Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key Grade: 10
advertisement

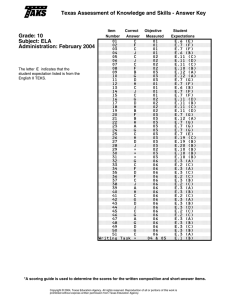
Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key Grade: 10 Subject: ELA Administration: February 2006 The letter E indicates that the student expectation listed is from the English II TEKS. Item Number Correct Answer 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 Writing Task C G B F B J B J C J B F A H D G C J A H A H D F D F D F * * * H B F A G C J A F B H B G C G C J C J A * Objective Measured 01 01 01 01 02 02 02 02 03 03 03 01 01 01 01 02 02 02 03 03 03 03 02 03 03 03 03 03 02 03 03 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 06 04 & 05 Student Expectations E.7 (F) E.6 (E) E.7 (F) E.7 (F) E.11 (A) E.11 (C) E.11 (C) E.11 (F) E.7 (G) E.7 (G) E.12 (A) E.6 (B) E.7 (F) E.7 (F) E.7 (F) E.11 (A) E.10 (B) E.11 (D) E.12 (A) E.10 (B) E.10 (B) E.6 (F) E.11 (A) E.7 (G) E.10 (B) E.20 (B) E.19 (C) E.19 (C) E.10 (B) E.10 (B) E.10 (B) E.3 (A) E.2 (C) E.2 (C) E.2 (C) E.3 (B) E.3 (B) E.3 (A) E.2 (C) E.2 (C) E.3 (A) E.3 (B) E.3 (B) E.3 (A) E.3 (B) E.2 (C) E.3 (A) E.2 (C) E.2 (C) E.2 (C) E.2 (C) E.1 (B) *A scoring guide is used to determine the scores for the written composition and short-answer items. Copyright © 2006, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited without express written permission from Texas Education Agency. Grade 10 English Language Arts For a more complete description of the objectives measured, please refer to the Revised TAKS Information Booklet for Grade 10 English Language Arts at http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/taks/booklets/index.html. Objective 1: (6) (7) Reading/word identification/vocabulary development. The student acquires an extensive vocabulary through reading and systematic word study. The student is expected to (B) rely on context to determine meanings of words and phrases such as figurative language, [idioms,] multiple-meaning words, and technical vocabulary; (C) apply meanings of prefixes, roots, and suffixes in order to comprehend; and (E) use reference material such as glossary, dictionary, [thesaurus, and available technology] to determine precise meanings and usage. Reading/comprehension. The student comprehends selections using a variety of strategies. The student is expected to (F) (8) produce summaries of texts by identifying main ideas and their supporting details. Reading/variety of texts. The student reads extensively and intensively for different purposes in varied sources, including world literature. The student is expected to (B) read in varied sources such as diaries, journals, textbooks, maps, newspapers, letters, speeches, memoranda, [electronic texts, and other media]. Objective 2: (10) The student will demonstrate an understanding of the effects of literary elements and techniques in culturally diverse written texts. Reading/literary response. The student expresses and supports responses to various types of texts. The student is expected to (B) (11) The student will demonstrate a basic understanding of culturally diverse written texts. use elements of text to defend his/her own responses and interpretations. Reading/literary concepts. The student analyzes literary elements for their contributions to meaning in literary texts. The student is expected to (A) compare and contrast varying aspects of texts such as themes, conflicts, and allusions; (B) analyze relevance of setting and time frame to text's meaning; (C) describe and analyze the development of plot and identify conflicts and how they are addressed and resolved; (D) analyze [the melodies of] literary language, including its use of evocative words and rhythms; (E) connect literature to historical contexts, current events, [and his/her own experiences]; and Page 1 Grade 10 English Language Arts (continued) (F) understand literary forms and terms such as author, drama, biography, autobiography, myth, tall tale, dialogue, tragedy and comedy, [structure in poetry, epic, ballad,] protagonist, antagonist, paradox, analogy, dialect, and comic relief as appropriate to the selections being read. Objective 3: (6) (7) (8) The student will demonstrate the ability to analyze and critically evaluate culturally diverse written texts and visual representations. Reading/word identification/vocabulary development. The student acquires an extensive vocabulary through reading and systematic word study. The student is expected to (F) discriminate between connotative and denotative meanings and interpret the connotative power of words; and (G) read and understand analogies. Reading/comprehension. The student comprehends selections using a variety of strategies. The student is expected to (E) analyze text structures such as compare and contrast, cause and effect, and chronological ordering for how they influence understanding; and (G) draw inferences such as conclusions, generalizations, and predictions and support them with text evidence [and experience]. Reading/variety of texts. The student reads extensively and intensively for different purposes in varied sources, including world literature. The student is expected to (D) interpret the possible influences of the historical context on a literary work. (10) Reading/literary response. The student expresses and supports responses to various types of texts. The student is