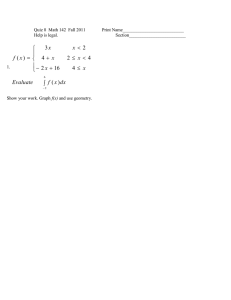
9. 2 3 4
advertisement

2
2
2
2
2
9. 2 − 3 + 4 − 5 + · · · − 99 =
99
X
i =2
(−1)i i 2
X i
1 2 3
4
n
+ + +
+···+ n =
2 4 8 16
2
2i
n
14.
i =1
P
41. The formula in=1 i 3 = n 2 (n + 1)2 /4 holds for n = 1, since it says 1 = 1 in this case.
Now assume that it holds for n = some number k ≥ 1; that is,
P
k
3
2
2
i =1 i = k (k + 1) /4. Then for n = k + 1, we have
k+1
X
3
i =
i =1
k
X
i 3 + (k + 1)3
i =1
k 2 (k
(k + 1)2 2
+ 1)2
+ (k + 1)3 =
[k + 4(k + 1)]
4
4
(k + 1)2
(k + 2)2 .
=
4
=
Thus the formula also holds for n = k + 1. By induction, it holds for all positive integers
n.
7. The required area is (see the figure)
3 2
3
3
−1 +
+ 2 −1 +
+3
A = lim
n→∞ n
n
n
6 2
6
+ −1 +
+ 2 −1 +
+3
n
n
3n
3n 2
+ 2 −1 +
+ · · · + −1 +
+3
n
n
32
6
6
3
1− + 2 −2+ +3
= lim
n→∞ n
n
n
n
2
12 6
12
+ 1−
+ 2 −2+
+3
n
n
n
6n
9n 2
6n
+···+ 1−
+ 2 −2+
+3
n
n
n
27 n(n + 1)(2n + 1)
= lim 6 + 3 ·
n→∞
n
6
= 6 + 9 = 15sq. units.
y
y=x 2 +2x+3
−1
x
3n
−1+ n =2
3
−1+ n
Fig. 2-7
10.
y
2
x
A
y = x 2 − 2x
Fig. 2-10
The height of the region at position x is
0 − (x 2 − 2x) = 2x − x 2 . The “base” is an interval of length 2, so we approximate using
n rectangles of width 2/n. The shaded area is
n
X
2
4i 2
2i
A = lim
2 − 2
n→∞
n
n
n
i =1
n X
8i
8i 2
= lim
− 3
n→∞
n2
n
i =1
8 n(n + 1)(2n + 1)
8 n(n + 1)
− 3
= lim
n→∞ n 2
2
6
n
4
8
= 4 − = sq. units.
3
3
18.
P = {x0 < x1 < · · · < xn },
P ′ = {x0 < x1 < · · · < x j −1 < x ′ < x j < · · · < xn }.
Let m i and Mi be, respectively, the minimum and maximum values of f (x) on the interval
[xi −1 , xi ], for 1 ≤ i ≤ n. Then
L( f, P) =
n
X
U ( f, P) =
n
X
m i (xi − xi −1 ),
i =1
Mi (xi − xi −1 ).
i =1
If m ′j and M j′ are the minimum and maximum values of f (x) on [x j −1 , x ′ ], and if m ′′j and
M j′′ are the corresponding values for [x ′ , x j ], then
m ′j ≥ m j ,
m ′′j ≥ m j ,
M j′ ≤ M j ,
M j′′ ≤ M j .
Therefore we have
m j (x j − x j −1 ) ≤ m ′j (x ′ − x j −1 ) + m ′′j (x j − x ′ ),
M j (x j − x j −1 ) ≥ M j′ (x ′ − x j −1 ) + M j′′ (x j − x ′ ).
Hence L( f, P) ≤ L( f, P ′ ) and U ( f, P) ≥ U ( f, P ′ ).
If P ′′ is any refinement of P we can add the new points in P ′′ to those in P one at a time,
and thus obtain
L( f, P) ≤ L( f, P ′′ ),
U ( f, P ′′ ) ≤ U ( f, P).
18.
y
y = 2 + 3x
A
1
x
Fig. 2-18
n
X
1
3i
sn =
=
2+
represents a sum of areas of n rectangles each of
n2
n
n
i =1
i =1
width 1/n and having heights equal to the height to the graph y = 2 + 3x at the points
x = i /n. Thus limn→∞ Sn is the area of the trapezoid in the figure above, and has the value
1(2 + 5)/2 = 7/2.
n
X
2n + 3i
14.
Z
Z 3p
Z 3 p
p
2
2
(2 + t) 9 − t dt = 2
t 9 − t 2 dt
9 − t dt +
−3
−3
−3
1 2
=2
π 3 + 0 = 9π
2
3
33.
R2
−1 sgn x
dx = 2 − 1 = 1
y
1
y=sgn x
−1
2
−1
Fig. 4-33
x
39.
y
A1
y = |x + 1| − |x − 1| + |x + 2|
x
A2
Fig. 4-39
Z
4
(|x + 1| − |x − 1| + |x + 2|) d x
−3
= area A1 − area A2
1 5
5+8
1+2
1+2
1 1
41
=
(5) +
(3) −
(1) −
(1) −
(1) =
2 3
2
2
2
2 3
2
40.
y
y=
x2 − x
|x − 1|
A1
3
A2
Fig. 4-40
Z
3
x2 − x
dx
0 |x − 1|
= area A1 − area A2
1+3
1
7
=
(2) − (1)(1) =
2
2
2
x
43.
Z
b
f (x) − k
a
=
Z
b
a
Z
2
dx
2
f (x) d x − 2k
Z
b
f (x) d x + k
a
2
Z
b
dx
a
2
f (x) d x − 2k(b − a) f + k 2 (b − a)
a
Z b
2
2
2
= (b − a)(k − f ) +
f (x) d x − (b − a) f
=
b
a
This is minimum if k = f .