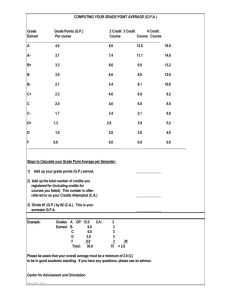
ÓBUDA UNIVERSITY Study and Examination Regulations For students enrolled from September 2012
advertisement

Organizational Rules of Óbuda University 3rd annex Student Requirement 1. Appendix ÓBUDA UNIVERSITY Study and Examination Regulations For students enrolled from September 2012 BUDAPEST, September 2012 1 Contents RECITALS .................................................................................................................................................. 5 The effect of the regulation 1. § .......................................................................................................... 5 Training system 2. § ............................................................................................................................. 5 The fundamentals of the credit system 3. § ........................................................................................ 6 The curriculum and the model curriculum 4. § ................................................................................... 7 Courses, course accreditation 5. § ...................................................................................................... 8 Learning languages, language exams 6. § ........................................................................................... 9 The committees and persons acting in study matters 7. § ............................................................... 10 Legal remedies of students 8. § ......................................................................................................... 11 The student’s legal relationship with the university 9. § .................................................................. 12 Interruption of studies 10. § ............................................................................................................. 13 Closure of studies 11. § ..................................................................................................................... 13 Forms of funding 12.§ ....................................................................................................................... 14 The schedule of reclassification 13. §................................................................................................ 15 Part II. Provisions on the studies ........................................................................................................... 16 Duration of studies 14. § .................................................................................................................. 16 Enrollment and registration obligations of the student 15. § ........................................................... 16 Advertising of and enrollment onto courses 16. § ............................................................................ 17 Information about the requirements 17. § ....................................................................................... 18 Subject requirements 18. § ............................................................................................................... 18 Special provisions for studies held in partnership with foreign institutions 19. § ............................ 19 Major, specialization and training modification requests within the university 21. § ...................... 20 Study in other HEI abroad 22. § ........................................................................................................ 20 Part III. Provisions related to knowledge checks .................................................................................. 21 Participation in courses 23. § ............................................................................................................ 21 Knowledge checks 24. § .................................................................................................................... 21 The scheme of exams, complex exams, examination period 25. § ................................................... 22 2 Successful exam repetition 26. § ....................................................................................................... 23 Academic achievement records, indicators 27. § ............................................................................. 23 Procedure of acceptance of substituting and optional courses, credit transfer 28. § ...................... 25 Concessional study load 29. § ........................................................................................................... 26 Exercising equity and guaranteeing equal opportunities 30. § ......................................................... 26 Part IV. Provisions on thesis, final exam and diplom ............................................................................ 27 The finals 31. § .................................................................................................................................. 27 Degree thesis, dissertation 32. § ....................................................................................................... 27 The finals 33. § .................................................................................................................................. 28 The finals committee 34. § ................................................................................................................ 29 The result of the final 35. § ............................................................................................................... 29 Retaking unsuccessful finals 36. § ..................................................................................................... 30 The degree certificate 37. § ............................................................................................................... 30 Degree with honor 38. § .................................................................................................................... 31 Part V. Miscellaneous provisions ........................................................................................................... 32 Special provisions for students with disabilities 39. § ....................................................................... 32 Internships 40. § ............................................................................................................................... 32 Cooperative trainings 41. § ............................................................................................................... 32 Helping disadvantaged students 42. § .............................................................................................. 33 Student card 43. § ............................................................................................................................. 33 Student identification number 44. § ................................................................................................. 33 NEPTUN code 45. § ............................................................................................................................ 33 Study Statue 46. § ............................................................................................................................. 33 Retake exam fees, special procedure charge, service fees 47. § ...................................................... 34 National Conference of Student’s Scholarly Circles, State Scholarship 48. § ................................... 34 Disciplinary and liability 49. § ........................................................................................................... 34 In matters not covered 50. § ............................................................................................................. 34 3 Rules of cohabitation 51. § ................................................................................................................ 34 Part VI. Closing provisions52. § ............................................................................................................. 35 4 RECITALS The Senate of the Óbuda University (henceforth: university) has issued the Study and Examination Regulations (henceforth: TVSZ) taking into consideration the relevant statutes, particularly law CCIV/2001 on national higher education, (henceforth: Nftv.), as well as government decree 79/2006. (IV. 5.), and with the agreement of the University Student’s Union (henceforth: EHÖK). PartI. Generalprovisions The effect of the regulation 1. § (1)The TVSZ covers the study and exam matters of all Hungarian students who began their studies after 1st September 2012 participating in full-time, part-time (correspondance) BSc and MSc studies, with full or partial state scholarship or fee-paying together with - if the law or any other international agreement does not provide otherwise – foreign citizen students participating in Hungarian programs. (2)Special provisions are applied for students participating in higher-level vocational training, postgraduate training, distance learning and doctoral programs. (3)The Regulations are binding for and apply to the entire university, its constituent parts, students and employees as well as other persons as set out herein. Training system 2§ (1)In the higher education institution (henceforth: HEI) the training is based on the training program. The syllabus as part of the training program must be compiled by the training and outcome requirements issued by the Secretary. The training program becomes effective by the Senate's acceptance. (2)The definition of curriculum policy and curriculum frame number of hours and the multi- faculty curricular modules require approval of the Senate. The individual faculty’s program based on the guidelines of the Senate – the Faculty Councils of the faculties and centers responsible for the trainings (henceforth: Faculty Council), the training will be determined in consultation with the Councils of the cooperating faculties and presented to the Senate. (3)In the first undergraduate (BSc or BA) training bachelor degree and qualifications can be achieved. This is the basic condition for starting the master studies. The training and outcome requirements determine the obtainable qualifications. At least a 6 months long internship must be organized during practice-demanding trainings (henceforth: internship). The fulfillment of the internship is the condition of the final examination. During the BSc trainings at least 180 credit points, if the training includes internship, at least 210 and maximum 240 credit points must be obtained. The training time is minimum 6, maximum 8 semesters. 