expected to (B) use elements of text to defend his/her own responses and interpretations. (12) Reading/analysis/evaluation. The student reads critically to evaluate texts and the authority of sources. The student is expected to (A) analyze the characteristics of clearly written texts, including the patterns of organization, syntax, and word choice; (B) evaluate the credibility of information sources, including how the writer's motivation may affect that credibility; and (C) recognize logical, deceptive, and/or faulty modes of persuasion in texts. (19) Viewing/representing/interpretation. The student understands and interprets visual representations. The student is expected to (B) analyze relationships, ideas, [and cultures] as represented in various media; and Page 2 Grade 10 English Language Arts (continued) (C) distinguish the purposes of various media forms such as informative texts, entertaining texts, and advertisements. (20) Viewing/representing/analysis. The student analyzes and critiques the significance of visual representations. The student is expected to (B) deconstruct media to get the main idea of the message's content; and (C) evaluate and critique the persuasive techniques of media messages such as glittering generalities, logical fallacies, and symbols. Objective 4: (1) (2) (5) Writing/purposes. The student writes in a variety of forms, including business, personal, literary, and persuasive texts, for various audiences and purposes. The student is expected to (B) write in a voice and a style appropriate to audience and purpose; and (C) organize ideas in writing to ensure coherence, logical progression, and support for ideas. Writing/writing processes. The student uses recursive writing processes when appropriate. The student is expected to (B) develop drafts [both alone and collaboratively] by organizing and reorganizing content and by refining style to suit occasion, audience, and purpose; and (C) proofread writing for appropriateness of organization, content, style, and conventions. Writing/evaluation. The student evaluates his/her own writing and the writings of others. The student is expected to (A) evaluate writing for both mechanics and content. Objective 5: (2) The student will produce a piece of writing that demonstrates a command of the conventions of spelling, capitalization, punctuation, grammar, usage, and sentence structure. Writing/writing processes. The student uses recursive writing processes when appropriate. The student is expected to (C) (3) The student will, within a given context, produce an effective composition for a specific purpose. proofread writing for appropriateness of organization, content, style, and conventions. Writing/grammar/usage/conventions/spelling. The student relies increasingly on the conventions and mechanics of written English, including the rules of usage and grammar, to write clearly and effectively. The student is expected to (A) produce legible work that shows accurate spelling and correct use of the conventions of punctuation and capitalization [such as italics and ellipses]; Page 3 Grade 10 English Language Arts (continued) (5) (B) demonstrate control over grammatical elements such as subject-verb agreement, pronounantecedent agreement, verb forms, and parallelism; and (C) compose increasingly more involved sentences that contain gerunds, participles, and infinitives in their various functions. Writing/evaluation. The student evaluates his/her own writing and the writings of others. The student is expected to (A) evaluate writing for both mechanics and content. Objective 6: (2) Writing/writing processes. The student uses recursive writing processes when appropriate. The student is expected to (C) (3) (5) The student will demonstrate the ability to revise and proofread to improve the clarity and effectiveness of a piece of writing. proofread writing for appropriateness of organization, content, style, and conventions. Writing/grammar/usage/conventions/spelling. The student relies increasingly on the conventions and mechanics of written English, including the rules of usage and grammar, to write clearly and effectively. The student is expected to (A) produce legible work that shows accurate spelling and correct use of the conventions of punctuation and capitalization [such as italics and ellipses]; (B) demonstrate control over grammatical elements such as subject-verb agreement, pronounantecedent agreement, verb forms, and parallelism; (C) compose increasingly more involved sentences that contain gerunds, participles, and infinitives in their various functions; and (D) produce error-free writing in the final draft. Writing/evaluation. The student evaluates his/her own writing and the writings of others. The student is expected to (A) evaluate writing for both mechanics and content. Page 4 Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key Grade: 10 Subject: Mathematics Administration: April 2006 The letter A indicates that the student expectation listed is from the Algebra I TEKS. Item Number 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 Correct Answer C F B J D G A H B H D J C G D F B J B G 2.75 J C G C J D G C G D H A H C J B J A H D G C F B H D H A H C J C G C J Objective Measured 07 03 10 06 01 06 08 07 10 01 07 03 10 01 07 02 09 05 09 04 09 05 08 10 08 03 08 02 10 10 08 04 10 06 06 02 05 02 04 03 