2t = 3e2t
dt
d 2t e y = 3e2t
dt
h
is=t
3 h it
e2s y(s)
= e2s
2
0
s=0
e2t y(t) − 10 =
y(t) = 10e−2t +
i
3 h 2t
e −1
2
i 3 17
3h
1 − e−2t = + e−2t .
2
2
2
October 2009
(10 points) 3. Consider
Math 215/255 Midterm 1, Section 102
y + (2x − y −1 ey )
dy
= 0.
dx
(a) Show it is not exact.
N = 2x − y −1 ey .
M = y,
∂M
= 1,
∂y
∂N
= 2.
∂x
Not equal.
(b) There is an integrating factor µ = µ(y). Find it.
∂(µN )
∂(µM )
=
,
∂y
∂x
Since µ = µ(y) and M = y, same as
µ0 (y)y + µ = µNx = 2µ.
Simplifies to µ0 (y)y = µ, or
dµ/µ = dy/y.
Solved by
µ = y.
(c) Solve for y given that y = 1 when x = 1.
After multiplying by µ
dy
= 0.
y 2 + (2xy − ey )
|{z} | {z } dx
∂ψ
∂x
∂ψ
∂y
Z
ψ=
y 2 dx = xy 2 + g(y).
ψy = 2xy + g 0 (y) = 2xy − ey ,
g 0 (y) = −ey ,
Z
g(y) = − ey dy = −ey + c.
ψ = xy 2 − ey + c = 0.
Plug in (x, y) = (1, 1), we get c = −1 + e.
xy 2 − ey − 1 + e = 0.
Page 4 of 5
October 2009
Math 215/255 Midterm 1, Section 102
y 00 − 4y 0 − 5y = 0,
(10 points) 4. For real a, solve for y = y(t):
y(0) = 6,
Page 5 of 5
y 0 (0) = 6a.
Then find the value of a so that the solution approaches zero as t → ∞.
Try y = ert ,
r2 ert − 4rert − 5ert = 0.
Characteristic equation
r2 − 4r − 5 = 0.
Two real roots
r1 = 5,
r2 = −1.
General solution
y(t) = c1 e5t + c2 e−t .
y 0 (t) = 5c1 e5t − c2 e−t .
Match boundary conditions
c1 + c2 = 6
5c1 − c2 = 6a
Their sum shows 6c1 = 6 + 6a, i.e.,
c1 = 1 + a.
The first equation then shows
c2 = 5 − a.
Solution is
y(t) = (1 + a)e5t + (5 − a)e−t .
To decay as t → ∞, the first term should vanish. We need 1 + a = 0, i.e.,
a = −1.