5 (4)Master trainings result in a master degree. The master’s degree is the second level of higher education (henceforth: HE). The training and outcome requirements of masters training determine the obtainable qualifications. During the master trainings at least 60 and maximum 120 credit points can be obtained and this takes at least two and maximum four semesters. (5)In HE, trainings shall be organized as a full-time training, part-time training and as distance-learning. Full-time trainings consist of at least 300 training hours per semester. (6)Full-time trainings shall be organized according to the appropriate full-time work schedule which consists of five working days per week. (7)Part-time trainings shall be organized according to the appropriate part-time work schedule. Duration of the part-time trainings - except of professional trainings - is at least 30 and maximum 50% of the full-time trainings. (8)The work schedule of the evening programs is an educational form according to which lessons are scheduled during the training period on weekdays after 4 pm or at weekends. (9)The work schedule of the distance learning programs is an educational form according to which – if otherwise not agreed with the relevant students - lessons are contracted to maximum two working days per week or at weekends. Distance learning programs shall be organized according to the distance learning program methods. The fundamentals of the credit system 3. § (1)In order to meet the academic requirements during the studies - belonging to each course must be expressed by credits and evaluated by grades. The academic progress of the student depends on the amount of credits earned and on the quality of the given grade. (2)The value of the credit includes the participation on lessons, as well as the individual preparation (library, home). In order to obtain credits, students need to fulfill the minimum requirements of the course. The value of the credit is not related to the given grade. One credit point requires thirty hours of work of students. A semester work equals 30 credit points. (3)The university provides the students with a recommended curriculum. This can differ from the student’s individual curriculum. In order to receive a degree, the student can obtain the necessary credits in a shorter or longer period of time. (4)The value of credits per semester cannot diverge more than 3 credits out of the 30 credits. (5)Credits are only available in courses with grades on three or five point scale. Only integer credits are available for the courses. (6)Based on the Organizational and Operational Regulations of the University, the students are provided – for at least for five percent of the required credit amount – to have optional courses or instead to participate in voluntary activities. Students are entitled at least twenty 6 percent of all credits in excess of credits worth of courses to choose from. Ensure that the student's individual learning order - special manufacturing cost and without paying a service fee - ten percent of the total credits required credits worth of items able to take over. The student's individual learning order must be ensured to have maximum ten percent of credits in excess of the total credits without paying a service fee. The student can take subjects of his/her own studies in another program of the HEI or as a guest student. (7)Credits assigned to the part-time trainings equal with the credits assigned to the full-time one. (8)The number of average individual learning hours must not exceed three times the number of contact hours in full-time, seven times in part-time and twelve times in correspondence training. (9)The pre-conditions and requirements of each subject must be specified in the curriculum. These requirements could be defined as simultaneous subject admissions not necessarily previous ones. One subject can have maximum three other subjects or a module - connecting by content - consisting of subjects maximum 15 total credits as preliminary requirements. (10)Students do not need to fulfill the defined requirements if they already did and they are able to prove so. To the recognition of the work experience requirements, the institution shall have a written, oral or practical prove of the acquired knowledge on the condition of which, the student – in order to obtain the pre-degree certificate - is obliged to fulfill at least 35% of the training’s credits in the institution. (11)Students can register for lectures, seminars, laboratory courses and exam courses through the Neptun study system after fulfilling the preliminary requirements. (12)All semesters after the enrollment counts as active, if the student registered for at least one course or in case of part-time training abroad makes a declaration. The semester is passive when the student does not register for any courses or requests the suspension of his/her studies (15.§) or does not make any statement. The curriculum and the model curriculum 4. § (1) The specific objectives of the programs, the detailed requirements (training elements, especially the subjects, their curriculum, and formal features) determined by the curriculum, based on the training and outcome requirements. In the curriculum teaching hours and credits must be assigned to the subjects (credit allocation). (2) There are compulsory, compulsory elective and optional courses in the curriculum. a)The completion of compulsory courses is a condition of obtaining the qualification. These courses are part of the professional training, partially linked to the general intellectual function. b)The curriculum contains a group of compulsory elective courses, which students can choose from (faculty specializations, specific professional courses and degree thesis). 7 c)Optional courses are courses not defined specially by the curriculum. The University does not limit the student’s choices regarding the optional courses. At least 5% of the credits can be obtained from the optional courses. (3)Criteria requirements are mandatory requirements that do not have credit points. This include internship (usually 6 weeks), participation in PE classes, (for 2 semesters with 0+2 hours per week). (4)Modules are units of a curriculum which form the curriculum of a degree program and are composed of subjects which cover knowledge which is thematically related to the training purpose of the degree program, or which include knowledge common to more than one degree program, modules and specializations can build upon or be substituted for each other. (5)Students have the right to choose between the simultaneously announced specialized modules, but the number of students applying to each specialized module may be limited. In order to announce the specialized modules, the dean of the faculty may define the minimum number of the students applying. (6)The model curriculum includes a periodic breakdown of all compulsory, elective subjects and optional subjects, number of teaching hours per week or per semester (lectures, seminars, and laboratory practice), number of credit points, type of the checks (approval, mid-term or exam mark, the semesters of advertising the subject (fall and/or spring), pre-conditions of the subjects and the subjects of the finals. (8) The number of recommended classes per week in the model curriculum is twenty five (excluding the language and PE classes) (9) Within the examination period, the maximum number of exams is five, excluding the exams of optional courses. Courses, course accreditation 5. § (1) The requirements of each course are defined in the course programs. (2) The elements of the curriculum documentation: a)Curriculum data sheet: training objectives, number of classes, language requirements, number of credits, qualifications, specialization, final exam, b)Curriculum tables: name of the course, Neptun code, number of classes, credit value, requirements, pre-requirements, c)Subject description: requirements, lecturer, code, method of evaluation, course description (10 lines) d)Detailed course programme by semester, which is prepared by the instructor, approved by the director of the institution (3) The content of the detailed course program by semester: a)Topics in weekly breakdown (fourteen weeks) b)References (written material and other technical devices) c)The course requirements must be specified (time schedule): participation requirements, mid-semester study checks (written exams, reports) requirements, number, date conditions of signature and mid-term marks the method of determining the marks, absences, as well as the conditions, numbers, methods and dates of the retake exams the system of exams and reports, and its methods (oral, written) offered grades and its conditions, 8 retake options in the examination period (within 10 working days) (4) Access to the elements of curriculum documentation: curriculum data sheets, curriculum tables and subject descriptions must be displayed on the faculty’s website. The program of courses for one semester must be displayed on the website of the institute until the registration date. On the first class the schedule must be specified, changes are possible only with the agreement of students. (5) The programs of each course are approved by the faculties in charge. Learning languages, language exams 6. § (1) The aim of the university’s language courses – as prescribed in the training requirements in order to achieve a degree– is to develop the language skills and to successful pass the language exam. (2) English, German, Spanish, Italian, French, Portuguese and Russian language exams are accepted as a condition of receiving the diploma. In addition to the above mentioned languages, for the student’s request – by individual decision - the rector of the university shall authorize the issue of the degree if the student has a complex C1 exam of any existing language, in addition to a complex B2 English language exam. The request has to be submitted in written form to the rector’s office, including the official letter of the dean’s opinion and the proper justification. (3) In case of foreign students of the university, the graduation certificate - issued in one of the above mention languages – is accepted as the condition for receiving the diploma. (4) Conditions for issuing the final certificate: a) Full time students have to take criteria courses in English or German language advertised by the university and have to meet the previously set requirements. b) If the student had another criteria course than English language, then he/she is obliged to demonstrate his/her basic knowledge of English. As long as the student does not fulfill this obligation – as the absence of proven language knowledge – the final certificate can not be issued and the student status is suspended. (1)The condition of issuing the final certificate: In order to graduate, B2- complex language exam is required. Studying on the following faculties - Business and Management, Sales and Marketing BA and Business Development MA - terminological, B2-complex or C1-complex language exam is required. Students participating in Enterprise Development master program need to have either a complex B2 English language exam, a complex B2 exam of the languages listed in (2) or a complex C1 level exam. (2)There are three options when selecting the criteria courses: a) Professional subjects in the curriculum announced by the faculty (if they were not fulfilled earlier in Hungarian language), students can take the subject in English or German language and fulfill its initial requirements. In this case, the subject is listed with its initial credit value. Students are allowed to take any subject of the curriculum taught in foreign language, unless he/she already took the given subject earlier in Hungarian. b) Students can choose a course in English or German language announced by the faculty if he/she has already fulfilled its requirements in Hungarian language earlier. The knowledge of students is being evaluated by mid-semester marks, and the duration of the course is one semester long, two-three lessons/week. In this case, the course count as optional course and has two credit points. 