08 05 10 09 07 02 04 01 01 04 10 06 08 05 03 09 Student Expectations 8.7 (A) A.C2 (D) 8.16 (A) 8.6 (B) A.B1 (C) 8.7 (D) 8.9 (B) 8.7 (B) 8.14 (B) A.B1 (A) 8.7 (A) A.C2 (B) 8.14 (B) A.B1 (B) 8.7 (C) A.B4 (B) 8.11 (A) A.D1 (C) 8.13 (B) A.C3 (C) 8.3 (B) A.D1 (D) 8.10 (A) 8.16 (B) 8.8 (A) A.C2 (E) 8.8 (C) A.B2 (A) 8.14 (C) 8.16 (A) 8.8 (B) A.C4 (A) 8.15 (A) 8.6 (B) 8.6 (A) A.B3 (A) A.D1 (B) A.B3 (B) A.C3 (B) A.C2 (A) 8.9 (B) A.D2 (B) 8.14 (B) 8.11 (B) 8.7 (A) A.B4 (A) A.C4 (B) A.B1 (D) A.B1 (E) A.C3 (A) 8.16 (A) 8.7 (D) 8.9 (A) A.D3 (A) A.C1 (C) 8.12 (C) Copyright © 2006, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited without express written permission from Texas Education Agency. Grade 10 Mathematics For a more complete description of the objectives measured, please refer to the Revised TAKS Information Booklet for Grade 10 Mathematics at http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/taks/booklets/index.html. Objective 1: The student will describe functional relationships in a variety of ways. A(b)(1) Foundations for functions. The student understands that a function represents a dependence of one quantity on another and can be described in a variety of ways. (A) The student describes independent and dependent quantities in functional relationships. (B) The student [gathers and records data, or] uses data sets, to determine functional (systematic) relationships between quantities. (C) The student describes functional relationships for given problem situations and writes equations or inequalities to answer questions arising from the situations. (D) The student represents relationships among quantities using [concrete] models, tables, graphs, diagrams, verbal descriptions, equations, and inequalities. (E) The student interprets and makes inferences from functional relationships. Objective 2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the properties and attributes of functions. A(b)(2) Foundations for functions. The student uses the properties and attributes of functions. (A) The student identifies [and sketches] the general forms of linear ( y = x ) and quadratic ( y = x 2) parent functions. (B) For a variety of situations, the student identifies the mathematical domains and ranges and determines reasonable domain and range values for given situations. (C) The student interprets situations in terms of given graphs [or creates situations that fit given graphs]. (D) In solving problems, the student [collects and] organizes data, [makes and] interprets scatterplots, and models, predicts, and makes decisions and critical judgments. A(b)(3) Foundations for functions. The student understands how algebra can be used to express generalizations and recognizes and uses the power of symbols to represent situations. (A) The student uses symbols to represent unknowns and variables. (B) Given situations, the student looks for patterns and represents generalizations algebraically. A(b)(4) Foundations for functions. The student understands the importance of the skills required to manipulate symbols in order to solve problems and uses the necessary algebraic skills required to simplify algebraic expressions and solve equations and inequalities in problem situations. (A) The student finds specific function values, simplifies polynomial expressions, transforms and solves equations, and factors as necessary in problem situations. Page 1 Grade 10 Mathematics (continued) (B) The student uses the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to simplify algebraic expressions. Objective 3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of linear functions. A(c)(1) Linear functions. The student understands that linear functions can be represented in different ways and translates among their various representations. (A) The student determines whether or not given situations can be represented by linear functions. (C) The student translates among and uses algebraic, tabular, graphical, or verbal descriptions of linear functions. A(c)(2) Linear functions. The student understands the meaning of the slope and intercepts of linear functions and interprets and describes the effects of changes in parameters of linear functions in real-world and mathematical situations. (A) The student develops the concept of slope as rate of change and determines slopes from graphs, tables, and algebraic representations. (B) The student interprets the meaning of slope and intercepts in situations using data, symbolic representations, or graphs. (C) The student investigates, describes, and predicts the effects of changes in m and b on the graph of y = mx + b . (D) The student graphs and writes equations of lines given characteristics such as two points, a point and a slope, or a slope and y-intercept. (E) The student determines the intercepts of linear functions from graphs, tables, and algebraic representations. (F) The student interprets and predicts the effects of changing slope and y-intercept in applied situations. (G) The student relates direct variation to linear functions and solves problems involving proportional change. Objective 4: The student will formulate and use linear equations and inequalities. A(c)(3) Linear functions. The student formulates equations and inequalities based on linear functions, uses a variety of methods to solve them, and analyzes the solutions in terms of the