5.2 Relations and Functions
advertisement

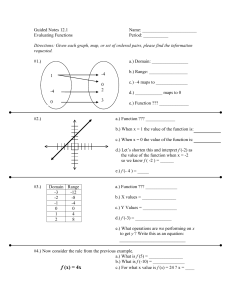
5.2 Relations and Functions Identifying Relations and Functions Relation: A set of ordered pairs. Speed (mph) 12 24 36 48 60 Braking Distance (feet) 7 29 66 117 183 Independent Variable: Speed input (domain) Dependent Variable: Braking Distance output (range) You can list the set of ordered pairs in a relation using braces. (12,7),(24, 29),(36,66),(48,117),(60,183) A function is a relation that assigns exactly one output (range) value for each input (domain) value. Identifying Relations and Functions One way to tell if a relation is a function is by making a mapping diagram. Determine whether the relation is a function. Ex1) (12, 4),(14,0),(16, 2),(18,3),(20, 2) domain range 12 14 16 18 20 4 2 0 3 Ex2) (0,0),(1,1),(4, 2),(1, 1),(3,0) Identifying Relations and Functions Vertical Line Test: If any vertical line passes through more than one point of a graph, then the relation is not a function. Identifying Relations and Functions Vertical Line Test: Function or not? 5 Ex3) 5 Ex4) 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 -1 -1 -2 -2 -3 -3 -4 -4 -5 -5 2 3 4 5 Evaluating Functions A function rule is an equation that describes a function. can also be written using function notation: Evaluating Functions Ex5) Make a table of values for the function f(x) = 2x – 4. Use 1, 2, 3, and 4 for the domain (input values). input x domain output f(x)= 2x - 4 y range Evaluating Functions Ex6) Make a table to find the range of the function rule for the given domain. g (n) 3 2n 2 , 3, 1,0,2,4 5.2 Relations and Functions Homework #:35 Page 259 # 1-3, 9-12, 32-35