Document 10904956
advertisement
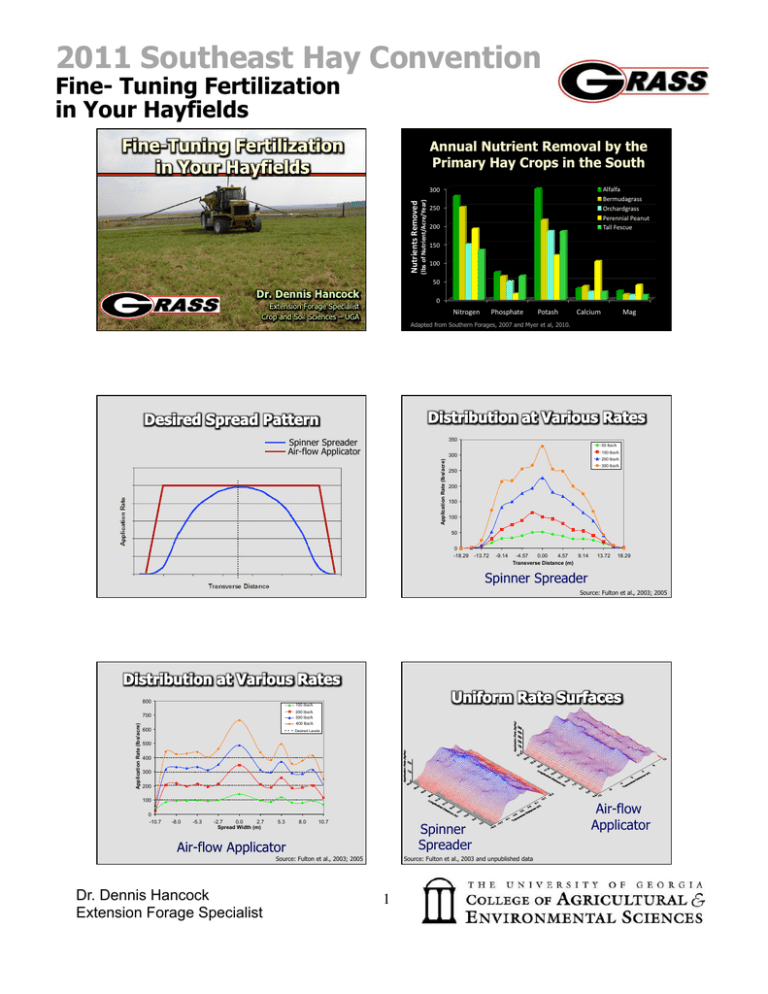
2011 Southeast Hay Convention Fine- Tuning Fertilization in Your Hayfields Annual Nutrient Removal by the Primary Hay Crops in the South Alfalfa Bermudagrass Orchardgrass Perennial Peanut Tall Fescue Nutrients Removed (lbs of Nutrient/Acre/Year) 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 Nitrogen Phosphate Potash Calcium Mag Adapted from Southern Forages, 2007 and Myer et al, 2010. 350 Spinner Spreader Air-flow Applicator 50 lbs/A 100 lbs/A Application Rate (lbs/acre) 300 200 lbs/A 300 lbs/A 250 200 150 100 50 0 -18.29 -13.72 -9.14 -4.57 0.00 4.57 9.14 Transverse Distance (m) 13.72 18.29 Spinner Spreader Source: Fulton et al., 2003; 2005 800 100 lbs/A 200 lbs/A 300 lbs/A 400 lbs/A Application Rate (lbs/acre) 700 600 Desired Levels 500 400 300 200 100 0 -10.7 -8.0 -5.3 -2.7 0.0 2.7 Spread Width (m) 5.3 8.0 10.7 Spinner Spreader Air-flow Applicator Source: Fulton et al., 2003; 2005 Dr. Dennis Hancock Extension Forage Specialist Source: Fulton et al., 2003 and unpublished data 1 Air-flow Applicator 2011 Southeast Hay Convention Fine- Tuning Fertilization in Your Hayfields Fertilization Trick Account for N Loss from Urea-based Products High to Low Source: Fulton et al., 2003 Low to High N Fertilizer Application Urea + H20 Urea urease + H20 Ammonia urease + Ammonium Urea + H20 Ammonia The Effectiveness of Some Alternative N Sources at Low, Medium, and High Fertilization Rates on Hybrid Bermudagrasses (Relative to Ammonium Nitrate). AN 34-0-0 urease Nitrogen Source + Nitrate Dr. Dennis Hancock Extension Forage Specialist 250-350 lbs 100% 100% 100% Amm. Sulfate 95-97% 95-105% 60-70% Anhyd. Ammonia UAN Solution 92-94% 93-95% 94-95% 80-85% 85-92% 92-95% Urea 79-82% 82-92% 88-93% Ammonium Nitrate Ammonium Fertilization Rates < 200 lbs* * Actual lbs of N per acre per year. Source: Burton and Jackson, 1962; Silveria et al., 2007. 2 > 400 lbs 2011 Southeast Hay Convention Fine- Tuning Fertilization in Your Hayfields Fertilization Strategies New N Fertilizer Products Alternative N Sources Take-home message: If you have to use a urea-based product, be careful about cutting your rate back too much. - They are relatively less effective at low rates. Introduction Ammonia Volatilization Trap Data 2008-2009 (avg. over two locations) Ammonia (NH4-­‐N) Vola=liza=on • Without AN, users of N face risky alternatives. NH3 volatilization loss • Urease is abundant in thatch & organic layers Urea NBPT High N use in hay. Polymer Coating • Enhanced Efficiency N Fertilizer Products may reduce volatilization loss Urease inhibition Encapsulate & release 100 80 60 40 20 0 maleic-itaconic co-polymer Urea Ammonia Volatilization Trap Data NSN ESN 2008-2009 (Calhoun) 2009 2008 20,000 2009 120 100 (lbs/acre) Forage Yield (ppm) Ammonia (NH4-­‐N) Vola=liza=on 140 ATU Bermudagrass Hay Yield 2008-2009 (avg. over two locations) 2008 2009 120 (ppm) Ammonium Nitrate 2008 140 80 60 40 15,000 10,000 5,000 20 0 0 AN4 U4 AN2 U2 ATU SU NSN ESN CON Dr. Dennis Hancock Extension Forage Specialist Urea 3 ATU NSN ESN 2011 Southeast Hay Convention Fine- Tuning Fertilization in Your Hayfields Bermudagrass Hay Yield Results: Yield Data 2010 (Equal splits, 4 applications, 300 lbs N/ac total) 2008-09: Forage Yield of ‘Russell’ Bermudagrass Source Equal Splits† 12,000 2008 2009 Eatonton Calhoun Eatonton Calhoun 19291 16033 16985 17302 18500 18218 10009 1552 11431 8163 10226 10730 8142 12106 2178 1059 17525 17019 16464 14955 15948 17604 10409 2460 (lbs/acre) 8908‡ 6430 8704 8490 7211 9641 2688 1204 Forage Yield 2 2 2 2 4 4 -­‐ 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 † Equal split applicaVons of N that occurred during the season. ‡ Eatonton 10,000 -­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐ (lbs of DM/acre) -­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐-­‐ ATU ESN NSN Urea Urea AN Check LSD0.05 Calhoun Total N applied = 300 lbs N/acre. Items that are in bold font are not significantly different from the highest value in the column. 0 AN ATU Urea Another Fertilization Trick Summary of EE N products Agrotain Treated Urea Split Your Potassium Applications! as compared to urea applied in the same way (averaged over 4 site-yrs): • Reduced ammonia volatilization by over 63%. • Produced 11% more forage yield. • Recovered 19% more of the applied N. • Did not substantially affect crude protein content. • Did not substantially affect the risk of nitrate toxicity. 40-50% in the Spring K is the Key to a Good Stand K is for Persistence Not Competitive Leafspot Diseases Poor Winterhardiness Grows Very Slow Poor Stress Tolerance The Stand is Gone! Dr. Dennis Hancock Extension Forage Specialist 50-60% in mid – late season 4 2011 Southeast Hay Convention Fine- Tuning Fertilization in Your Hayfields Aluminum Toxicity – Low Soil pH Alfalfa Low Soil pH control Effect of Gypsum (CaSO4) on Root Growth - Alfalfa treated Tissue Sampling and Troubleshooting Source: Dr. M.E. Sumner Tissue Sampling Troubleshooting 6 in. Dr. Dennis Hancock Extension Forage Specialist 5 2011 Southeast Hay Convention Fine- Tuning Fertilization in Your Hayfields Which is the better hay? Chlorophyll and Nutrient Which is the better hay? Foliar Fertilizer Applications Mg N • Even if the product is 100% efficient (likely isn’t) H • The most a plant can take up across via the leaves is the equivalent of 1-2 lbs/acre of the nutrient Works for many micro-nutrients (small quantities needed) Not feasible for macro-nutrients without multiple applications. (large quantities needed) C O www.georgiaforages.com Dr. Dennis Hancock Extension Forage Specialist 6