situation. (A) The student analyzes situations involving linear functions and formulates linear equations or inequalities to solve problems. (B) The student investigates methods for solving linear equations and inequalities using [concrete] models, graphs, and the properties of equality, selects a method, and solves the equations and inequalities. Page 2 Grade 10 Mathematics (continued) (C) For given contexts, the student interprets and determines the reasonableness of solutions to linear equations and inequalities. A(c)(4) Linear functions. The student formulates systems of linear equations from problem situations, uses a variety of methods to solve them, and analyzes the solutions in terms of the situation. (A) The student analyzes situations and formulates systems of linear equations to solve problems. (B) The student solves systems of linear equations using [concrete] models, graphs, tables, and algebraic methods. (C) For given contexts, the student interprets and determines the reasonableness of solutions to systems of linear equations. Objective 5: The student will demonstrate an understanding of quadratic and other nonlinear functions. A(d)(1) Quadratic and other nonlinear functions. The student understands that the graphs of quadratic functions are affected by the parameters of the function and can interpret and describe the effects of changes in the parameters of quadratic functions. (B) The student investigates, describes, and predicts the effects of changes in a on the graph of y = ax 2. (C) The student investigates, describes, and predicts the effects of changes in c on the graph of y = x 2 + c . (D) For problem situations, the student analyzes graphs of quadratic functions and draws conclusions. A(d)(2) Quadratic and other nonlinear functions. The student understands there is more than one way to solve a quadratic equation and solves them using appropriate methods. (A) The student solves quadratic equations using [concrete] models, tables, graphs, and algebraic methods. (B) The student relates the solutions of quadratic equations to the roots of their functions. A(d)(3) Quadratic and other nonlinear functions. The student understands there are situations modeled by functions that are neither linear nor quadratic and models the situations. (A) The student uses [patterns to generate] the laws of exponents and applies them in problemsolving situations. Objective 6: (8.6) The student will demonstrate an understanding of geometric relationships and spatial reasoning. Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses transformational geometry to develop spatial sense. The student is expected to (A) generate similar shapes using dilations including enlargements and reductions; and Page 3 Grade 10 Mathematics (continued) (B) (8.7) graph dilations, reflections, and translations on a coordinate plane. Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses geometry to model and describe the physical world. The student is expected to (D) locate and name points on a coordinate plane using ordered pairs of rational numbers. Objective 7: (8.7) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses geometry to model and describe the physical world. The student is expected to (A) draw solids from different perspectives; (B) use geometric concepts and properties to solve problems in fields such as art and architecture; and (C) use pictures or models to demonstrate the Pythagorean Theorem. Objective 8: (8.8) (8.9) The student will demonstrate an understanding of two- and three-dimensional representations of geometric relationships and shapes. The student will demonstrate an understanding of the concepts and uses of measurement and similarity. Measurement. The student uses procedures to determine measures of solids. The student is expected to (A) find surface area of prisms and cylinders using [concrete] models and nets (twodimensional models); (B) connect models to formulas for volume of prisms, cylinders, pyramids, and cones; and (C) estimate answers and use formulas to solve application problems involving surface area and volume. Measurement. The student uses indirect measurement to solve problems. The student is expected to (A) use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve real-life problems; and (B) use proportional relationships in similar shapes to find missing measurements. (8.10) Measurement. The student describes how changes in dimensions affect linear, area, and volume measures. The student is expected to (A) describe the resulting effects on perimeter and area when dimensions of a shape are changed proportionally; and (B) describe the resulting effect on volume when dimensions of a solid are changed proportionally. Page 4 Grade 10 Mathematics (continued) Objective 9: (8.3) The student will demonstrate an understanding of percents, proportional relationships, probability, and statistics in application problems. Patterns, relationships, and algebraic thinking. The student identifies proportional relationships in problem situations and solves problems. The student is expected to (B) estimate and find solutions to application problems involving percents and proportional relationships such as similarity and rates. (8.11) Probability and statistics. The student applies concepts of theoretical and experimental probability to make predictions. The student is