Document 10823399
advertisement

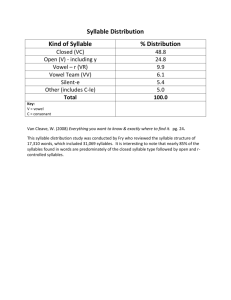
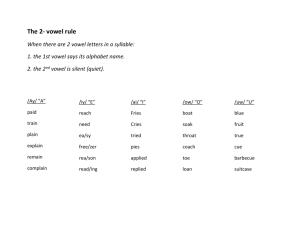
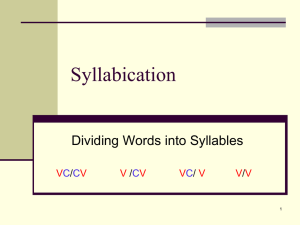
SYLLABICATION INSTRUCTION: THE SOLUTION TO DECODING PROBLEMS Jennifer A. Diliberto, Ph.D. Greensboro College Session Outcomes • Define syllabica:on. • State the importance of teaching syllabica:on. • Explain how to embed decoding instruc:on in the content area. • Describe specific decoding strategies for empowering middle and high school struggling readers. Decoding in the Content Area Taken from What Content-Area Teachers Should Know About Adolescent Literacy, NICHHD, 2007 • Preteach challenging content-area words • Articulate each syllable slowly and repeat pronunciation when introducing the new word • Point out patterns in the pronunciation and spellings of prefixes, suffixes, and vowels in segmented words • Point out similarities and differences among words that belong to “word families” (e.g., define, definitely, definition) • Model using new and difficult words in various contexts • Provide opportunities for practice and reinforce correct pronunciation and usage • Ask open-ended questions requiring students to respond using new or difficult words Overall instruction should… • Emphasize syllable patterns and morphology. • Integrate phonics instruction within the context of the content area to develop and support reading comprehension. • Focus on one or two decoding strategies at a time. What is syllabication? “the act, process, or method of forming or dividing words into syllables.” hFp://www.merriam-­‐webster.com/dic:onary/ syllabica:on Why teach syllabication? • Are these word parts or syllables easy to read? How many multisyllabic words can you make from the word parts? pub stant or doc ance in din chant ly main ing de ary ed port er port can im trans lic re ent cy Why teach syllabication? • Syllabication teaches students to read unknown words, increases their sight-word vocabulary, and aids in learning how to spell words (Torgesen, 2004; Moats, 2001; Curtis & Longo, 1999). • Instruction in syllable skills helps remediate and increase achievement in word attack, word identification, reading comprehension, and increases fluency at a faster rate (Diliberto, Beattie, Flowers, & Algozzine, 2009). Practical Reasons for Teaching Syllabication It’s a tool for attacking large intimidating words that many struggling readers would pass over or shut down without a strategy for chunking the larger word into decodable parts and less intimidating parts. It’s a chunking strategy that is consistent with English language spelling and used in dictionaries. What is a syllable? Characteristics: • A syllable may be one vowel sound per syllable. • A syllable may be one small word. • A syllable may be part of a larger word. • The number of vowel sounds in a word usually equals the number of syllables in a word. • The letter u is not counted as a vowel when it appears after the letter q. • The schwa vowel is present in an unaccented syllable. Six Syllable Types • Closed (cvc) • Open • Silent e (magic e) • Vowel team (vowel digraph) • Vowel r (bossy r, r controlled, crazy r) • Consonant-l-e (c-l-e) – Final Stable CVC, or Closed Syllables Definition: has one vowel, ends in a consonant, the vowel is short, we mark it with a breve căt stĕp sĭt pŏp ŭp Silent e Syllables Definition: has one vowel, one consonant, one e. The e is silent and makes the vowel long. cāke Pēte mīne hōme flūme cūte Open Definition: ends in one vowel, the vowel is long, we mark it with a macron. mā (cron) mē mī (crophone) mō (tion) mū (sic) dū (ty) Vowel Teams (short sounds not shown) Definition: two vowels that say one sound (vowel digraph) ā ai ay ea ey ei eigh ē ee ey ea i ie/ei y ī ie igh y ō oa oe ow ū ue eu ew ǖ ue ou eu ew oe ui other oo oo Vowel R • Definition: one vowel, followed by an r. The r makes the vowel say an unexpected sound. • ar ____ ____ ____ • er ____ • ir ____ • or ____ ____ • ur ____ Consonant l-e Definition: one consonant, one l, one e. Usually comes at the end of a two syllable word. • bub[ble] (count back 3) • cir[cle] • i[dle] • truf[fle] • gig[gle] Activities to Embed in Content Area Instruction to Promote Literacy Across the Curriculum Remember…We are all teachers of reading. Dividing Words into Syllables • Separate the prefix and suffix • Label the vowels and consonants in the word. (ALWAYS start labeling with the 1st vowel.) • Look for patterns. • VC/CV • V/CV or VC/V • VC/CCV or VCC/CV • V/V • /cle • Prefix/ • /Suffix HOW TO USE: teach students to divide multisyllabic words into smaller decodable parts Kansas University Word IdentiLication Strategy Lenz & Hughes (1990) • DISSECT • Discover the context. • Isolate the prefix. • Separate the suffix. • Say the stem. • Examine the stem. • Check with someone. • Try the dic:onary. HOW TO USE: students can prac:ce the strategy while reading relevant texts at their instruc:onal level. Syllable IdentiLication • Closed Word Sort • Labeling HOW TO USE: use when introducing new vocabulary, connect to meeting by finding and defining meaningful parts Closed Word Sort • Organize into groups of 4 • Categorize vocabulary words by syllable type More practice: label each syllable type ___ in ___ pro ___ -ple ___ treme ___ en ___ lost ___ turb ___ fork ___ sky ___ vote ___ poach ___ ite ___ seem ___ mass ___ -zle ___ re More practice: label each syllable type CL O CLE SE CL CL VR VR in pro -ple treme en lost turb fork O SE VT SE VT CL CLE O sky vote poach ite seem mass -zle re Word Making • List syllables and make multisyllabic words HOW TO USE: use when introducing new vocabulary, break new vocabulary into syllables and have students turn syllables into words, include prefixes and suffixes for more word play and instruction in prefixes and suffixes • ly • port • im • cycle • bi • ing • air • plant Vocabulary Development • Choose prefix or suffix – brainstorm words and define • Figure out definitions from pre/suffix or figure out meaning of pre/suffix from word meanings HOW TO USE: use when introducing teaching prefixes and suffixes, provide students with prefixes and/ or suffixes, then have students make words • bi• bicycle • binoculars • bicentennial Review O utcomes • How should decoding instruction be taught in the content areas? • What is syllabication? • Why is it important to teach syllabication? • What does the research say about instruction in syllabication? • What are some activities to do to promote literacy in the content areas and aid with increasing reading achievement? Questions??? Contact Information Jennifer A. Diliberto, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Special Education Greensboro College jdiliberto@greensboro.edu