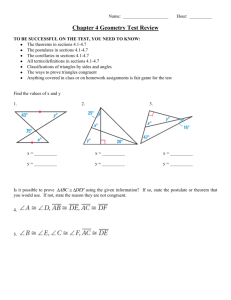
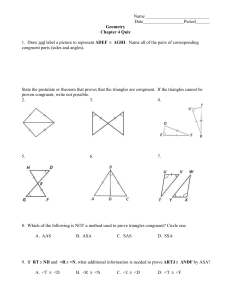
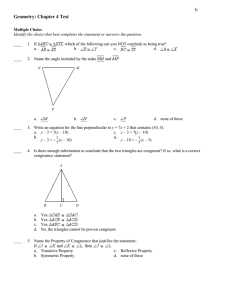
Geometry – Fall 2009 Name __________________________ Final Exam Part II
advertisement
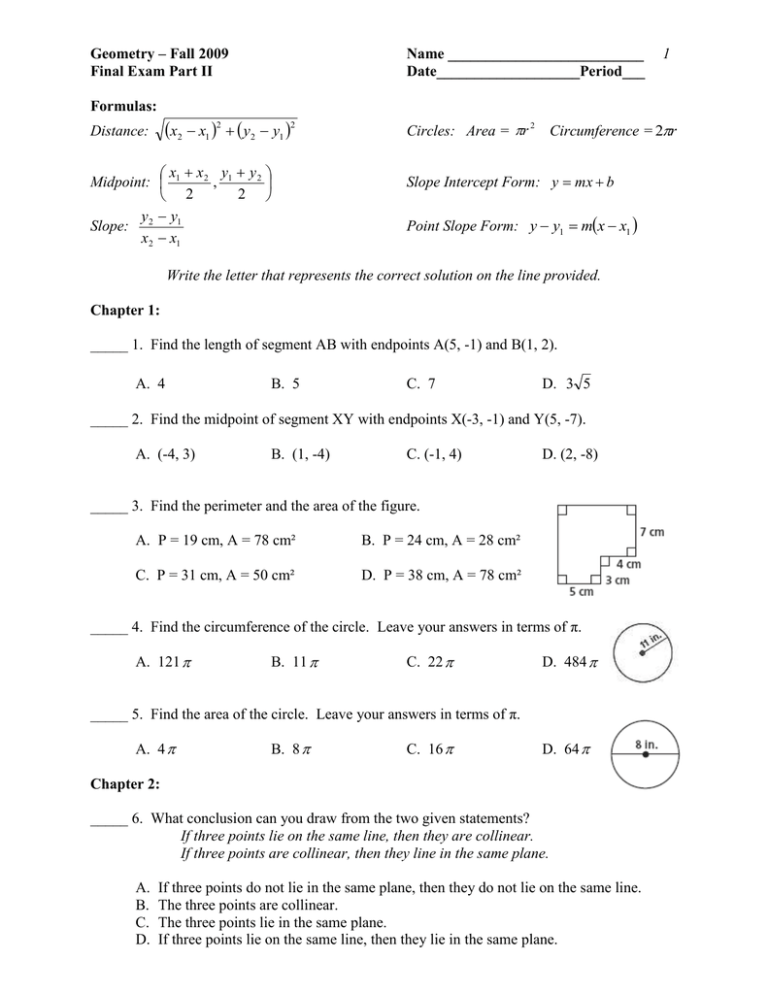
Geometry – Fall 2009 Final Exam Part II Name __________________________ Date___________________Period___ 1 Formulas: x2 x1 2 y2 y1 2 Distance: x x 2 y1 y 2 Midpoint: 1 , 2 2 y y1 Slope: 2 x2 x1 Circles: Area = r 2 Circumference = 2r Slope Intercept Form: y mx b Point Slope Form: y y1 mx x1 Write the letter that represents the correct solution on the line provided. Chapter 1: _____ 1. Find the length of segment AB with endpoints A(5, -1) and B(1, 2). A. 4 B. 5 C. 7 D. 3 5 _____ 2. Find the midpoint of segment XY with endpoints X(-3, -1) and Y(5, -7). A. (-4, 3) B. (1, -4) C. (-1, 4) D. (2, -8) _____ 3. Find the perimeter and the area of the figure. A. P = 19 cm, A = 78 cm² B. P = 24 cm, A = 28 cm² C. P = 31 cm, A = 50 cm² D. P = 38 cm, A = 78 cm² _____ 4. Find the circumference of the circle. Leave your answers in terms of π. A. 121 B. 11 C. 22 D. 484 _____ 5. Find the area of the circle. Leave your answers in terms of π. A. 4 B. 8 C. 16 D. 64 Chapter 2: _____ 6. What conclusion can you draw from the two given statements? If three points lie on the same line, then they are collinear. If three points are collinear, then they line in the same plane. A. B. C. D. If three points do not lie in the same plane, then they do not lie on the same line. The three points are collinear. The three points lie in the same plane. If three points lie on the same line, then they lie in the same plane. _____ 7. Which statement provides a counterexample to the following faulty definition? A square is a figure with four congruent sides. A. B. C. D. A six-sided figure can have four sides congruent. Some triangles have all sides congruent. A square has four congruent angles. A rectangle has four sides. _____ 8. Use the diagram at the right to find the measure of A. 26° B. 38° C. 52° D. 90° _____ 9. Use the diagram at the right to find the measure of A. 64° B. 76° . C. 128° . D. 90° _____ 10. Find the value of x in the figure at the right. A. 13 B. 50 C. 51.5 D. 87 _____ 11. Find the value of x in the figure at the right. A. 4 B. 9 C. 10 D. 12 12. Complete the two-column proof. Given: C is the midpoint of FH. Prove: x = 6 Statements Reasons___________ 1. C is the midpoint of FH. a. __________________________________ 2. FC = CH b. __________________________________ 3. 4x = 2x + 12 c. __________________________________ 4. 2x = 12 d. __________________________________ 5. x = 6 e. __________________________________ Chapter 3: _____ 13. Find the value of x for which l // m. A. x = 35 B. x = 26 C. x = 10 D. x = 40 _____________ _____ 14. Find the values of x and y. A. x = 22, y = 120 B. x = 38, y = 104 C. x = 60, y = 102 D. x = 120, y = 22 _____ 15. Find the values of x, y, and z. A. x = 45, y = 35, z = 45 B. x = 55, y = 125, z = 35 C. x = 35, y = 35, z = 55 D. x = 55, y = 55, z = 55 _____ 16. Find the values of x and y. A. x = 91, y = 108 B. x = 90, y = 109 C. x = 94, y = 105 D. x = 94, y = 81 _____ 17. Find the value of the missing angle measure. A. x = 53 B. x = 307 C. x = 100 D. x = 127 _____ 18. Write an equation, in point-slope form, of the line that is perpendicular to y = 2x + 17 and contains (8, -1). 