expected to (A) find the probabilities of compound events (dependent and independent); and (B) use theoretical probabilities and experimental results to make predictions and decisions. (8.12) Probability and statistics. The student uses statistical procedures to describe data. The student is expected to (A) select the appropriate measure of central tendency to describe a set of data for a particular purpose; and (C) construct circle graphs, bar graphs, and histograms, with and without technology. (8.13) Probability and statistics. The student evaluates predictions and conclusions based on statistical data. The student is expected to (B) recognize misuses of graphical or numerical information and evaluate predictions and conclusions based on data analysis. Objective 10: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the mathematical processes and tools used in problem solving. (8.14) Underlying processes and mathematical tools. The student applies Grade 8 mathematics to solve problems connected to everyday experiences, investigations in other disciplines, and activities in and outside of school. The student is expected to (A) identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics; (B) use a problem-solving model that incorporates understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness; and (C) select or develop an appropriate problem-solving strategy from a variety of different types, including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, acting it out, making a table, working a simpler problem, or working backwards to solve a problem. (8.15) Underlying processes and mathematical tools. The student communicates about Grade 8 mathematics through informal and mathematical language, representations, and models. The student is expected to (A) communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models. Page 5 Grade 10 Mathematics (continued) (8.16) Underlying processes and mathematical tools. The student uses logical reasoning to make conjectures and verify conclusions. The student is expected to (A) make conjectures from patterns or sets of examples and nonexamples; and (B) validate his/her conclusions using mathematical properties and relationships. Page 6 Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key Grade: 10 Subject: Science Administration: April 2006 The letter B indicates that the student expectation listed is from the Biology I TEKS. The letter I indicates that the student expectation listed is from the Integrated Physics and Chemistry TEKS. Item Number 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 Correct Answer A G B H D J B H C F B H D H A H B G A 7 C H D H A J B J C H D F D H A J A G D F D H B F C H B J D G C H D F D Objective Measured 01 01 05 01 02 01 05 03 04 05 01 04 02 05 02 03 03 04 05 02 03 04 01 03 03 01 03 01 04 03 02 04 01 02 05 03 04 05 02 04 02 01 01 03 01 01 02 03 01 01 05 02 01 01 02 Student Expectations B.2 (D) I.3 (B) I.4 (A) I.3 (B) B.4 (B) B.2 (A) I.4 (A) B.7 (B) I.8 (C) I.5 (A) I.3 (B) I.8 (A) B.4 (B) I.6 (B) B.10 (A) B.13 (A) B.4 (C) I.8 (A) I.6 (B) B.6 (C) B.4 (C) I.7 (A) I.3 (A) B.4 (D) B.12 (B) B.2 (C) B.13 (A) I.3 (A) I.7 (A) B.12 (E) B.8 (C) I.7 (E) B.2 (A) B.6 (D) I.6 (F) B.4 (C) I.9 (D) I.4 (A) B.6 (C) I.8 (C) B.6 (A) B.2 (B) B.2 (B) B.13 (A) B.2 (C) B.1 (A) B.10 (A) B.7 (B) B.2 (D) B.2 (C) I.6 (F) B.8 (C) I.3 (B) I.3 (B) B.6 (D) Copyright © 2006, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited without express written permission from Texas Education Agency. Grade 10 Science For a more complete description of the objectives measured, please refer to the Revised TAKS Information Booklet for Grade 10 Science at http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/taks/booklets/index.html. Objective 1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of science. Biology (1) and Integrated Physics and Chemistry (1) Scientific Processes. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, conducts field and laboratory investigations using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices. The student is expected to (A) demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory investigations. Biology (2) and Integrated Physics and Chemistry (2) Scientific Processes. The student uses scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. The student is expected to (A) plan and implement investigative procedures including asking questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and selecting equipment and technology; (B) collect data and make measurements with precision; (C) organize, analyze, evaluate, make inferences, and predict trends from data; and (D) communicate valid conclusions. Integrated Physics and Chemistry (3) Scientific Processes. The student uses critical thinking and scientific problem solving to make informed decisions. The student is expected to (A) analyze, review, [and critique] scientific explanations, including hypotheses and theories, as to their strengths and weaknesses using scientific evidence and information; and (B) draw inferences based on data related to [promotional materials for] products and services. Objective 2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the organization of living systems. Biology (4) Science Concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things and have specialized parts that perform specific