RIGOROUS INSTRUCTION – IT IS BRAIN SURGERY!
advertisement

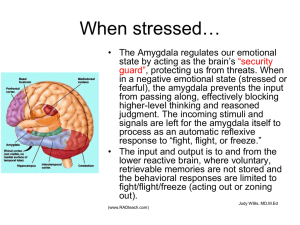
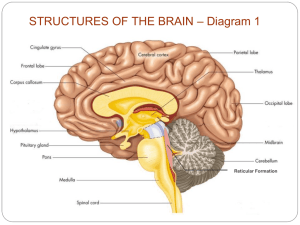
RIGOROUS INSTRUCTION – IT IS BRAIN SURGERY! Label the brain parts on page 3 of your handout. (Best guesses – no pressure!) If it's an educator’s job to develop the mind, shouldn't we know how the brain works? • Educators should understand the processes operating within the cerebral "inner space" of the mind. Kenneth Wesson The Science of Learning Focus Questions - Think Sheet on page 2 1. How does the brain impact the “choice” to learn? • Amygdala Hijacking 2. How do teachers impact students’ willingness to think and learn? • Relaxed Alertness 3. How does the brain process information? • The Information Processing Model 4. What are neural schema, and do they ever stop growing? • Neuroplasicity BRAIN 101 – How Learning Initiates Pg. 3 The BRAIN STEM is responsible for basic vital life functions - breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure. It is referred to a reptilian brain because a reptile’s entire brain resembles our brain stem. • Basic vital life functions • Reptilian brain The CEREBELLUM, or "little brain", it has two hemispheres. • Regulates and coordinates movement, posture, and balance. • higher brain function such as reasoning The CEREBRUM, or cerebral cortex, controls higher brain functions such as reasoning. The Frontal Lobe is the location of reasoning, planning, and problem solving. The LIMBIC SYSTEM, mid-brain, is buried within the cerebrum and often referred to as the "emotional brain“. It contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus • Emotional brain • Thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus Brain Basics for Learning • The brain evolved to protect the well-being of its owner and species. • Therefore, the processes for effort and attention are first directed to protect wellbeing. • The brain filters information by predicting its risk for harm, or value for pleasure. IN Coming… Filtering System • The thalamus is first part of the brain to receive all the signals gathered from the environment . • There is a direct connection from the thalamus to the amygdala and to the cerebral cortex. Key Understanding The amygdala receives information from the thalamus… Split seconds BEFORE the cerebral cortex! • The amygdala is the brain’s repository of emotional memory and acts as its emergency broadcasting system. • If a signal arrives that the amygdala perceives as dangerous (fear) and could cause possible harm to the self… (“I see a gorilla!”), … it instantaneously sends a message to the brain and body… FEAR, emergency…possible harm… Run! Amygdala Hijack • Amygdala Hijack is a term coined by Daniel Goleman in his 1996 book Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ. • Goleman uses the term to describe responses which are immediate and overwhelming, and often out of measure with the actual stimulus because the amygdala triggers a reaction to a “protect” from threat... Before the cerebrum can intercede. What can the amygdala do to learning? • Amygdala » DANGER SIGNAL » (fear/anxiety) floods the body with adrenaline. • Adrenaline directs the brain to react automatically … low level thinking… “Just Do It!” • Adrenaline also inhibits neurotransmitters and interferes with messages to the cerebrum, thus reduces higher level thinking. Learning Caution! • If the amygdala signals DANGER to self… the brain/body will react accordingly. Gorilla and adverbs are merely information input to the brain. OR… based on prior experience the amygdala might pause a split second and give the cerebral cortex a chance to mediate the thought. The cerebrum has a chance to think about the information and recognize it as not dangerous… It is valuable or helpful. What can the amygdala do to learning? • Amygdala » Valuable » signals the body to produce endorphins. • Endorphins increase neurotransmitters and the ability to carry messages to the cerebrum… higher level thinking. **Humor and exercise also increase endorphin production. Remember! The amygdala can hijack thought and actions before the cerebrum gets a chance to consider options. The learning environment and teachers must prevent amygdala hijacking! Amygdala Impact on Learning Positive experiences (and the connected emotions) improve our ability to divert an amygdala hijacking. BUT negative experiences (and the connected emotions) can increase reactions that are out of measure with the actual stimulus because the amygdala triggers a signal to “protect” from threat... Amygdala Hijacking BOREDOM IS NOT PLEASURABLE Some brain researchers explain the amygdala’s interpretation of boredom as: Harmful to self » Fear Increase adrenaline ↗ increase aggression No-stimulation » No pleasure Limits endorphin production ↘ messages to the cerebrum. Judy Willis, M.D., M.Ed. Amygdala Impact on Learning How does the brain impact the “choice” to learn? Experience can intervene or assist amygdala hijacking. Let’s put it all together! Cerebral Cortex Higher Order Thinking “DOWNSHIFTING” Mid-Brain – Limbic System Emotions Brain Stem Instincts Neural Downshifting 24 Neural Downshifting