9 c) Students can choose a professional course in English or German language announced by the faculty (or another faculty) which is not included in the curriculum. The knowledge of students is being evaluated by mid-semester marks, and the duration of the course is one semester long, two-three lessons/week. In this case the course counts as optional course and has two credit points. (3)Faculties announce a semi-annual, 4 hour per week professional language lesson which aims to prepare students to successfully pass the criteria requirements of the subject. The content of the course is defined by the faculty. The professional language subject may be taken as optional subject that worths two credit points and ends with a mid-semester mark. (4) The faculties offer the following: a) Intermediate (B2) complex exam preparation course, 4 hours per week for one semester for students who do not have this type of language exam yet. Students can register for this course as optional course with a credit value of two (evaluated with grade) b) German language course can be advertised as well, with the condition that students applying must pass the criteria course in German language. c) English A1 exam preparation course for those who fulfilled the criteria subject in German language (60 hours, one semester long). This subject may be taken as optional subject (two credit points, ends with a mid-semester grade). d) Business Management and Sales and Marketing faculties also provide professional language training (credit values and requirements included in the curriculum) (5)In order to fulfill the language requirements, the university offers several languages on different levels for reasonable prices. (6)If issuing a certificate or degree is on the condition of passing a language exam. This last provision is applicable to those who schedule their final exam latest in year 2015/16. (7)The detailed regulations of the language trainings (criteria courses, registration conditions, order of placement exams etc.) are included in the Study Statute. The committees and persons acting in study matters 7. § (1) The Faculty Credit Transfer Committee (henceforth KKB) takes academic decisions about the acceptance of subjects. (2) The Faculty Study Committee (henceforth KTB) is responsible for the study and exam matters of students. (3) All matters usually considered belonging to the sphere of study and exam matters fall under the jurisdiction of the KTB, in particular: a) making decisions regarding special curriculum (29.§), b) after successfully completing the first semester the closure of the student status, c) granting guest student status, d) transfers between faculties, programmes and institutions, e) specialization within the university. (4) Any student or lecturer can apply to the KTB to take measures via the head of department if he/she thinks that some study matter has not been handled according to the TVSZ. president: 1 lecturer members: 2-4 lecturer (depending on the number and characteristics of the faculty) non-voting member: 1 student delegated by the KHÖK KTB consists of: president: 1 lecturer 10 members: 2 lecturer 3 students The president and lecturer members if the KTB and KKB are elected for a 4 year period, student members are delegated by the KHÖK every year. (6) The Study Statute contains the work order of the committee. KTB may delegate its responsibilities – defined in written form – to its president, to the educational vice dean or to the director of the institute. (7) Students have the right to appeal for the first instance decision according to 8.§. (8) Against the academic requirements and performance evaluation, appeal can be made according to 8.§ (3). (9) Previous studies and work experience can be recognized as academic requirement by the Credit Transfer Committee. As for the work experience, the given credits can not exceed the 30 points. Legal remedies of students 8. § (1)The university’s student related decisions are defined in law, in governmental regulations, in organizational and operational rules and in special cases – for student’s requests – in written form. The university’s student related decisions are legally binding, if the student does not submit remedy request within the period of appeal. (2)Violation of the student’s rights: a) students may request legal assistance from HÖK, b) may request educational mediational assistance , c) may place an appeal which shall be judged by the higher educational institution according to the National Higher Educational Act d) students can request the intervention of educational ombudsman if he/she already used all legal remedies provided by law - with the exception of litigation. (3)Students are entitled to file legal remedies against the university’s decisions or in case the university fails to make a decision (henceforth: decision) – from the announcement, or in lack of it within 15 days from coming into notice – unless the decision concerns study evaluation matters. Legal procedure can be started against decisions concerning study evaluation matters, if the decision is not based on the requirements accepted by the HEI, the decision is contrary to the HEI’s operational and organizational rules or the provisions on organizing exams were violated. (4)Students can appeal against the decision made by the higher educational institution when it was announced or in lack of it, within 15 days from coming into notice. The appeal must be submitted to the rector in written form. The rector shall consider the request in case of hurting personal interests. (5) The mandatory content of the request: a) the exact indication of the decision complained, b) the exact indication of the legislation or provisions about the legal student relationship, which was violated according to the applicant c) the clear indication to what the grievance relates to, d) all other evidence or documents supporting the case. (6)The incomplete or late submissions shall be rejected without indicating the reason of refusal. (7)The person in charge for decision making can not be: a) by whom the contested decision was made or failed to make the decision 11 b) close relative of the person mentioned in point a), c) from whom objective decision making can not be expected. (8)The following decisions shall be made by the higher educational institution regarding the appeal: to reject the appeal, to order the decision maker to make the omitted decision, to change the decision, to annul the decision and to request a new procedure. (9)The General Rules and Provisions of Administrative Procedures Act shall me applied in the following matters: to clarify the facts, to calculate the deadlines, to issue a certification, to the form, content and announcement of a decision, to request, correct, replace, amend or withdraw a decision. (10)The appellate decision is final and legally binding, unless the student has a judicial review. (11)The student may appeal against the decision within 30 days after notification by referring to the violation of the student status. (12)During the juridical process the rules of administrative litigation of the Code of Civil Procedure shall be applied. The court may change the decision. The court will assess the matter out of turn. (13)According to the above mentioned provisions, the laws and university regulations concerning the student’s rights and obligations must be used at the student’s legal relationship. a) b) c) d) The student’s legal relationship with the university 9. § (1)A student’s legal relationship with the university begins when he/she enrolls at the university. Prior the enrollment; students with Hungarian state (partial) scholarship have to sign a student scholarship contract. Students financing their own study, have to sign a student training contract. (2)Successfully admitted candidates can start legal relationship with the university in the same semester when he/she was admitted. (3)During an existing student status, the student does not need to enroll in each new semester. Students – as defined in the regulation of the university – when starting a new semester must sign up for the training period. Students who fail to fulfill their financial obligations can not sign up for the new semester. (4)The student a) are allowed to have a guest relationship with other institutions as part of their studies b) can request to be transferred within the same or to another institution faculty within the same training cycle (5)The higher education institution may accept students for partial studies – with whom the institution does not have legal relationship but who already have college degree – for any training or module advertised by the university without any additional recruitment process as fee-paying students. The institution shall issue a certificate proving the academic performance. The completed course or module shall be accepted as part of the higher educational performance according to the rules of credit transfer. 12 (6)The conditions of fulfillments of the above mentioned requests – in paragraph 4 and 5 – are set by the university. (7)According to the laws and regulation of the institution, students are entitled to receive full, accurate, accessible information when starting and continuing their studies at the university in order to set their curriculum, to benefit from educational opportunities, its capacity, regarding his/her status, personal endowments and disability. (8)The student is obliged to: a) follow the regulations of the institution, b) respect the traditions of the institution. Interruption of studies 10. § (1)The student’s studies may be interrupted on his/her request. The duration of the interruption of the student status shall not be longer than two semesters. Students have the right to interrupt their studies many times. For the interruption of the first semester of the study – of the student’s request – the Study Committee is responsible. (2)The number of passive semester shall not exceed half of the training period (in half years, rounded up). In special cases, two additional passive semesters can be granted. (3)Interruption periods taking place due to unexpected, serious health related issues, accidents and/or maternal, parental leaves are likewise exempt from this clause. (4)After starting an active semester, within one month, the student can change his/her student status for passive. (5)If the student is prohibited from his/her studies as a disciplinary measure, his/her student status is considered as interrupted. (6)In order to continue their studies, students can sign up for an active semester and continue their studies according to the curriculum. Closure of studies 11. § (1)Closure of the studies may take place in the following ways: a) if the student continues his/her studies in a different institution, b) if the student asks for the closure of his/her legal relationship with the institution, c) if the student can not continue his/her studies supported with the Hungarian (partial) scholarship and wishes to finance