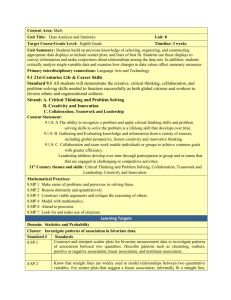
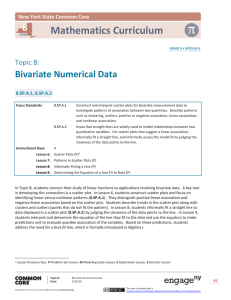
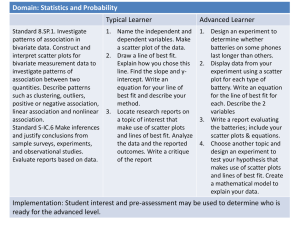
2.4: Using Linear Models
advertisement

2.4: Using Linear Models
You can't choose the ways in which you'll be tested.
Writing Equations
Ex1) Suppose an airplane descends at a rate of 300 ft/min from an
elevation of 8000 ft. Write and graph an equation to model the plane’s
elevation as a function of the time it has been descending. Interpret the
intercept at which the graph intersects the vertical axis.
Using Points
A spring has a length of 8 cm when a 20-g mass is hanging at the bottom
end. The same spring has a length of 11 cm when a 40-g mass is hanging
at the bottom end. Write an equation for the length y of the spring as a
function of the mass x of the attached weight. Graph the equation. What
mass would be needed to stretch the spring to a length of 12 cm?
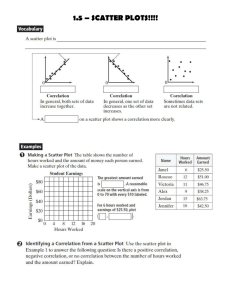
Scatter Plots
Graphs that relate two different sets of data by plotting the data
as ordered pairs. Used to determine the relationship between data
sets (for example, x and y values).
Trend line: a line that approximates the relationship between the
data sets of a scatter plot. Used to make predictions.
Scatter Plots
Graph the set of data. Decide whether a linear model is reasonable. If so,
draw a trend line and write its equation by hand. Then use a graphing
utility to determine the equation of the trend line.
{(1, 2), (3, 3), (3, 3.75), (4, 4), (5, 3.25), (6, 4.5)}
2.4: Using Linear Models
HW: 1-8 all, 13, 15, 16, 19, 21
You can't choose the ways in which you'll be tested.