Polynomials and Linear Factors: Zeros and Graphing
advertisement

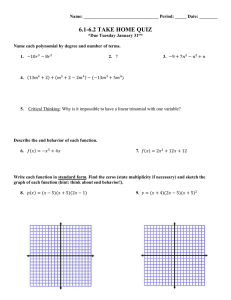
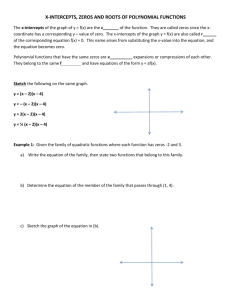
Lesson 6.2 (pt 2) Polynomials and Factors.notebook January 19, 2012 6.2 Polynomials and Linear Factors Objectives: • Be able to write a polynomial in standard form and factored form • Be able to find the zeros of a polynomial function • Be able to graph a polynomial function using its zeros Relative Maximum: Largest y-value on the graph Relative Minimum: Smallest y-value on the graph Zeros The solution(s); x-intercepts 1 Lesson 6.2 (pt 2) Polynomials and Factors.notebook January 19, 2012 P. 312 in Book NO CALCULATOR! Find the zeros of the function f(x) = (x - 2)(x + 1)(x + 3) Sketch a graph of your equation. (Hint: what is the end behavior of your graph? What are the zeros?) 2 Lesson 6.2 (pt 2) Polynomials and Factors.notebook January 19, 2012 NO CALCULATOR! Find the zeros of the function f(x) = (2x + 1)(x - 2)(x + 4) Sketch a graph of your equation. (Hint: what is the end behavior of your graph? What are the zeros?) NO CALCULATOR! Find the zeros of the function f(x) = x(x + 3)(x - 4) Sketch a graph of your equation. (Hint: what is the end behavior of your graph? What are the zeros?) 3 Lesson 6.2 (pt 2) Polynomials and Factors.notebook January 19, 2012 If a zero occurs more than once, this is called multiplicity Find the zeros of the function f(x) = (x-2)(x+1)2 and state any multiplicity Sketch a graph of your equation. (Hint: what is the end behavior of your graph? What are the zeros?) Even multiplicity: BOUNCE Odd multiplicity: THROUGH If a zero occurs more than once, this is called multiplicity Find the zeros of the function f(x) = x3 - 4x2 + 4x and state any multiplicity Sketch a graph of your equation. (Hint: what is the end behavior of your graph? What are the zeros?) Even multiplicity: BOUNCE Odd multiplicity: THROUGH 4