functions, and that viruses are different from cells and have different properties and functions. The student is expected to (B) investigate and identify cellular processes including homeostasis, permeability, energy production, transportation of molecules, disposal of wastes, function of cellular parts, and synthesis of new molecules. Biology (6) Science Concepts. The student knows the structures and functions of nucleic acids in the mechanisms of genetics. The student is expected to (A) describe components of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and illustrate how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA; (C) identify and illustrate how changes in DNA cause mutations [and evaluate the significance of these changes]; and Page 1 Grade 10 Science (continued) (D) compare genetic variations observed in plants and animals. Biology (8) Science Concepts. The student knows applications of taxonomy and can identify its limitations. The student is expected to (C) identify characteristics of kingdoms including monerans, protists, fungi, plants, and animals. ** **The TAKS will use the most current classification system. Biology (10) Science Concepts. The student knows that, at all levels of nature, living systems are found within other living systems, each with its own boundary and limits. The student is expected to (A) interpret the functions of systems in organisms including circulatory, digestive, nervous, endocrine, reproductive, integumentary, skeletal, respiratory, muscular, excretory, and immune. Objective 3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the interdependence of organisms and the environment. Biology (4) Science Concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things and have specialized parts that perform specific functions, and that viruses are different from cells and have different properties and functions. The student is expected to (C) compare the structures and functions of viruses to cells and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases and conditions such as acquired immune deficiency syndrome, common colds, smallpox, influenza, and warts; and (D) identify and describe the role of bacteria in maintaining health such as in digestion and in causing diseases such as in streptococcus infections and diphtheria. Biology (7) Science Concepts. The student knows the theory of biological evolution. The student is expected to (B) illustrate the results of natural selection in speciation, diversity, phylogeny, adaptation, behavior, and extinction. Biology (12) Science Concepts . The student knows that interdependence and interactions occur within an ecosystem. The student is expected to (B) interpret interactions among organisms exhibiting predation, parasitism, commensalism, and mutualism; and (E) investigate and explain the interactions in an ecosystem including food chains, food webs, and food pyramids. Biology (13) Science Concepts. The student knows the significance of plants in the environment. The student is expected to (A) evaluate the significance of structural and physiological adaptations of plants to their environments. Page 2 Grade 10 Science (continued) Objective 4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structures and properties of matter. Integrated Physics and Chemistry (7) Science Concepts. The student knows relationships exist between properties of matter and its components. The student is expected to (A) investigate and identify properties of fluids including density, viscosity, and buoyancy; and (E) classify samples of matter from everyday life as being elements, compounds, or mixtures. Integrated Physics and Chemistry (8) Science Concepts. The student knows that changes in matter affect everyday life. The student is expected to (A) distinguish between physical and chemical changes in matter such as oxidation, digestion, changes in states, and stages in the rock cycle; and (C) investigate and identify the law of conservation of mass. Integrated Physics and Chemistry (9) Science Concepts. The student knows how solution chemistry is a part of everyday life. The student is expected to (A) relate the structure of water to its function [as the universal solvent]; and (D) demonstrate how various factors influence solubility including temperature, pressure, and nature of the solute and solvent. Objective 5: The student will demonstrate an understanding of motion, forces, and energy. Integrated Physics and Chemistry (4) Science Concepts. The student knows concepts of force and motion evident in everyday life. The student is expected to (A) calculate speed, momentum, acceleration, work, and power in systems such as in the human body, moving toys, and machines; and (B) investigate and describe [applications of] Newton's laws such as in vehicle restraints, sports activities, geological processes, and satellite orbits. Integrated Physics and Chemistry (5) Science Concepts. The student knows the effects of waves on everyday life. The student is expected to (A) demonstrate wave types and their characteristics through a variety of activities such as modeling with ropes and coils, activating tuning forks, and interpreting data on seismic waves. Integrated Physics and Chemistry (6) Science Concepts. The student knows the impact of energy transformations in everyday life. The student is expected to (A) describe the law of conservation of energy; (B) investigate and demonstrate the movement of heat through solids, liquids, and gases by convection, conduction, and radiation; and (F) investigate and compare series and parallel circuits. Page 3 Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key Grade: 10 Subject: Social Studies Administration: April 2006 The letter W indicates that the student expectation listed is from the World History TEKS. The letter G indicates that the student expectation listed is from the World Geography TEKS. Item Number 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Correct Answer A G B J C H A J C H B H B G D J A J A G B F A H C G D H D F B F A H A F C F A J C G C H A J D F B G Objective Measured 02 03 02 05 02 02 05 05 02 02 01 03 02 04 04 02 04 01 05 02 01 04 05 05 04 03 01 05 04 01 02 04 03 04 02 04 05 01 04 05 03 05 04 04 02 05 05 03 01 03 Student Expectations 8.10 (B) G.10 (C) 8.10 (B) W.26 (C) W.23 (A) G.6 (A) 8.30 (D) W.26 (C) G.6 (A) G.6 (A) 8.16 (C) G.18 (A) G.1 (A) 8.20 (A) 8.3 (A) W.23 (A) 8.16 (A) 8.4 (B) G.8 (B) G.1 (B) 8.1 (C) 8.18 (B) G.8 (B) 8.30 (D) 8.3 (A) G.10 (C) 8.1 (C) G.8 (B) 8.16 (D) 8.4 (C) W.12 (C) 8.3 (A) G.18 (A) 8.22 (B) W.12 (C) 8.16 (D) 8.30 (A) 8.4 (B) 8.17 (B) G.21 (C) G.18 (A) G.21 (C) 8.20 (B) 8.20 (B) W.23 (A) W.25 (C) W.26 (C) G.18 (A) 8.4 (C) G.5 (B) Copyright © 2006, Texas Education Agency. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited without express written permission from Texas Education Agency. Grade 10 Social Studies For a more complete description of the objectives measured, please refer to the Revised TAKS Information Booklet for Grade 10 Social Studies at http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/taks/booklets/index.html. Objective 1: (8.1) History. The student understands traditional historical points of reference in U.S. history through 1877. The student is expected to (C) (8.4) The student will demonstrate an understanding of issues and events in U.S. history. explain the significance of the following dates: [1607,] 1776, 1787, [1803,] and 1861-1865. History. The student understands significant political and economic issues of the revolutionary era. The student is expected to (B) explain the roles played by significant individuals during the Revolution, including [Samuel Adams, Benjamin Franklin, King George III,] Thomas Jefferson, [the Marquis de Lafayette, Thomas Paine,] and George Washington; and (C) explain the issues surrounding [important events of] the American Revolution, including declaring independence; [writing] the Articles of Confederation; [fighting the battles of Lexington, Concord, Saratoga, and Yorktown; and signing the Treaty of Paris]. (8.16) Government. The student understands the American beliefs and principles reflected in the U.S. Constitution and other important historic documents. The student is expected to (C) identify colonial grievances listed in the Declaration of Independence and explain how those grievances were addressed in the U.S. Constitution and the Bill of Rights. Objective 2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of geographic influences on historical issues and events. (8.10) Geography. The student uses geographic tools to collect, analyze, and interpret data. The student is expected to (B) [pose and] answer questions about geographic distributions and patterns shown on maps, graphs, charts, [models, and databases]. (WG1) History. The student understands how geographic contexts (the geography of places in the past) and processes of spatial exchange (diffusion) influenced events in the past and helped to shape the present. The student is expected to (A) analyze the effects of physical and human geographic patterns and processes on events in the past and describe their effects on present conditions, including significant physical features and environmental conditions that influenced migration patterns in the past and shaped the distribution of culture groups today (correlates with WH12B); and (B) trace the spatial diffusion of a phenomenon and describe its effects on regions of contact such as the spread of bubonic plague, the diffusion and exchange of foods between the New and Old Worlds, [or the diffusion of American slang] (correlates with WH11B). Page 1 Grade 10 Social Studies (continued) (WG6) Geography. The student understands the types and patterns of settlement, the factors that affect where people settle, and processes of settlement development over time. The student is expected to (A) [locate settlements and] observe patterns in the size and distribution of cities using maps, graphics, and other information (correlates with WH26C). (WH12) Geography. The student understands the impact of geographic factors on major historic events. The student is expected to (C) interpret historical [and contemporary] maps to identify and explain geographic factors [such as control of the Straits of Hormuz] that have influenced people and events in the past (correlates with WG21C). (WH23) Science, technology, and society. The student understands how major scientific and mathematical discoveries and technological innovations have affected societies throughout history. The student is expected to (A) give examples of [major mathematical and scientific discoveries and] technological innovations that occurred at different