his/her studies by him/herself, d) successful completion of the final state examination, e) if the student status is terminated by the rector - due to arrears – after unsuccessful appeals and taking to consideration the student’s social situation, f) exclusion disciplinary (when the decision becomes final), g) if the statutory condition of the establishment of the legal student status no longer exists, the decision comes into force on the day of termination (2)In accordance with subsection 1, letter d), the student status is not terminated if the student is accepted for a master program the following semester (3)The university is allowed to terminate the student’s legal relationship of those who: a) does not fulfill his/her obligations as defined in the study and examination regulations and in the curriculum b) for the third time in a row does not sign up for an active semester, c) after the suspension of the student status he/she does not start his/her studies, 13 d) the number of credit points obtained after 4 enrolled semester does not exceed the 55 points in case of full-time, and 40 in case of part-time trainings. (The maximum value of the credits of the optional courses listed in the curriculum shall be included), if the student was informed in written from about his/her obligations must be fulfilled until a certain deadline and was informed about the legal consequences. (4)The university is entitled to terminate the student’s legal status with a unilateral declaration, if the number of the unsuccessful retake exams is five. The study unit is a subject or curriculum unit completed in one semester assigned with credit points. (5)A course can be retaken maximum six times. (6)The available training time for BA trainings is twelve, for the MA trainings 7 semesters. Students, who are not able to complete their studies and obtain the final certificate within this period of time, must be dismissed from the university. (7)Those students, whose student status is ceased, must be removed from the student list. Books, sport equipments and other liabilities borrowed from the university must be returned. (8)In case, the student was dismissed and then re-accepted to the same faculty again, according to paragraph 11/3 the following points must be applied: a) semesters completed before the dismissal must be taken into consideration, b) starting from the new enrollment, credit points shall be calculated without the accredited credit points Forms of funding 12§ (1)The form of funding the studies could be the following: a) Hungarian state scholarship, b) Hungarian state (partial) scholarship, c) Fee-paying student. (2)Students participating on any training can be granted with the Hungarian (partial) state scholarship, regardless of its form (full-time. part-time etc) (3)One student during his/her training period - including both BA and MA programs - can apply for the maximum period of 12 semesters for the Hungarian (partial) scholarship. The maximum period modifies to 14 semesters, if the student is participating in an undivided training program (there is no separate BA and MA). (4)In order to receive the given degree, the period of support can not exceed the total training period with more than two and a half years. When calculating the given programme’s period of support, the previously used period of support shall be taken into account as well. If the student does not receive the degree within this certain period, he/she can finance his/her studies him/herself, even though – as mentioned in point 3).- he/she did not exceed the period of support and if the university has free capacity. (5)Disabled students are provided with extra four and a half years period of support by the university. (6)Each semester the student has signed up for counts as an availed period of support. (7)When calculating the period of support, the following shall not be taken into account: a) if the student fails to complete the semester because of illness, childbirth or any other unexpected reasons, b) semesters completed during the period of support, if the higher educational institution is ceased and the student could not complete his/her studies neither could he/she continue his/her studies in another higher educational institution, 14 c) the semester that was not acknowledged by the ceased higher educational institution – in case the student continues his/her studies in another higher educational institution (8)If the above mentioned reasons occur – defined in subsection 7/a – they must be reported immediately in written form to the Study Commission. (9) Having a high education degree or other professional qualification, does not mean, that students can not apply for the Hungarian (partial) scholarship. Participating in Hungarian (partial) scholarship training parallel (simultaneously) with a similar training decreases the number of supported semesters. (10)If the student has used already the available support time, he/she can only continue his/her studies financing him/herself. In order to finish a particular course, the students have – regardless of the form of funding of the training – twelve semesters on the BA and seven semesters on the MA trainings available. The available training time The schedule of reclassification 13§ (1)In the academic year the university is obliged to reclassify the student’s financial status - from Hungarian (partial) scholarship to self- financed – of those who in the last two active semesters did not fulfill at least 50 % of the prescribed credit amount or the average amount of credits prescribed by the faculties. When exercising equity, the university can waive this provision. (2)If the legal relationship of students funded by Hungarian government (partial) scholarship is terminated before graduating, or he/she decides to continue paying the studies by him/herself, the university approves this request and reclassifies the student’s financial status as self-paying. The decision of reclassification is based on the student’s academic performance and is made by the university. (3)Having two active semesters, self-paying students can apply each semester for reclassification. In the semester of reclassification, students reclassified as fee-paying from state-financed are not allowed to apply. Applications will be evaluated with the involvement of HÖK. Completed credits and academic average performance should be considered by the evaluation of applications. (4)The decision of reclassification must be made after the end of the training period, but latest 30 days before the new semester starts. 15 PartII. Provisionsonthestudies Duration of studies 14. § (1)One academic year consists of two training periods (two semesters). The training period includes the study and examination periods. The evaluation of the student’s work is based on his/her performance during the study and examination periods. (2)Internships can be organized during the summer period. The study period is (3) The registration week takes place during the first week of the study period. During this time students have to finalize their application for the courses according to the 16th §. There are no classes during the registration week; however preparational sessions for the seminars can be organized. (4) In the study period, students are participating in seminars and lectures. Students can register for the exams only if all the conditions set in the TVSZ are met. (5) The exam period is the period in which the fulfillment of the academic term requirements are only possible in special cases according to the Regulations of Grants and Fees (henceforth: TTSZ) and students can be charged with fees. (6) The types of the classes are as follows: lectures, seminars and laboratory classes. The duration of one class is 45 minutes long and there is a 10 minutes break between each - 5 minutes during the evening classes or in aggregate form. (7) The next academic year’s schedule – training, examination period and the dates of the final exam – are defined by the rector with the cooperation of EHÖK not latest then the end of the previous semester. (8) The rector of the university can grant 4 days per semester in addition to the statutory public holidays. Enrollment and registration obligations of the student 15. § (1) When the student status is established, the university issues a basic data sheet for each student. (2) The Registry provides the students with the sufficient informational plan in order to start their studies. (3) The index book is an official document containing the academic obligations in order to receive the final certificate. The personal data appearing in the student informational system is printed and attached to the index book. (4) During the existence of the student status, no new enrollment is required. Each student is obliged to declare whether he/she is going to continue his/her studies or suspend his/her legal relationship with the university by the end of the registration week each semester.Students having unfulfilled payment obligations can not register. (5) According to the Rules and Procedures of Study, the enrollment procedure is complete, if the student fulfilled the registration requirements – including the registration for the chosen courses - in the student information system. (6) If the student fails to oblige his/her enrollment requirements, his/her status is automatically considered as passive, and - as a consequence is obliged to pay a certain fee defined in the TTSZ. 16 (7) A student may apply to withdraw his/her declaration about continuing his/her studies in a particularly justified case up prior one month of the term and to declare the semester passive. If the student does not suspend his/her studies, the semester is considered as active. (8) Students are obliged to announce any changes to their personal data appearing in the student information system without fail. There is no legal remedy at the Óbuda University against any losses incurred by the legligence of students. One shall not receive the scholarship and tax certificates shall not be issued as long as the student specifies his/her tax identification number, social security number and bank account number. Advertising of and enrollment onto courses 16. § (1) Courses of subjects ending in a grade can be announced and launched with lesson being held. Courses of subjects ending in an exam can be announced and launched without lessons being held. In such cases the condition of enrolment in the subject is a signiture confirming the fulfilment of mid-semester requirements in the student’s information system. (2) The faculty shall announce courses of subjects for the semester two weeks prior the end of the current semester (including the lecturers of the course, the scheduled dates of the course, the minimum number of students necessary for the course to start and the maximum number that can enrol on it). In case of possible over-application for the course, the criteria for ranking (if it is not the order of application), which may include the completion of the specialisation requirements. (3) The number of students that can be accepted on a given course may be limited by the faculty responsible for the subject based on the capacity of the lecturer, the limited number of teaching