6. Navigation Design
advertisement

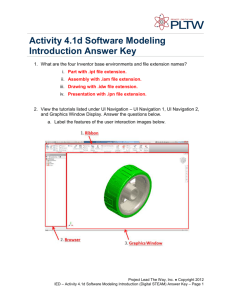
6. Navigation Design Site-level navigation: making it easy for the user to get around the site Page-level navigation: making it easy for the user to find things on a page Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Navigation Choosing a path through the web site’s information space Goals: Let user know where he is Give user confidence in knowing where he is going next Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Navigation: Connections Good navigation builds on good content organization (Chapter 4) Choose a navigation system that reflects the content’s organizational structure Visual design (Chapter5) and navigation design are interrelated Choose visual navigation elements that build context for a user Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Navigation: Connections A Navigational System is a visual representation of an organizational structure Navigation Bar: collection of links grouped together on a page Site-level navigation vs. Page-level Navigation Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Three types of navigation systems Hierarchical Derived from hierarchical organization Ad hoc Hyperlinks Database Search engines Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Rare to use only one Most websites build on a judicious combination of these three, with one dominant theme Hierarchical plus hyperlinks (ad hoc) is most common Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall A pure hierarchy is rare We add links to facilitate moving around the hierarchy without going all the way to the top; note extra links at bottom level Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Global navigation For a small site, it may be possible to show the major links on every page Global navigation Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Global navigation bar can be vertical Global navigation Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Showing more levels in the hierarchy Drop-downs or pull-outs can show the next level Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Other items Breadcrumbs: a sequence of links showing user how he got to current location Subsite: a collection of pages that share a common navigation system, perhaps different from the website as a whole Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Breadcrumbs show user “This is where you are how you got here” Breadcrumbs Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Many sites have subsites Subsites Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Ad hoc links are very common (created for one specific purpose) Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall The most familiar example of database navigation: Google Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Building Context Helping the user to understand where he is and where is can go in the web site Navigation can be used to build context Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Building context for the user with navigation bars Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Graphical navigation bar Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Labels vs. Graphics Graphical representations are nice but slower to download Should always include label with graphic Be careful in selecting both labels and graphics Consider conventions Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Be careful with metaphors: what do these mean? Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Intended meanings. Moral: add words, too! Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall So add words! Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Some Standard Conventions Home: the main entry point of a Web site, generally containing the top-level links to the site Search: find related pages by supplying a word or a phrase About Us: information about the company that created the site Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Some Standard Conventions Shop: browse for merchandise Check Out: supply shipping and billing information, complete transaction Contact Us: initiate interactive dialog with customer representative – phone or email Consistency + Conventions Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Menus List of possible links Usually in drop-down form Provides many more options without clutter Disadvantages Not all options are visible User must act to activate a menu Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Menus pack in a lot of informationNote the dropdown from Software Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Site maps Graphical representation of the site Textual For a big site, must be selective Graphical A site map is no substitute for good navigation Trend away from site maps Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Graphical site map Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Frames Frame: an area of a browser window that stays visible as the user moves from page to page Simple way to provide global navigation: scrolls But hogs screen real estate: you can’t do anything else with that space May not print Hard (impossible?) to bookmark Used much less often than formerly See Jakob Nielsen, “Why Frames “Suck (Most of the Time)” Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Built-in browser services Take advantage of these History of pages visited Back & Forward Buttons Color coding of links Unvisited vs. Visited vs. Active Don’t mess with built in conventions e.g. Blue is an unvisited link. Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Page-level navigation aids Remember proximity, alignment, consistency: make the layout obvious Make size of text box appropriate to amount of data Show which fields are required with * or Required Use error messages Make button placement consistent: before or after its associated text Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Make error reports clear Explicitly state the problem Perhaps change the color of the offending box Show as many errors as possible on one page; don’t make user correct one error per attempt to send the data Don’t make user re-enter correct data Sounds obvious, huh? Then why are so many forms terrible? Sales are lost at this point, in big bad quantities Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall Summary Effective navigation is a combination of good content organization and good visual organization The main navigational system is hierarchical, with hyperlinks added You can learn from all the bad sites you’ve suffered with Chapter 6: Navigation Copyright © 2004 by Prentice Hall