1.1 and 1.5 Rectangular Coordinates and Circles
advertisement

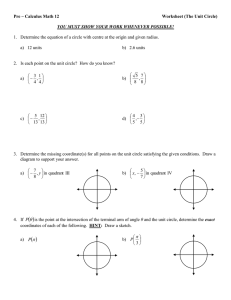
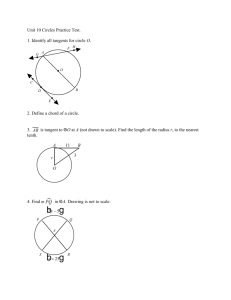
1.1 and 1.5 Rectangular Coordinates and Circles Every man dies, not every man really lives. -William Wallace Coordinate Plane y-axis Quadrant II x < 0, y > 0 Quadrant I x > 0, y > 0 x-axis Quadrant III x < 0, y < 0 Quadrant IV x > 0, y < 0 Distance Formula Distance Formula d(P1,P2 ) (x2 x1)2 (y2 y1)2 Midpoint Formula Midpoint Formula x1 x 2 y1 y 2 M , 2 2 Distance and Midpoint Practice Practice: Given the points (-9,5) and (4,2) 1) Find the length of the line segment joining the two points 2) Find the midpoint of the line segment joining the two points Applying Distance Formula Verify that the triangle with the following vertices is a right triangle and find its area. A = (-6,3); B = (3, -5); C = (-1,5) Equation of a Circle 2 2 2 Standard Form: (x h) (y k) r General Form: x 2 y 2 ax by c 0 Circle Practice 1) Write the standard form and general form of the equation of a circle with center at (4, -3) and radius r = 4 Circle Practice 2) Determine the center (h,k) and radius r of the given circle. Determine the intercepts and sketch the graph. 2x 2 2y 2 8x 16y 8 0 Circle Practice – Turn In 3) Determine the equation in standard form and general form for the circle with endpoints of diameter at (4,3) and (0,1). 4) Determine the center (h,k) and radius r of the given circle. Determine the intercepts. Graph in the calculator to check your answer. 1.1 and 1.5 Rectangular Coordinates and Circles Pg 9 #35, 37, 55, 57, 65 Pg 49 #5, 13, 15, 23*, 29 * Graph on calculator Every man dies, not every man really lives. -William Wallace