aids available and other objective reasons. (4) Students have the right (taking the regulations and of the model curriculum into account) to choose from the lecturers, the courses, the modules and the specialization announced at the same time. (5) In case, the student wishes to register for the given subject’s course in another progam or training form, his/her application must be authorized by the relevant institution according to § 16, section 3. If the choosen course is fee-paying, a certain fee should be paid according to the TTSZ. (6) If the student can not fulfill the credit amount of the given course in one semester, he/she can retake the subject in another semester as well. If the mid-term requirements are approved by the signiture of the institute, students are allowed to register straight away to the exam. If the subject is announced with lessons being held, students can request a new signiture. If the program of course is modified, the institution has to inform the students that the previously completed mid-term requirements can not be accepted. In this case, the acquired signiture is invalid and the mid-term requirements must be fulfilled again. (7) Students participating in trainings granted by Hungarian state (partial) scholarship are obliged to pay an extra fee – defined in the second annex of TTSZ - for applying for a course for the third time. (8) Compulsory subjects ending with a mid-term grade shall be announced with a sufficient number of courses, while in any other semesters – with exam possibility. Compulsory subjects ending with a mid-term grade are announced only in the current semester. (9) The given faculty’s dean is responsible for announcing the subjects and courses. 17 (10) Students participating in programs supported with Hungarian (partial) scholarship, taking subjects exceeding the 10% of the total credit amount (retaking a course does not count), for these subject a certain fee has to be paid, proportional to the amount of the given credit. (11) In fee-paying trainings, the actual fee is calculated as the following: on the top of the basic fee, an extra fee is charged in proportion of the credits taken – according to the TTSZ. (12) During the first two weeks of the term, in some special cases (with appropriate justification), students can request the dean’s approval in order to register and unregister to courses (the fees are set in the second annex of the TTSZ). Information about the requirements 17. § (1) The dean of the given faculty has to make sure ensure, that students enroling to the university receive the appropriate information regarding their obligations, rights and the conditions of obtaining the diplom, as well as the first semester’s schedule and requirements. (2) In order to inform the students, the university and the faculties have to provide certain guidlines, such as Organizational and Operational Rules, Study and Examination Regulations, as well as other policies, objectives, requirements, curriculum requirements, program of the courses and summaries. These should be available for the students in the university libraries, at HÖK and on the website of the university. (3) The institutional information – that was defined with the cooperation of the faculties – must contain the following: the different course, the curriculum, the rules and regulations concerning credits and credit transfers as well as the pre-study orders. (4) Prior each term, students must be informed about the following: a)schedule of the academic year, b) details of institutional student advisors, c) regulations for applying for special curriculum d) description of educational services and tools (libraries, studios, laboratories, other specific services and tools), e) introduction of institutions and subjects, f) list of acquired qualifications, g) model curriculum, h) list of courses (id, level of education, pre-conditions, lecturers, duration, teaching/learning methods, evaluation method, hours and credits) i) information regarding the acceptance of subjects advertised on other faculties j) credit equivalence, agreement between institutions. Subject requirements 18. § (1) Subject programme and subject requirements are prepared for each subjects announced by the university and approved by the faculties. (2) The subject requirements contain the following: a) requirements for participating in the lessons, b) the number, topic and approximate date of mid-term checks, c) examination/signatures conditions, d) all information connected to the evaluation of the completion of the subject, including the way the grades awarded are determined, e) list of required and recommended study materials, 18 f) credits assigned to subjects, g) the ways of making up for absences, as well as the opportunities available for students to repeat the exams and improve their marks, h) the system of exams and reports (oral/written etc.), i) conditions of preliminary exams. (3) The subject programme and subject requirements should be made available on the internet in the language of the academic programme from the earliest possible date on which the subjects can be enrolled for. The students should also be told about the subject requirements orally in the first lesson. This is carried out by the person responsible for the subject and the lecturer of the course. (4) The KHÖK can raise an objection against the subject requirements at the relevant director of the faculty within 8 days after the announcement. (5) During the semester the subject requirements can not be changed without the agreement of the students concerned. Special provisions for studies held in partnership with foreign institutions 19. § (1) The student a) in order to participate in part-time programs, he/she can have a legal guest relationship with other institutions , b) can request his/her acceptance to the same cycle of training of education. (2) The student can have a legal guest relationship with other institutions and receive credits for the courses completed. (3) Students supported with the Hungarian (partial) scholarship: a) Have the following services available: a. To the fulfillment of the educational and academical requirements set in the training program; the lectures, seminars, tutorials, practical sessions, field practices that are required in order to obtain the diploma or pre-degree certificate. Report, exams, unsuccessful reports or exams have to be retaken for the first time, passing final exam, furthermore to obtain a degree during the legal student relationship according to the 53. §, second paragraph. b. special college trainings, c. all the facilities of the institution, such as library, laboratory, computer, sport and leisure facilities and the free usage of related assets, d. protective clothing, personal protective equipments, hygienic supplies when participating in practical trainings, e. student consultancy, f. issuing all training and Phd training related documents. b) Trainings supported with the Hungarian (partial) scholarship – unless otherwise specified – the institution can not request administrative service fee. (4) Students from other institutions need to have a written permission issued by the dean of the faculty in order to attend a given subject/course. This permission is sent both to the head of the institution and to the registrars department. (5) If a student from the university wishes to register for a subject/course in another institution, he/she needs to have the permission of both institution’s Academic Committee. The Academic Committee – upon the proposal of the head of faculty – forms a decision based on the opinion of the Credit Transfer Committee regarding the acceptance. Such exams are considered as if they were taken in the home institution. Courses covered in other institutions are entered into the electronic registration system by the student affairs clerk as “accepted courses”. 19 Specialized further trainings 20. § (1) As a second specialisation, students can specialize in any of the announced majors, if they meet the criteria conditions. The Study Committee is responsible for the admission procedure of the second specialisation. Major, specialization and training modification requests within the university 21. § (1)Those students, who completed subjects for at least 30 credits, can request for changing their specialisation. When making the decison, the given faculty’s admission limit must be taken into account. When submitting the application, students are obliged to pay the fee of the process – as defined in the TTSZ. (2) Changing the major is only possible, when the other specialisation is related to the current one. (3) The final decision rgarding the change of specialisation is made by the head of the Academic Committee. When submitting the request, students are obliged to pay the fee of the process as defined in the TTSZ. (4) Regarding the full-time, part-time and distance learning request, the Academic Committee is in charge. When submitting the application, students are obliged to pay fee of the process – as specified in the TTSZ. (5) The higher educational institution – considering the capacity – shall establish legal student relationship as a fee-paying training based on the training program – only once and maximum for two semesters with students who do not have a legal relationship with the university yet. (6) Considering this legal relationship of the student, he/she is not eligible for participating in further qualifications or vocational trainigs, requesting his/her acceptance, have simultaneous or guest student status, suspend student status, apply for state-financed trainings or apply for support period. (7) The duration of the legal relationship that was established in order to gain partial knowledge shall be taken into account when calculating the stautory allowance or other allowances. Study in other HEI abroad 22. § (1) Studies in other HEI abroad are regulated as part of the annex of the Study and Examination Regulations. (2) When issuing the permission for studying in other HEI abroad, initiated by the university, the list of acceptable courses must be defined. The Credit Committee decides on the acceptance of individually initiated studies in other HEI abroad. (3) Students participating in part-time trainings abroad can request a special study system and continue his/her studies that way. (4) In the given semester, students participating in part-time trainings abroad are obliged – prior starting the semester – to have the list of the abroad chosen subjects accepted if he/she wishes to have an active semester (ERASMUS status and scholarship is received only by students with an active student status). 