Introduction to Microeconomics- L1 EG – University of Orleans
advertisement

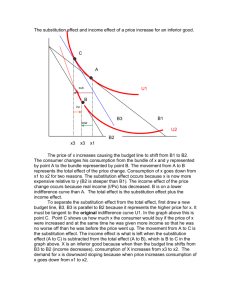
Introduction to Microeconomics- L1 EG – University of Orleans Tutorial n.3 1) Consider a consumer whose preferences over the goods X1 and X2 are described by the following utility function: U(X1, X2) = 2X1X2+3X1. Let P1 and P2 the prices of these goods, respectively. x1 27 * a- Verify that the bundle C * is optimal if P1=1 euro and P2 = 2 euros and the * x2 12 revenue is 51. b- Write down the equation of the indifference curve containing C* (recall that we give this equation in the (X1, X2) space, where X1 is on the horizontal axes and X2 on the vertical axes). c- Suppose now that P1 increases to 2 euros. If only the substitution effect, measured by H following Hick’s definition, exists, which would be the bundle CS chosen by the consumer? H By which revenue should the consumer be provided in order to get CS ? Why, and in what H way, can we say that his purchase power needed to get CS has remained constant? d- Following Stutsky, by which revenue should the consumer be provided for his purchase power to remain constant? Suppose to give him this revenue. The consumer would then choose 𝐶𝑆𝑆 . What can you say about the comparison between 𝑀𝑅𝑆𝑋1 𝑋2 (𝐶𝑆𝑆 ) and 𝑀𝑅𝑆𝑋1 𝑋2 (𝐶𝑆𝐻 )? And what about 𝑈(𝐶𝑆𝑆 ) with respect to 𝑈(𝐶𝑆𝐻 )? What can you conclude about the income adjustment following Slutsky and that following Hicks? e- Suppose that the consumer won’t receive any monetary compensation. Check that when P1=2 the chosen bundle is 13,5 . Concerning the demand of X2, what can you conclude about the 12 size of the income and substitution effects induced by the increase in P1? And what about the demand of X1? Consider the consumers of exercise 1) abcdef- Could you write down the equations of the demand functions of X1 and X2? Is X1 substitute, complement or indifferent to X2? Is X2 substitute, complement or indifferent to X1? Is X1 an inferior good? And X2? Does X1 verify the law of demand? And X2? Compute the price elasticity, the cross-elasticity and the income elasticity of the demand of X1. g- Compute the price elasticity, the cross-elasticity and the income elasticity of the demand of X2. h- Compute the composition of the bundle corresponding to the substitution effect, following Slutsky definition. 1