MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF THE OCEAN AND ATMOSPHERE SM415 (3-0-3)
advertisement

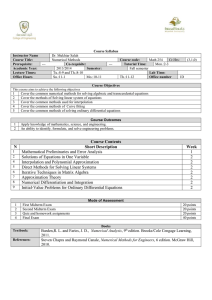
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF THE OCEAN AND ATMOSPHERE SM415 (3-0-3) Course Coordinator (2013-2014): CAPT Schulz 1. Text: None required 2. Prerequisites: SO335, SO414 3. Objectives: • Understand the practice of discretizing partial derivative terms in the equations of motion • Understand the concepts of consistency and stability in a numerical model • Gain insight into the complexity of mathematical descriptions of geophysical fluid phenomena • Gain familiarity with model characteristics including grid schemes, order and parameterizations 4. Course Content: • Partial Differential Equations Review • Numerical Stability • Advection Modeling • Shallow Water Equations • Long-wave modeling • Operational Models 5. Acquired Knowledge: Upon completion the student will be able to • Implement boundary conditions in solutions to physical modeling problems • Explain the derivation of the shallow water equations • Compare and contrast the dispersion relations for Rossby and Kelvin waves • Describe the primitive equations used in Air-Ocean modeling • Demonstrate the concept of numerical stability, including the CFL criteria, and its application to advection modeling • Provide examples of parameterized sub-grid scale phenomena • Construct numerical models of basin scale circulation using various forcing mechanisms • Demonstrate familiarity of operational Air/Ocean predictive models Updated: 25 July 2013 1