20 PartIII. Provisionsrelatedtoknowledgechecks Participation in courses 23. § (1) Participation in seminars, laboratory sessions and PE classes is mandatory. For full-time students, the participation in lectures, for correspondence students the participation in consultation sessions is mandatory. Participating in lectures is recommended, but it is defined in more details in the requirements system of the given course. (2) The form of the presence control and the absence certificate methods are described in the Academic Board. (3) If the student’s absences exceed 30% of the total number of lessons per semester, the signature and grade is denied from the student. (4) Absence is not an exemption from complying the subject’s requirements. In case of assence, the student is obliged to meet the criteria set in the course’s requirements. Knowledge checks 24. § (1) The final evaluation of the subject could be either a grade: a) from scale 1 to 5: excellent (5), good (4), satisfactory (3), pass (2), fail (1), b) or one of the following terms: excellent (5), completed (3), not completed (1). (2) When evaluating their performance, students can not be distinguished by their financial status – whether they are self-financing their studies or are supported by Hungarian state scholarship. (3) The method of the checks could be the following: a) oral or written mid-term tests, evaluation of home assignments b) pre-examination, c) exam during the examination period, d) comprehensive exam e) final exam. (4) End-semester evaluations: a) mid-semester grade (with mark „é”), in case of both theoretical and practical courses, based on mid-term grade, b) exam grade (with mark „v”) – this mark can be based on: only on the performance on the exam or both on the performance on the exam and on the mid-term tests. In the latter case, minimum 50% can be based on the exam and maximum 50% can be based on the mid-term checks. c) acceptance (with mark „e”) – PE classes are evaluated in three scale terms. (5) If the student did not fulfilled the requirements of the mid-term grade (ie. did not take or pass the mid-term test etc.), then he/she must be provided with an alternative date to retake it. If the student still can not obtain a mid-term grade – and if in the subject requirements there is a possibility – then, within the first 10 days of the examination period, students can attempt to obtain the mid-term grade after paying the special procedure charge defined in the TTSZ. (6) For subjects ending in an exam the completion of mid-semester requirements will result in the student is either being granted a signature or the expression „signature denied”. Students are only allowed to take an exam if they have obtained the appropriate signature. The prescribed condition of receiving a signature is to score at least 50% on the mid-term checks or to have a 2.00 average. If the student does not fulfill one of the prescribed requirements 21 which is the condition for exam registration, then this requirement can be fulfilled within the first 10 days of the examination period – only once and under the condition of paying the special procedure charge defined in the TTSZ. (7) The final exam (with mark „s”) at least 12 credit-worth (integrative) knowledge check in front of a committee, to which students can register earliest after completing the last exam of the comprehensive exam subjects and receiving the mid-term grade. (8) An offered grade can be given in a subject ending in an exam based on excellent academic achievement - on conditions set in the subject requirements - which the student is not obliged to accept. The scheme of exams, complex exams, examination period 25. § (1) Exams can be taken on certain exam dates. The exam dates and the number of students who can attend the exam are determined by the lecturers and the student’s representatives. The number of advertised exam dates must be at least 3, evenly distributed in the exam period, so students can retake the unsuccessful exams within the exam period. The number of examination places shall cover 1.5 times the number of the students. The advertised exam dates can not be cancelled, except with the agreement of the students. (2) In the last two weeks of the exam period, departments can announce exam dates for those students are allowed to register who already failed the given exam. (3) The departments make the suggested exam dates available at least 3 weeks prior the beginning of the exam period, so that the KHÖK can exercise its power. (4) Students can prove their identity with any document suitable for the purpose – identity card, passport, driving license. The exam mark has to be recorded in the Neptun study system latest the third day after the exam. (5) Oral examinations are opened to the public, the dean may limits this and students may also request that the examinations be closed to the public. (6) The examiner and the head of the examination board is responsible for the calm, undisturbed atmosphere of the exam. The examinee should have a minimum of 15 minutes to prepare before the oral part of the exams. (7) Every student is entitled to repeat the exam maximum 5 times, but in one particular exam period each exam can be retaken twice. (8) It is the inalienable right of students to re-sit an exam, but they have to pay an extra charge specified in TVSZ. (9) Students can take or re-sit the repeat exam in front of another examiner or committee based on the decision of the head of the department about a student’s adequately justified request filed to the head of the department. This right is granted to the student even if he/she is retaking the exam in the new training period. (10) It is the duty of the student to turn up at an exam he/she has enrolled for in the student information system. Should he/she fail to do so, it is not possible to asses his/her knowledge. However, as specified in the TTSZ, he/she is obliged to pay the extra charge of the exam if he/she can not prove that his/her absence was justifiable. (11) The lecturer of the subject may announce a pre-exam in the week immediately preceding the beginning of the exam period. The conditions of applying for a pre-exam are defined in the course requirements of the subject. 22 Successful exam repetition 26. § (1) If the student wants to improve a grade, he/she has the possibility to retake the exam within the same exam period. (2) The result of the retaken exam is final, unless the student did not pass. In this case, he/she is obliged to retake the exam. Academic achievement records, indicators 27. § (1) Authorized personnel input the academic achievement of students in the student information system and write it on the grade sheet. The results students have achieved during the semester must be input in the student academic administration system. The grade sheet shall be kept at least for a year in the institution. Any unauthorized entry to the student information system implies legal consequences. (2) After the exam period, a verified copy of the list of subjects students are registered for and the results are printed and placed in the student’s credit book. The credit book is an official document. (3) The amount of the student's academic work in a semester or the beginning of the study is indicated by the number of credits earned. (4) The quantitative and qualitative evaluation of student performance is indicated by the credit index and adjusted credit index. Adjusted credit index= ( ∑credits obtained/∑ credits taken) x credit index Full-time trainings: Credit index=Σ(credit point x mark)/30 The credit index is applied per semester. When calculating, the accepted subjects shall be taken into account only if it was covered in the same semester for which the credit index is applied. (5) The semester scholarship is based on the previous scholarship indicator. The scholarship indicator is used to evaluate the quality and quantity of the student’s performance. Method of calculation: Scholarship indicator=(Σ(creditpoint x mark)/30) x M, where M = all credits obtained / number of active semesters x 30 The scholarship indicator is applied per semester. (6) The semi-annual scholarship is based on the group index. The group index is for evaluating the quality and quantity of work. a) The group index regardless of the homogeneous group of minimum and maximum average, and the homogeneous group average, with a scale of 0-2, where the highest scholarship index of the group is assigned with 2, the smallest with 0 and the group average with 1. 23 b) The group index is an indicator that compares the performance of students of your choice. Method of calculation: a) The group index is calculated in more steps and is based on the stipend index. stipend index= credit index * M, where M = all credits obtained /number of active semesters x 30 b) The homogeneous group average is being deducted from the stipend index. stipend index – group average c) Those student’s group index, whose stipend index is higher then the average group index is calculated as the following: the difference calculated from his/her stipend index is divided by the largest difference within the group and add 1 to the result. d) (This way, students with the largest stipend index are having a group index of 2, student with academic average are having a group index of 1.) (stipend index – group average) largest (stipend index – group average) e) Those students group index, whose stipend index lower then the average group index is calculated as the following: the difference calculated from his/her stipend index is divided by the smallest difference within the group, multiple this amount by 1 and then add 1. (This way, the student’s group index - with the worst stipend index in the group - is going to be 0.) -1 * (stipend index – group average) smallest (stipend index- group index) +1 (7) The weighted academic average is a qualitative index measuring the academic performance of one semester. Weighted academic average = ∑(credits obtained x mark) / ∑credits obtained (8) The overall adjusted index is the qualitative and quantitative index of the student’s performance of more semesters. This is the base of reclassification between state financed and privatly funded trainings. The overall adjusted credit index = Adjusted credit index (where the number of obtained and taken credits during the whole period or 30 credits per semester (8 semester-long correspondence trainings: 26) must be taken into account) 24 (9) Transferred credits and credits accepted in the virtual (before the very first semester) semester are calculated in the stipend index as the following: Stipend index=(Σ(credit points x marks)/30 ) x M where M = (total credits completed–number of accepted credits) / Number of active semesters x 30 This compensation shall be applied until the student is reached Procedure of acceptance of substituting and optional courses, credit transfer 28. § (1) The acceptance of subjects advertised in other faculties and institutions, determination of its credit points is the substitutability of the subject and the differentiation of other subjects. (2) Some subjects or group of subjects can be substituted with another subject or group of subjects if the syllabus of the substituting subjects and the syllabus of the substituted subjects overlap by at least 75%. In higher education institution for the comparison of knowledge a dedicated committee (henceforth: Credit Transfer Committee) is responsible. (3) The Credit Transfer Committee can recognize the previously acquired knowledge and work experience as a fulfillment of academic requirements. (4) In order to obtain the final certificate (absolutorium) – during higher educational studies, previous studies, as well as in case of recognition of previously earned credits, at least 35% of the trainings credits must be fulfilled in the given institution. (5) Academic performance recognized by credits – if it is a pre-condition- any course obtained in any higher educational institution must be recognized regardless of the faculty, higher education institute or the level of training. The recognition – based on the program of the subject – is done by knowledge comparison that determines the credits. Credits must be recognized if the knowledges compared are at least 75% identical and if the value of the obtained credits does not significantly differ from the one fulfilled. (6) The credit value of the substituting subject given in the curriculum must be accepted as the credit of the substituted and the mark originally awarded as the mark for the subject. (7) A subject differs from another when at least 75% of its syllabus differs. (8) To the fulfillment of the curriculum related requirements only those courses can be considered that previously have not been taken into account. (9) Students prior the registration to the semester – as defined in the Study Statute – can request that the faculty accept subjects completed perviously or taken and yet to be completed at another faculty, higher education institute or at another level of training. The decision about the acceptance of these subjects is made by the KKB by taking into account (1-4) and the agreements regarding credit transfer with other higher institutes. The committee decides about the requests filed latest the first day of the registration week. (10) The faculties of the university mutually recognize the credit value of advertised subjects. Any subjects advertised at the university at a particular level of training can be added as an optional subject. 