periods in history and describe the changes produced by these discoveries and innovations (correlates with WG19A and WG20A). Objective 3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of economic and social influences on historical issues and events. (WG5) Geography. The student understands how political, economic, and social processes shape cultural patterns and characteristics in various places and regions. The student is expected to (B) analyze political, economic, social, and demographic data to determine the level of development and standard of living in nations (correlates with WH14C). (WG10) Economics. The student understands the distribution and characteristics of economic systems throughout the world. The student is expected to (C) compare the ways people satisfy their basic needs through the production of goods and services such as subsistence agriculture versus market-oriented agriculture or cottage industries versus commercial industries (correlates with WH14C). (WG18) Culture. The student understands the ways in which cultures change and maintain continuity. The student is expected to (A) describe the impact of general processes such as migration, war, trade, independent inventions, and diffusion of ideas and motivations on cultural change (correlates with WH1B). Objective 4: (8.3) The student will demonstate an understanding of political influences on historical issues and events. History. The student understands the foundations of representative government in the United States. The student is expected to (A) explain the reasons for the growth of representative government and institutions during the colonial period. Page 2 Grade 10 Social Studies (continued) (8.16) Government. The student understands the American beliefs and principles reflected in the U.S. Constitution and other important historic documents. The student is expected to (A) identify the influence of ideas from historic documents including the Magna Carta, the English Bill of Rights, [the Mayflower Compact,] the Declaration of Independence, the Federalist Papers, [and selected anti-federalist writings] on the U.S. system of government; and (D) analyze how the U.S. Constitution reflects the principles of limited government, republicanism, checks and balances, federalism, separation of powers, popular sovereignty, and individual rights. (8.17) Government. The student understands the process of changing the U.S. Constitution and the impact of amendments on American society. The student is expected to (B) describe the impact of 19th-century amendments including the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments on life in the United States. (8.18) Government. The student understands the dynamic nature of the powers of the national government and state governments in a federal system. The student is expected to (B) describe historical conflicts arising over the issue of states' rights, including the Nullification Crisis and the Civil War. (8.20) Citizenship. The student understands the rights and responsibilities of citizens of the United States. The student is expected to (A) define and give examples of unalienable rights; and (B) summarize rights guaranteed in the Bill of Rights. (8.22) Citizenship. The student understands the importance of the expression of different points of view in a democratic society. The student is expected to (B) describe the importance of free speech and press in a democratic society. Objective 5: The student will use critical thinking skills to analyze social studies information. (8.30) Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of sources including electronic technology. The student is expected to (A) [differentiate between, locate, and] use primary and secondary sources [such as computer software, databases, media and news services, biographies, interviews, and artifacts] to acquire information about the United States; (D) identify points of view from the historical context surrounding an event and the frame of reference which influenced the participants; and (F) identify bias in written, [oral,] and visual material. Page 3 Grade 10 Social Studies (continued) (WG8) Geography. The student understands how people, places, and environments are connected and interdependent. The student is expected to (B) compare ways that humans depend on, adapt to, and modify the physical environment using [local,] state, national, and international human activities in a variety of cultural and technological contexts (correlates with WH12B and WH12C). (WG21) Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of sources including electronic technology. The student is expected to (C) [construct and] interpret maps to answer geographic questions, infer geographic relationships, and analyze geographic change (correlates with WH11B and WH12C). (WH25) Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of sources including electronic technology. The student is expected to (C) analyze information by sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations [and predictions,] and drawing inferences and conclusions (correlates with WG21A). (WH26) Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to (C) interpret [and create databases, research outlines, bibliographies, and] visuals including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps (correlates with WG21C). Page 4