1 A. y 1 ( x 8) 2 B. y 1 2( x 8) C. y 8 1 x 1 2 D. y 1 1 ( x 8) 2 _____ 19. Write the equation of the line that passes through the points (6, 4) and (-3, 1). A. y 3 x 14 B. y 3 x 10 C. y 1 x6 3 D. y _____ 20. Determine whether the lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. A. Parallel B. Perpendicular C. Neither 1 x2 3 2x 3y 6 4 x 6 y 24 Chapter 4: _____ 21. State the postulate or theorem you would use to prove the pair of triangles congruent. If the triangles cannot be proved congruent, write not possible. A. SAS B. ASA C. AAS D. Not Possible _____ 22. State the postulate or theorem you would use to prove the pair of triangles congruent. If the triangles cannot be proved congruent, write not possible. A. SSS B. ASA C. AAS D. Not Possible _____ 23. What other information do you need in order to prove the triangles congruent using the SAS Congruence Postulate? A. CBA CDA _____ B. BAC DAC _____ _____ _____ D. BC DC C. AB AD _____ 24. If ΔMNO ΔPQR, which of the following can you NOT conclude as being true? _____ _____ A. MN PR B. M P _____ _____ C. NO QR D. N Q 25. Complete the two-column proof. Given: AB // DC, B D Prove: BC DA Statements _____ Reasons_________________ _____________ _____ 1. AB // DC a. ________________________________________ 2. BAC DCA b. ________________________________________ 3. B D c. ________________________________________ 4. AC AC d. ________________________________________ 5. ΔABC ΔCDA e. ________________________________________ 6. BC DA f. ________________________________________ _____ 26. Find the value of y in the isosceles triangle. A. 50 B. 65 C. 80 D. 130 Chapter 5: _____ 27. is the midsegment of A. 18 B. 36 . NO = 36, find MP. C. 54 D. 72 C. 7 D. 2 C. 9 D. 18 _____ 28. Find the value of x. A. 8 B. 1 _____ 29. Find the value of y. A. 16.2 B. 27 _____ 30. List the sides of the triangle in order from shortest to longest. A. BC, CA, AB B. AB, CA, BC C. CA, BC, AB D. BC, AB, CA _____ 31. If a triangle has side lengths 18ft and 20ft, what are the possible lengths of the third side? A. 2 < x < 38 B. 18 < x < 20 C. 2 < x < 20 _____ 32. Which line contains an altitude of ΔABC? A. l B. k C. n D. m _____ 33. In ΔTUV, Y is the centroid. If YW = 5, find TY and TW. A. TY = 5, TW = 10 B. TY = 7.5, TW = 12.5 C. TY = 10, TW = 15 D. TY = 2.5, TW = 7.5 Chapter 6: _____ 34. Find the measure of 1 and 2. A. 1 = 28°, 2 = 28° C. 1 = 28°, 2 = 56° B. 1 = 56°, 2 = 28° D. 1 = 56°, 2 = 56° D. 2 < x < 18 _____ 35. FCHS is a rectangle. If FH = 9x – 14 and CS = 7x + 4, find the value of x and the length of each diagonal. A. x = 9; FH = 95; CS = 95 B. x = 6; FH = 46; CS = 46 C. x = 9; FH = 67; CS = 67 D. x = 6; FH = 40; CS = 46 _____ 36. Find the measure of 1 and 2. A. 1 = 75°, 2 = 105° B. 1 = 105°, 2 = 75° C. 1 = 75°, 2 = 75° D. 1 = 105°, 2 = 105° _____ 37. Find the side lengths of the kite. A. 9, 9, 13, 13 B. 11, 11, 20, 20 C. 9, 9, 11, 13 D. 11, 13, 20, 20 _____ 38. Find the measure of 1 and 2. A. 1 = 90°, 2 = 40° B. 1 = 40°, 2 = 90° C. 1 = 40°, 2 = 50° D. 1 = 50°, 2 = 90° _____ 39. Find the value of x and y. A. x = 33, y = 81 B. x = 99, y = 81 C. x = 33, y = 147 D. x = 40, y = 140 _____ 40. Which statement is true for some, but not all, rectangles? A. B. C. D. Opposite sides are parallel. It is a parallelogram. Adjacent sides are perpendicular. All sides are congruent.