Slope Re-Test Review: Linear Equations Worksheet
advertisement
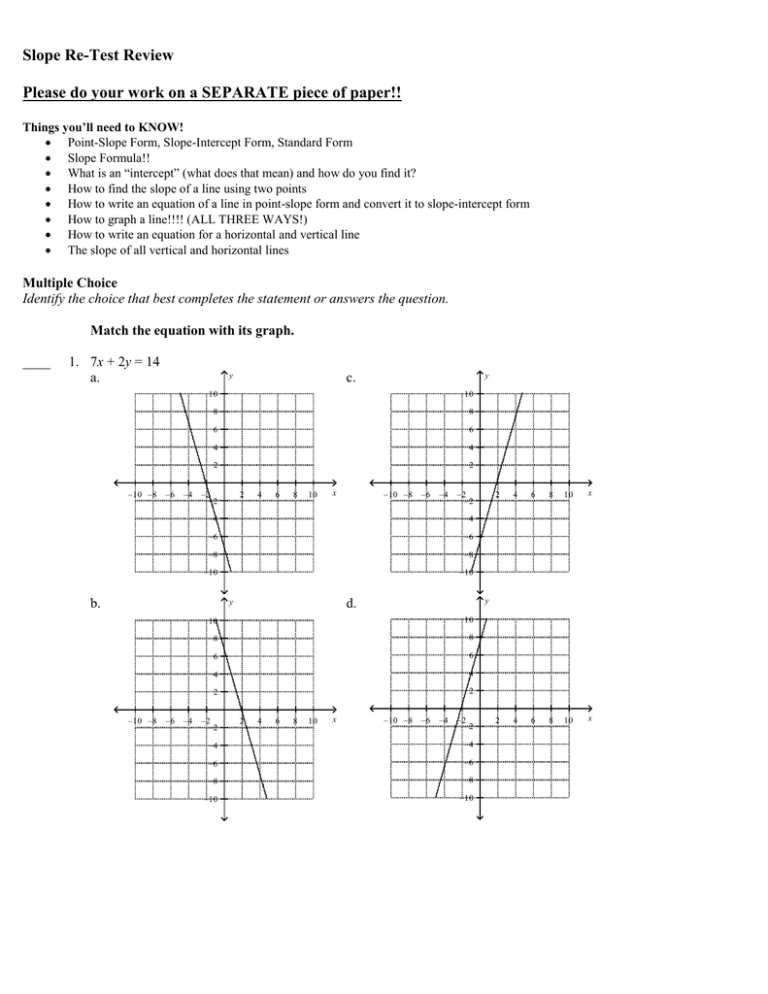
Slope Re-Test Review Please do your work on a SEPARATE piece of paper!! Things you’ll need to KNOW! Point-Slope Form, Slope-Intercept Form, Standard Form Slope Formula!! What is an “intercept” (what does that mean) and how do you find it? How to find the slope of a line using two points How to write an equation of a line in point-slope form and convert it to slope-intercept form How to graph a line!!!! (ALL THREE WAYS!) How to write an equation for a horizontal and vertical line The slope of all vertical and horizontal lines Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Match the equation with its graph. ____ 1. 7x + 2y = 14 a. –10 –8 y –6 –4 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 –2 –2 2 4 6 8 10 x –4 –6 –4 –2 –2 –4 –6 –6 –8 –8 –10 –10 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 –2 –2 2 4 6 8 10 x 2 4 6 8 10 x 2 4 6 8 10 x y d. y –6 –10 –8 –4 b. –10 –8 y c. –10 –8 –6 –4 –2 –2 –4 –4 –6 –6 –8 –8 –10 –10 Find the slope of the line using the formula for slope. 2. y 5 4 3 2 1 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 –1 1 2 3 4 5 x –2 –3 –4 –5 Find the slope of the line that passes through the pair of points. 3. (2, 8), (9, –3) 4. Use the slope and y-intercept to graph the equation. 3 y= x–3 4 Find the x- and y-intercept of the line. 5. –8x – 3y = 96 Graph the equation. 6. y = –3 7. x = –4 4 8. y – 2 = (x + 3) 3 Are the graphs of the lines in the pair parallel? Explain. 1 x – 11 11 x – 11y = –9 9. y = 10. y = 6x + 3 –15x + 3y = –45 Write an equation for the line that is parallel to the given line and that passes through the given point. 9 11. y = x + 9; (–5, –2) 5 Tell whether the lines for each pair of equations are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. 3 12. y = x + 2 4 16x – 12y = 16 Write the equation of a line that is perpendicular to the given line and that passes through the given point. 13. –x + 12y = 18; (–2, –6) pe Re-Test swer Section ULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: KEY: B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-4 Standard Form 6-4.1 Graphing Equations Using Intercepts NAEP 2005 A1h | ADP J.4.1 | ADP J.4.2 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.4.a | CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.5.a 6-4 Example 2 graphing | x-intercept | y-intercept | standard form of a linear equation ORT ANSWER 2. ANS: 3 PTS: OBJ: NAT: STA: KEY: 3. ANS: 11 7 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-1 Rate of Change and Slope 6-1.2 Finding Slope NAEP 2005 A2a | NAEP 2005 A2b | ADP J.4.1 | ADP K.10.1 CO 9.5.1.b | CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.2.c TOP: 6-1 Example 3 graphing | finding slope using a graph | slope PTS: OBJ: NAT: STA: KEY: 4. ANS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-1 Rate of Change and Slope 6-1.2 Finding Slope NAEP 2005 A2a | NAEP 2005 A2b | ADP J.4.1 | ADP K.10.1 CO 9.5.1.b | CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.2.c TOP: 6-1 Example 4 finding slope using points | slope y 5 4 3 2 1 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 –1 1 2 3 4 5 x –2 –3 –4 –5 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-2 Slope-Intercept Form OBJ: 6-2.2 Graphing Linear Equations NAT: NAEP 2005 A1h | ADP J.4.1 | ADP J.4.2 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.4.a | CO 9.2.5.a TOP: 6-2 Example 4 KEY: linear equation | graphing equations | slope | y-intercept 5. ANS: x-intercept is –12; y-intercept is –32. PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: KEY: 6. ANS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-4 Standard Form 6-4.1 Graphing Equations Using Intercepts NAEP 2005 A1h | ADP J.4.1 | ADP J.4.2 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.4.a | CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.5.a 6-4 Example 1 x-intercept | y-intercept | standard form of a linear equation y 5 4 3 2 1 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 –1 1 2 3 4 5 x –2 –3 –4 –5 PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: 7. ANS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-4 Standard Form 6-4.1 Graphing Equations Using Intercepts NAEP 2005 A1h | ADP J.4.1 | ADP J.4.2 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.4.a | CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.5.a 6-4 Example 3 KEY: graphing | horizontal and vertical lines y 5 4 3 2 1 –5 –4 –3 –2 –1 –1 1 2 3 4 5 x –2 –3 –4 –5 PTS: OBJ: NAT: TOP: 8. ANS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-4 Standard Form 6-4.1 Graphing Equations Using Intercepts NAEP 2005 A1h | ADP J.4.1 | ADP J.4.2 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.4.a | CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.5.a 6-4 Example 3 KEY: graphing | horizontal and vertical lines y 10 8 6 4 2 –10 –8 –6 –4 –2 –2 2 4 6 8 10 x –4 –6 –8 –10 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-5 Point-Slope Form and Writing Linear Equations OBJ: 6-5.1 Using Point-Slope Form NAT: NAEP 2005 A1h | NAEP 2005 A1i | NAEP 2005 A2a | NAEP 2005 A2b | NAEP 2005 A3a | ADP J.4.1 | ADP J.4.2 | ADP K.10.1 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.5.a TOP: 6-5 Example 1 KEY: point-slope form | graphing | linear equation 9. ANS: Yes, since the slopes are the same and the y-intercepts are different. PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-6 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines OBJ: 6-6.1 Parallel Lines NAT: NAEP 2005 G3g | NAEP 2005 A2e | ADP K.2.1 | ADP K.2.2 | ADP K.10.1 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.4.a TOP: 6-6 Example 1 KEY: parallel lines | slope 10. ANS: No, since the slopes are different. PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-6 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines OBJ: 6-6.1 Parallel Lines NAT: NAEP 2005 G3g | NAEP 2005 A2e | ADP K.2.1 | ADP K.2.2 | ADP K.10.1 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.4.a TOP: 6-6 Example 1 KEY: parallel lines | slope 11. ANS: 9 y= x+7 5 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-6 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines OBJ: 6-6.1 Parallel Lines NAT: NAEP 2005 G3g | NAEP 2005 A2e | ADP K.2.1 | ADP K.2.2 | ADP K.10.1 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.4.a TOP: 6-6 Example 2 KEY: parallel lines | linear equation 12. ANS: perpendicular PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 6-6 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines OBJ: 6-6.2 Perpendicular Lines NAT: NAEP 2005 G3g | NAEP 2005 A2e | ADP K.2.1 | ADP K.2.2 | ADP K.10.1 | ADP K.10.2 STA: CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.4.a TOP: 6-6 Example 3 KEY: perpendicular lines | parallel lines 13. ANS: y = 12x – 30 PTS: OBJ: NAT: STA: KEY: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 6-6 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 6-6.2 Perpendicular Lines NAEP 2005 G3g | NAEP 2005 A2e | ADP K.2.1 | ADP K.2.2 | ADP K.10.1 | ADP K.10.2 CO 9.2.1.a | CO 9.2.4.a TOP: 6-6 Example 3 perpendicular lines | linear equation