Deep Brain Stimulation of Parkinsonian Networks Kelly Toppin, Yixin Guo Parkinson's Disease
advertisement
DeepBrainStimulationofParkinsonianNetworks
Kelly Toppin, Yixin Guo
kpt26@drexel.edu
Parkinson's Disease
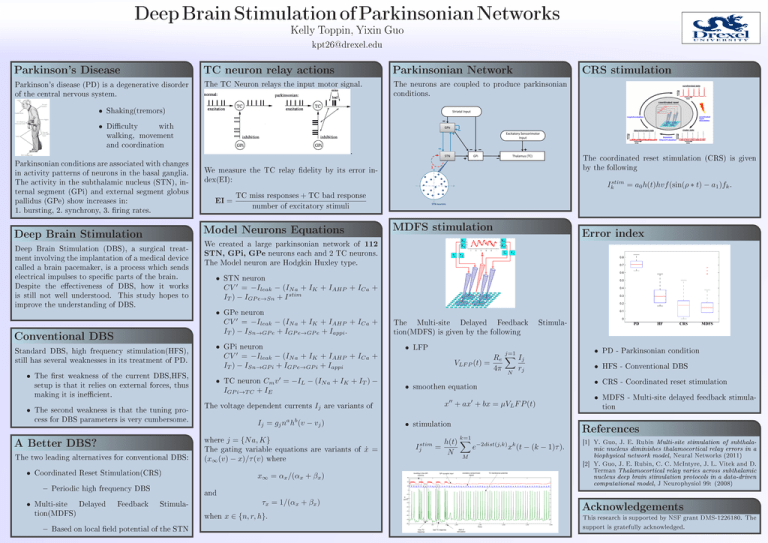
TC neuron relay actions
Parkinsonian Network
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder
of the central nervous system.
The TC Neuron relays the input motor signal.
The neurons are coupled to produce parkinsonian
conditions.
• Shaking(tremors)
Striatal Input
• Diculty
with
walking, movement
and coordination
Parkinsonian conditions are associated with changes
in activity patterns of neurons in the basal ganglia.
The activity in the subthalamic nucleus (STN), internal segment (GPi) and external segment globus
pallidus (GPe) show increases in:
1. bursting, 2. synchrony, 3. ring rates.
GPe
Excitatory Sensorimotor
Input
.
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), a surgical treatment involving the implantation of a medical device
called a brain pacemaker, is a process which sends
electrical impulses to specic parts of the brain.
Despite the eectiveness of DBS, how it works
is still not well understood. This study hopes to
improve the understanding of DBS.
Conventional DBS
Standard DBS, high frequency stimulation(HFS),
still has several weaknesses in its treatment of PD.
• The rst weakness of the current DBS,HFS,
setup is that it relies on external forces, thus
making it is inecient.
• The second weakness is that the tuning pro-
The two leading alternatives for conventional DBS:
tion(MDFS)
Feedback
stim
Ik
Stimula-
Based on local eld potential of the STN
= a0 h(t)hvf (sin(ρ ∗ t) − a1 )fk .
STN neurons
MDFS stimulation
Error index
0.8
0.7
0.6
• STN neuron
CV 0 = −Ileak − (IN a + IK + IAHP + ICa +
IT ) − IGP e→Sn + I stim
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
• GPe neuron
CV 0 = −Ileak − (IN a + IK + IAHP + ICa +
IT ) − ISn→GP e + IGP e→GP e + Iappi .
• GPi neuron
CV 0 = −Ileak − (IN a + IK + IAHP + ICa +
IT ) − ISn→GP i + IGP e→GP i + Iappi
• TC neuron Cm v 0 = −IL − (IN a + IK + IT ) −
IGP i→T C + IE
0.1
The Multi-site Delayed Feedback
tion(MDFS) is given by the following
• LFP
Re
VLF P (t) =
4π
Ij
rj
MDFS
• MDFS - Multi-site delayed feedback stimula-
tion
k=1
X
e
−2dist(j,k) k
x (t − (k − 1)τ ).
M
exictatory sensorimotor
signal
GPi synaptic input
[1] Y. Guo, J. E. Rubin Multi-site stimulation of subthalamic nucleus diminishes thalamocortical relay errors in a
biophysical network model, Neural Networks (2011)
[2] Y. Guo, J. E. Rubin, C. C. McIntyre, J. L. Vitek and D.
Terman Thalamocortical relay varies across subthalamic
TC membrance potential
nucleus deep brain stimulation protocols in a data-driven
computational model, J Neurophysiol 99: (2008)
30
10
and
CRS
References
h(t)
=
N
bursting in the GPi
nuerons
HF
• CRS - Coordinated reset stimulation
• stimulation
stim
Ij
PD
• HFS - Conventional DBS
x00 + ax0 + bx = µVL F P (t)
where j = {N a, K}
The gating variable equations are variants of ẋ =
(x∞ (v) − x)/τ (v) where
x∞ = αx /(αx + βx )
N
0
• PD - Parkinsonian condition
• smoothen equation
The voltage dependent currents Ij are variants of
Ij = gj na hb (v − vj )
j=1
X
Stimula-
20
Periodic high frequency DBS
Delayed
The coordinated reset stimulation (CRS) is given
by the following
Thalamus (TC)
We created a large parkinsonian network of 112
STN, GPi, GPe neurons each and 2 TC neurons.
The Model neuron are Hodgkin Huxley type.
• Coordinated Reset Stimulation(CRS)
• Multi-site
GPi
1
TC miss responses + TC bad response
EI =
number of excitatory stimuli
cess for DBS parameters is very cumbersome.
A Better DBS?
STN
We measure the TC relay delity by its error index(EI):
Model Neurons Equations
Deep Brain Stimulation
CRS stimulation
0
−10
τx = 1/(αx + βx )
when x ∈ {n, r, h}.
V
−20
(mV)
−30
Acknowledgements
−40
−50
−60
This research is supported by NSF grant DMS-1226180. The
−70
−80
0
500
800
1,000
1,500
Time
miss TC
response
bad TC response
start of
stimulation
2,000
2,500
3,000
support is gratefully acknowledged.