Document 10926664
advertisement

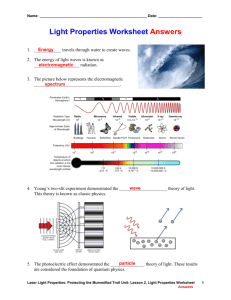
Waves from a source, which is receding from us, are perceived to have lower frequency and larger wavelength. λ ' = λ ⋅ (1 ± u / c) f ' = f ⋅ (1 ∓u / c) Red shift (shift toward larger wavelengths) in the spectra of distant galaxies is an evidence of expanding universe. Shock waves – sonic booms. Source moving with Vsource = Vsound ( Mach 1 - breaking the sound barrier ) Source moving with Vsource (Mach 1.4 - supersonic) > Vsound The shock waves are radiated by ANY object moving through a medium at a speed about the speed of waves in the medium, e.g. speed of sound. In other words, even object not emitting any waves at rest becomes a source of shock waves at a supersonic speed. Shock waves. Mach cone. When an object moves faster than the information about it can be propagated into the surrounding fluid, fluid near the disturbance cannot react or "get out of the way" before the disturbance arrives. In a shock wave the properties of the fluid change abruptly and almost instantaneously. Shock waves. Mach cone. A triangle in the cone: a side a = T⋅v – the travel distance of the wave within one period. v a θ b u The hypotenuse b = T⋅u – the travel distance of the moving object. a T⋅v v sin θ = = = <١ b T⋅u u θ − the Mach angle u v - Mach number The sharper the Mach angle, the higher the speed of the object Electromagnetic spectrum. fλ = c Frequency of visible light: 4.3×1014 to 7.5×1014 Hz fλ = c Why a single wave phenomenon is called so many names? EM waves of different frequencies/lengths originate from different sources and interact with matter essentially differently. US toxicoligists discover UV rays cause mutations in frogs...... 'Now don't forget to put on your UV sun-screen.’ Ear of bat, tail of newt DING!!.. Somehow it’s just not the same with a microwave You are right. Your dog did eat your homework. Electromagnetic Waves http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/java/emWave/emWave.html http://www.amanogawa.com/archive/PlaneWave/PlaneWave-2.html http://www.walter-fendt.de/ph14e/emwave.htm http://www.educypedia.be/electronics/javawaves.htm Electromagnetic Waves • The E and B fields are perpendicular to each other • Both fields are perpendicular to the direction of motion – Therefore, EM waves are transverse waves • Propagate with the speed of light, which does not depend on either frequency or amplitude; • Speed of light in vacuum – a fundamental constant, c = 3⋅108 m/s E B= c In every point in space, at each moment of time Polarization is a property of electromagnetic waves that specifies the direction of electric field. Why do we pick the electric field out of the two? Aren’t they on an equal footing? They are on an equal footing, but it is mostly the electric field, which interacts with matter – atoms, electrons, nuclei… EM waves from a TV tower are perfectly polarized – the Electric field has a very well defined direction, which stays always the same. In contrast, the light coming from the Sun or from a light bulb is unpolarized. What does it mean unpolarized? Does not the electric field have some direction? It certainly does at every instant. BUT this direction does not stay constant and changes very rapidly and randomly. So, after averaging over any reasonable time interval, you do not find any particular polarization! polarized unpolarized The frequency of light is about 5×1014 Hz, which means 5×1014 wave crests per second. If the polarization changes once every 500 crests it will still be 1012 times per second. Too fast for us to detect!