25 (11) The obtained credits during higher level vocational trainings can be accepted to the bachelor training in the same field of study minimum 30, maximum 60 credits, irrespectively of the legal relationship: either higher or secondary education. (12) The KKB decides – based on (5) – for bachelor studies, the conditions and the acceptable credits for certificates and diploms issued according to Nftv. The knowledge comparison has to be made regardless of whether the student conducted his/her previous studies in a credit based or non-credit based training system. Concessional study load 29. § (1) The KTB may grant a concessional study load to students who completed the first two semesters of the curriculum and have a mininmum of 4.00 credit index for each semester. In addition to the above mentioned, concessional study load may be granted in special cases – particularly for student raising small children on their own or are physically disabled, having professional sport achievements, receiving persistant or regular medical treatments, participating in simultaneous programmes or taking part in public activities. (2) In case of part-time abroad trainings, granting concessional study load is mandatory if the student fulfilled the study requirements. (3) The concession granted for the student exempt him/her from the completion of the assessment requirements of the subject he/she has taken. These are authorized by the KTB. (4) The concessional study load is valid for a given period. Exercising equity and guaranteeing equal opportunities 30. § (1) During academic programmes and training courses students may be given exemption from certain regulations on the occasion at their request based on equity. No exemption may be given from the requirements appearing in the curriculum but the means of completions may be customized. (2) To the filed requests, a document should be attached proving its the neccesity. (3) When deciding about the filed requests for equity, circumstances and the impact on the education must be thoroughly ivestigated. 26 PartIV. Provisionsonthesis,finalexamanddiplom The finals 31. § (1) The HEI issues a leaving certificate (absolutorium) for students who fulfilled all the study and exam requirements – except of the language exam requirement - as well as the internship defined in the curriculum and also obtained the necessary number of credits. (2) The leaving certificate is signed by the dean in the student’s credit book. (3) When issuing the leaving certificate the followings must be taken into consideration: a) fulfillment of the institutional language criteria, b) basic English knowledge for those, who completed the criteria subject in German language, c) fulfillment of PE requirements, d) fulfillment of prescribed internships, e) at least 35% of the obtained credits must be completed at the Óbuda University (4) As long as the student does not fulfill the requirements mentioned in point b) and d), the leaving certificate not not be issued and his/her student status is suspended. (5) If all the conditions are met, the leaving certificate has to be issued. (6) Students participating in cooperative trainings are receiving the leaving certificate after completing all the cooperative semesters. Degree thesis, dissertation 32. § (1) In order to obtain the diplom, students have to prepare a thesis. This is a complex, individual work which requires the synthesis of the knowledge gained during his/her training and its creative application in practise. The preparation of the thesis requires individual work and plagiarism is stricktly forbidden. The credit value of the thesis is defined in the curriculum. (2) Thesis consultant can be lecturers or researchers of the student’s faculty or, with the permission of the head of the department, other experts who have a university degree. An external supervisor can only be called upon together with an internal consultant whose task is to do the administrative work at the university. (3) When studing abroad in a foreign higher educational institution, the thesis can be written on the given country’s language, though the summary and the evaluation must be handed in in Hungarian as well. The defense of the thesis is in front of the Finals Committee in Hungarian language. (4) The institution may refuse to issue the evaluation of the thesis if it does not meet the published requirements. In this case a new deadline is set in order to obtain the corrections. (5) The evaluation must be prepared in written form which one copy has to be made available to the candidate 3 days prior the defense of the thesis at the latest (without a grade). The referee and the supervisor each make a suggestion for the grading of the degree thesis. 27 (6) The consultant, the referee and the members of the finals committee pay special attention to prevent and detect the abuse of other intellectual products. (See: Study Statute Part V. Chapter 6.1) (7) The evaluation of the thesis is based on a five scale grading scheme. In case of failure, students have the chance to prepare the thesis two more times. (8) The Study Statute determines the followings: a) publishing and approving the topics of the thesis/dissertation, b) rules of the application, c) formal requirements of the thesis/dissertation, d) deadline of submission. (9) The final date of submission should be included among the thesis requirements for all students. (10) If the student has no legal relationnship with the university, in case of repeated thesis, the student has to pay the procedure fee defined in TTSZ. The finals 33. § (1)Students participating in BA and MA trainings are finishing their studies with the final exam. The final exam is the evaluation of the skills, knowledge and abilities that are the conditions of obtaining the degree certificate. During the final exam the student must prove that he/she is able to apply his/her knowledge in practice. (2) Conditions of the final exam: a) to obtain the leaving certificate (absolutorium); b) accepted thesis by the jury. c) If the student has any unfulfilled payment obligation towards the university, he/she may not apply for the final exam. (2) The student may obtain the final exam only after receiving the leaving certificate. The final exam may be obtained in the exam period after issuing the leaving certificate when the student still has the legal relationship with the university. After the termination of the student status – within two years – in any exam period according to the valid training requirements. If the legal relationship is terminated more then five years, the final exam may not be obtained. (3) The faculties set the rules for the final either part of the model curriculum or as a separate document. The final consists of: a) defending the degree thesis/dissertation b) written and/or oral exams with a set of syllabus to be taken either at the same time a sor separately from the defense c) completing pre-set exercises (for certain degree programmes) (4) The final consists of subjects of at least 20 and maximum 30 credit points. (5) The requirements of the final and the theme of the topics must be published. It is a mandatory for students completed their studies eralier as well. (6) The final consists of the defense of the thesis/dissertation and exams of the prescribed subjects. If possible, students must take the finals on one day. The final exam consists of oral exams where students have 30 minutes per subject to prepare. The committee examines one student at a time. (7) The candidate may obtain the final exam if his/her thesis is accepted and he/she was granted with the minimum grade of satisfactory (2). If a student does not pass his/her dissertation, the given faculty decides about the condition of the retake. 28 (8) The final exam period is set in the academic year schedule. (9) If a student applies to the final after his/her legal relationship with the university is terminated, he/he is obliged to pay the procedure fee defined by the TTSZ. The finals committee 34. § (1) The finals committee has at least two members in addition to the chairman. The chairman and the members can be university professor sor readers or acknowledged external experts of the field. At least one member of the committee should be an external expert. Minutes have to be kept of the finals. (2) The chairman is entrusted by the dean for a period of one to three years with the agreements of the faculty council. (3) The final committees are organized according to the faculties and to the proper number of members needed. (4) The final committee is responsible for: a) to approve whether the candidate is entitled to take the final exam, b) to mark the degree thesis, c) to determine the mark of the final exam. (5) The candidate is obliged to take an exam from all the subjects of finals, regardless if his/her result is unsatisfactory. (6) The mark of the final is determined by the finals committee behind closed doors. In case of equility, the vote of the chairman decides. (7) Minutes have to be kept of the final exam. The chairman of the final committee is responsible for informing the dean of the faculty about the results of the finals in written form. The committee shall prepare the suggestions regarding the degree thesis competition made by various professional organizations. The result of the final 35. § (1) The result of the final: a) in case of curriculum that includes comprehensive exam requirements: taking the average of the grades obtained for the degree thesis, comprehensive exam and final exam – considering the number of exam subjects. The result must be calculated as: Z =[(S1+S2)/2 + SZD + Z1+Z2+…+Zm]/(2+m). b) in case of curriculum that does not include comprehensive exam requirements: taking the average of the grades obtained for the degree thesis and for the oral part of the final exam – considering the number of the exam subjects. The result must be calculated as: Z =( SZD + Z1+Z2+…+Zm)/(1+m). (2) If the student did not pass any of the mentioned grades, he/she is failing the final exam. The result of the final is announced by the chairman of the committee. 