1S2 (Timoney) Tutorial sheet 7 [January 7 – 11, 2008] Name: Solutions
advertisement
![1S2 (Timoney) Tutorial sheet 7 [January 7 – 11, 2008] Name: Solutions](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/011011721_1-38e811b59e0f58e61108a5c182009186-768x994.png)
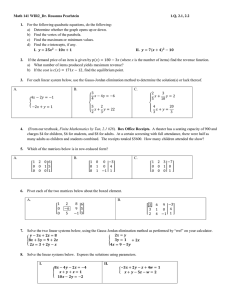
1S2 (Timoney) Tutorial sheet 7 [January 7 – 11, 2008] Name: Solutions 1. Write the system of linear equations 5x1 2x1 −x1 x1 − 2x2 + 3x2 − 12x2 + 2x2 + x3 + 7x3 − 11x3 − x3 − 4x4 + 2x4 − 16x4 − x4 = −3 = 18 = −37 = −3 in the form of a single matrix equation Ax = b for suitable matrices A, x and b. (Make it clear which matrices are A, x and b.) Solution: If we take 5 −2 1 −4 2 3 7 2 ,x = A= −1 −12 −11 −16 1 2 −1 −1 x1 x2 ,b = x3 x4 −3 18 , −37 −3 (so that A is the matrix of coefficients of the unknowns (4 × 4 in this case as we have 4 equations in 4 unknowns), x the column vector made up of the 4 unknowns, and b the column vector made up of the 4 constants on the right hand sides of the equations), then the system is the same as Ax = b 2. For 2 −1 3 A = 4 −4 −2 −4 3 −4 find the inverse matrix A−1 (using the method of row-reducing [A|I3 ] to reduced rowechelon form). Solution: We use Gauss-Jordan elimination on 2 −1 3 :1 0 0 4 −4 −2 : 0 1 0 −4 3 −4 : 0 0 1 3 1 − 21 : 12 0 0 oldRow1 × 21 2 4 −4 −2 : 0 1 0 −4 3 −4 : 0 0 1 3 1 − 12 : 12 0 0 2 0 −2 −8 : −2 1 0 oldRow2 − 4 × oldRow1 0 1 2 : 2 0 1 oldRow2 + 4 × oldRow1 1 − 12 23 : 12 0 0 0 1 4 : 1 − 12 0 oldRow2 × − 12 0 1 2 :2 0 1 3 1 − 12 : 21 0 0 2 0 1 4 : 1 − 12 0 1 1 OldRow3 − OldRow2 0 0 −2 : 1 2 1 − 12 32 : 12 0 0 1 0 1 4 : 1 −2 0 1 1 0 0 1 : − 2 − 4 − 12 OldRow3 × − 12 3 3 1 − 12 0 : 54 OldRow1 − 32 × OldRow3 8 4 1 0 1 0 : 3 2 OldRow2 − 4 × OldRow3 2 1 0 0 1 : − 2 − 14 − 12 5 7 1 0 0 : 11 OldRow1 + 12 × OldRow2 4 8 4 1 0 1 0 : 3 2 2 1 1 0 0 1 : − 2 − 4 − 12 Thus the inverse matrix is 11 4 A−1 = 3 − 21 Richard M. Timoney 2 5 8 1 2 − 14 7 4 2 − 12

![1S11 (Timoney) Tutorial sheet 6 [October 30 – November 2, 2012]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010731549_1-e7300c60c2acb7a65e259cc2eb50b060-300x300.png)
![1S2 (Timoney) Tutorial/exercise sheet 1 [October 22– 26, 2007]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/011011714_1-d64d79e2f1f65b411d42bdb19e1b6982-300x300.png)