Stress and threat cause the brain to downshift, which reduces the opportunity for neuron growth and causes learning to be inhibited. (Singh, Dalip. Emotional Intelligence at Work. India: Sage Publications Pvt. Ltd. 2006, p 189) 25 Have you experienced Neural Downshifting ? Describe the experience to your neighbor. Relaxed Alertness Learning is enhanced by challenge and inhibited by threat. • Classroom Connection - ZPD (zone of proximal development) What were you thinking? What is wrong with this question? What might be a better question? Why? Why should we count to ten before reacting to something that has made us angry? How can teachers prevent amygdala hijacking and neural downshifting? By creating a classroom environment that demonstrates Unconditional Positive Regard Unconditional Positive Regard is when one person is completely accepting toward another person. This is not just a show of acceptance, but is an attitude that is then demonstrated through behavior. Carl Rogers - On Becoming a Person Human beings have a well developed ability to quickly distinguish friend from foe. It’s part of our innate set of survival skills…Children and youth can quickly tell which of their teachers offer Unconditional Positive Regard to their students and which do not. Mike Rutherford Evidence of Teacher’s Respect As noted by students… Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement Research • • • • • • • • • • Is courteous to students Calls on everyone in the room equitably Uses “WAIT TIME.” Listens, and paraphrases student thoughts Probes and prompts students to reach “appropriate” responses Provides individual help. Provides timely, specific, and abundant performance feedback Gets within arms distance of each student everyday Shows personal interest and give compliments Responds to misbehavior with an effective level of response The Complexity of Learning Information Processing Decay Valve Pg. 5 Explain the Information Processing Model in your own words to a neighbor. Active Learning Martin Heiddegar Concept Attainment EXAMPLE EXAMPLE EXAMPLE Non - EXAMPLE EXAMPLE Non - EXAMPLE EXAMPLE EXAMPLE Non - EXAMPLE Non - EXAMPLE Neuroplasticity Neuroplasticity is the growth and reorganization of nerve webs or neural schema in the brain in response to the new life experiences. Teachers are Neuroplasticians Neuroplasticians aid in the brain’s natural ability to form new connections; aiding the function of dendrites and axioms, synapses and biochemical electricity; reaching untapped potential. bigstock_golden_brain_2557157.jpg 47 RIGOROUS INSTRUCTION – IT IS BRAIN SURGERY! Focus Questions - Think Sheet on page 2 1. How does the brain impact the “choice” to learn? • Amygdala Hijacking 2. How do teachers impact students’ willingness to think and learn? • Relaxed Alertness 3. How does the brain process information? • The Information Processing Model 4. What are neural schema, and do they ever stop growing? • Neuroplasicity Tammy Ramsey QTL Instructional Specialist tramsey@qtlcenters.org 919-247-7907 Please complete the plus/delta feedback page and turn it in before you leave. Thank you! Case sensitive RIGOROUS INSTRUCTION – IT IS BRAIN SURGERY! The Centers for Quality Teaching and Learning 4009 Barrett Dr., Suite 102 Raleigh, NC 27609 www.qtlcenters.org 919-878-0540 RIGOROUS INSTRUCTION –IT IS BRAIN SURGERY! Focus Questions 1. How does the brain impact the “choice” to learn? • Amygdala Hijacking 2. How do teachers impact students’ willingness to think and learn? • Relaxed Alertness 3. How does the brain process information? • The Information Processing Model 4. What are neural schema, and do they ever stop growing? • Neuroplasticity ©QTL 2012 www.qtlcenters.org The Centers for Quality Teaching and Learning 2 Notes: ©QTL 2012 www.qtlcenters.org The Centers for Quality Teaching and Learning 3 Unconditional Positive Regard Unconditional Positive Regard is when one person is completely accepting toward another person. This is not just a show of acceptance, but is an attitude that is then demonstrated through behavior. Carl Rogers - On Becoming a Person Human beings have a well developed ability to quickly distinguish friend from foe. It’s part of our innate set of survival skills…Children and youth can quickly tell which of their teachers offer Unconditional Positive Regard to their students and which do not. Mike Rutherford Evidence of Teacher’s Respect As noted by students… Teacher Expectations and Student Achievement Research • • • • • • • • • • Is courteous to students Calls on everyone in the room equitably Uses “WAIT TIME.” Listens, and paraphrases student thoughts Probes and prompts students to reach “appropriate” responses Provides individual help. Provides timely, specific, and abundant performance feedback Gets within arms distance of each student everyday Shows personal interest and give compliments Responds to misbehavior with an effective level of response ©QTL 2012 www.qtlcenters.org The Centers for Quality Teaching and Learning 4 Notes: ©QTL 2012 www.qtlcenters.org The Centers for Quality Teaching and Learning 5 ©QTL 2012 www.qtlcenters.org The Centers for Quality Teaching and Learning 6