29 Retaking unsuccessful finals 36. § (1) The unsuccessful final exam can be retaken twice. (2) A repeated final exam can be taken in the next final examination period. Registration is at least one month prior the final exam at the relevant instituitions – the student should be able to prove that he/she paid the defined examination fee. (3) When retaking the final, one must only retake the subject that he/she previously failed. (33.§) The degree certificate 37. § (1) Based on the successful finals and the completion of language criteria requirements, the faculty issues a certificate to the candidate which also contains details of the specifications of the qualification. (2) The first subsection shall not be applied – except of the final exam – if the language of the training is other than Hungarian. (3) The degree certificate has be issued within 30 days following the successful finals and after proving that the requirements concerning language skills have been met. (4) The university issues the a supplement for the certificate in English and in Hungarian according to the regulations drawn up by the European Commission and the Council of Europe within 30 days. (5) The certificate is a public document with the Hungarian coat of arms, which contains the name and the identification number of the institution, the serial number of the certificate, the certificate holder’s name, maiden name, date and place of birth, the level of education, the awarded qualification, place and date of issuing the certificate and the classification of the qualification according to the Hungarian Qualification Framework and to the European Qualification Framework. The certificate must also contain the original signature of the head of the institution and the official stamp of the institution. (6) A central record must be kept from the certificates issued. (7) The grade of the certificate must be given as follows based on the average results: outstanding 5,00 excellent at least 4,51 but less than 4,99 good at least 3,51 but less than 4,50 satisfactory at least 2,51 but less than 3,50 pass at least 2,00 but less than 2,50 (8) The certificate has to be issued in a bilingual version (in Hungarian and English or in Hungarian and in Latin languages, or in case of a foreign language academic programme, in the given foreign language). (9) The university issues the a supplement for the certificate in English and in Hungarian according to the regulations drawn up by the European Commission and the Council of Europe within 30 days. (10) The certificates issued for completing BA and MA programmes – as defined by law enable the students to fill a postion. (11) Those who hold a master certificate are having the „certified” designation in front of their qualification (certified engineer, certified economist, certified teacher etc.) 30 (12) If the only reason why it is not possible to issue the certificate is that the student has not been able to present a language certificate, the faculty issues a certificate which proves that the student has passed the finals. Degree with honor 38. § (1) One shall receive a degree with honour if he/she obtained outstanding results of the exam subjects, received excellent grades for his/her degree thesis and finals, the weighted average of all his/her other grades is at least 3.51 and does not have lower grade than satisfactory. 31 PartV. Miscellaneousprovisions Special provisions for students with disabilities 39. § (1) For students with disabilities – for special request – the requirements are partially or completly modified compared to the curriculum. Students are not obliged to fulfill the requirements. This does not lead to the exemption of the basic requirements certified by the qualification. (2) The principles regarding the study of students with disabilities are defined by separete regulations. Internships 40. § (1)The main goal of the internship is to link together the theoretical and practical knowledge and skills in a professional work environment, to improve the employee competences that are necessary for the profession during the workflow, to gain practical skills and material-tool technology knowledge, as well as to establish professional cooperations and develop personal competences, such as problemsolving skills and ability of innovation. (2)The internship is a training activity defined by the HEI or by both the HEI and the place of professional practise, is planned according to the program requirements and is evaluated as stated in the faculty’s curriculum. The internship is organized by the institution appointed by the faculty. (3)The duration of the undergraduate engineering internship is at least 6 weeks. Off-site internship is a criteria condition. (4)The internship can be fulfilled any time after obtaining 40 credits. (5)The HEI and the place of professional practice have a written agreement regarding the student’s internship. (6)In exceptional cases, with the permission of the dean, the internship may be fulfilled in one of the university’s institutions. (7)After completing the internship, the student receives a written evaluation about his/her professional performance. (8)The student status is suspended of those who fulfilled all the conditions of the finals except of the internship until he/she can hand in the certificate proving that he/she fulfilled the internship requirements. (9)The detailed rules of the internship are included in the Study Statute in part III, section 12. Cooperative trainings 41. § (1) Cooperative trainings are in connection with full-time trainings, voluntary, additional practice moduls in which the university and a business organization cooperate in order to ensure that students - according to the training’s aims – acquire work experience. (2) The modul of the cooperative training is a two-semester long additional part of the fulltime training.The trainings are organized by the faculties collaborating with educational and organizational departments. The conditions of the application are defined in the faculty’s cooperative curriculum. 32 (3) The detailes specifications of cooperative trainings are set in the Cooperative Training Regulations. Helping disadvantaged students 42. § (1) Disadvantaged students admitted to the university during their studies have the possibility to rely on the mentor program. (2) The mentor program involves lecturers and students offering their help to disadvantaged students. (3) The activity of the mentor program is coordinated by an organization appointed by the the Minister of Education and Culture. The Minister of Education and Culture and the organization coordinating the mentor program (hereinafter referred to as mentor program organization) have a contractual agreement which includes the tasks and functions of the organization, its financing regulations, general discription of the mentor’s activities and the professional requirements imposed on the mentors. (4) The conract also contains the contact obligations, the tasks of the mentor, duration of the program, remuneration and the rights and obligations of the organization. Student card 43. § (1) Students admitted to the university are entitled to request a student identification card. The student card is stating the student’s legal relationship with the university and qualifies certain benefits and discounts to students. The management of student cards is determined in governmental regulations. Lost student cards must be reported at the issuing administrator, at the Student Information Center or at the Student Center where the new student card will be issued. When the student’s legal relationship is suspended, the student card is not valid. Student identification number 44. § (1) All students are provided with a student identification number issued by the National Higher Education Information Center which is used to monitor the rights and obligations regarding the student’s legal relationship. (2) The rules and procedure of issuing the student identification number is included in the Study Statue. NEPTUN code 45. § (1) Students receive a Neptun code in order to access the student information system (Neptun system). The Neptun code is issued by the given faculty. Study Statue 46. § (1) The executive order of the TVSZ is the Study Satute which is issued by the rector – with the agreement of the EHÖK – and is the attachement of the TVSZ. 33 Retake exam fees, special procedure charge, service fees 47. § (1) Students retaking an unsuccessful exam or want to improve the grade of an exam are obliged to pay the retake exam fee. Students, who do not fulfill their administrative, payment or academic requirements before the deadline or are causing extra work or damages to the university, are obliged to pay the special procedure charge. The rekate exam fee and special procedure charge are determined according to the TTSZ. National Conference of Student’s Scholarly Circles, State Scholarship 48. § (1) Participation in the National Conference of Student’s Scholarly Cirles must be recorded in the student’s credit book. The student is required to hand in both the Hungarian and English title of his/her work to the Academic Department. (2) Students granted with state scholarship, this must be recorded in the student’s credit book. Disciplinary and liability 49. § (1) Concerning the student’s disciplinary liabilities and the university’s disciplinary liabilities other regulations are prevailing. In matters not covered 50. § (1) In all study and examination matters which these regulations do not address, the dean of the faculty and the Study Committee is responsible. (2) In all procedural, documentary etc. matters in respect of which these regulationsdo not give instructions, the dean of the faculty is responsible. Rules of cohabitation 51. § (1) Students during their studies are obliged to follow the written and unwritten rules of cohabitation. During exams, test and other curriculum requirements it is forbidden to use any devices not permitted. (2) During classes (lectures and seminars) and exams the use of mobile phones is prohibited. This prohibition is applies to both the lecturers and students. (3) If a student breaches his/her obligations, disciplinary actions may be taken. The detailed rules of the disciplinary procedure are included in the Disciplinary Rules of the University. 34 PartVI. Closingprovisions 52. § (1) The Study and Examination Regulations were discussed and approved by the Senate on the 29th August 2012. The TVSZ came into force 1st September 2012. (2) The Study and Examination Regulations of the university shall be made public on its website. Budapest, August 2012. Prof. Dr. Imre Rudas Rector In case of equivocality, the original Hungarian TVSZ is authoritative. 35